Commensalism Drawing
Commensalism Drawing - Web commensalisms, interactions between two species in which one species benefits and the other experiences no net effect, are frequently mentioned in the ecological literature but are surprisingly little studied. Web commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship between different species of organisms in which one species benefits from the relationship while the other species is neither harmed nor benefits. What could the benefiting species get from the other species? Web a commensal species benefits from another species by obtaining locomotion, shelter, food, or support from the host species, which (for the most part) neither benefits nor is harmed. One example is barnacles and whales. Mutualism and parasitism are more common than commensalism. Web 6 th grade. To survive, animals learn how to share — or not share — the spaces where they live. All of these different relationships are known as symbiosis. Web commensalism represents an interaction in which one species benefits while the other remains unharmed. Web 5 th grade. Web the commensal—the species that benefits from the association—may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is unaffected. Web commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism are the three main categories of symbiosis found in nature. Parasitism is also a symbiotic relationship, where one of the partners benefits while the other is harmed. Inquilinism is. An inquiline is an animal that lives commensally in the nest, burrow, or dwelling place of an animal of another species. In a commensal relationship, one species benefits and there is a neutral effect on the other—it neither benefits nor is harmed. Here we review and synthesize our limited understanding of. Web 6 th grade. Usually, the host species offers. The best example of commensalism is sea barnacles attached to the skin of whales. This can be contrasted with other types of symbiosis, such as mutualism and parasitism. How to draw adamsia showing commensalism step by step2. Creatures interact with one other in different ways. Web commensalism is a symbiotic relationship between two species, where one species benefits while the. Web commensalism represents an interaction in which one species benefits while the other remains unharmed. Web commensalism, which literally means to eat at the same table (thanks, latin!), is one form of symbiosis, a relationship between two organisms of different species. How to draw adamsia showing commensalism step by step2. Web 5 th grade. The species that benefits is called. Web commensalism represents an interaction in which one species benefits while the other remains unharmed. Web the commensal—the species that benefits from the association—may obtain nutrients, shelter, support, or locomotion from the host species, which is unaffected. This does not seem to. In this form of commensalism, one of the species is benefitted as it attains shelter while the other. Web commensalism is a symbiotic relationship between two species, where one species benefits while the other is neither helped nor significantly harmed. One example is barnacles and whales. The best example of commensalism is sea barnacles attached to the skin of whales. The commensal relation is often between a larger host and a smaller commensal. Community ecologists examine how different. In this form of commensalism, one of the species is benefitted as it attains shelter while the other species remain unaffected. Web commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism are the three main categories of symbiosis found in nature. Web in ecology and biology, commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship between two species in which one benefits without harming the other. To. An inquiline is an animal that lives commensally in the nest, burrow, or dwelling place of an animal of another species. Web 6 th grade. In contrast, both species in a mutualism benefit. Web commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship between different species in which one species benefits and the other is unaffected. In commensalism, one animal lives with. How to draw adamsia commensalism easily3. Barnacles are sea animals with shells. Interactions between two or more species are called interspecific interactions. The populations of all the different species that live together in an area make up an ecological community. The organism receiving the benefit is called the commensal. Web commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship between two species, where one species benefits without harming or benefiting the other. Web mutualism is a symbiotic association in which both organisms benefit. Mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, and competition. An inquiline is an animal that lives commensally in the nest, burrow, or dwelling place of an animal of another species. Web commensalism,. Here we review and synthesize our limited understanding of. The best example of commensalism is sea barnacles attached to the skin of whales. The other animal is called the host. They attach themselves to the skin of whales. The populations of all the different species that live together in an area make up an ecological community. In this form of commensalism, one of the species is benefitted as it attains shelter while the other species remain unaffected. For example, some organisms such as insects may live in the homes of gophers or the garages of human beings and feed on debris, fungi, and roots. Millions of species roam planet earth, and they have to figure out how to share resources such as food and shelter. Web commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism are the three main categories of symbiosis found in nature. In commensalism, animals do not help their host. This does not seem to. An example of this relationship is birds building nests in trees. The species that benefits is called the commensal, while the other species is referred to as the host. The organism receiving the benefit is called the commensal. Web commensalism occurs when one species benefits, and the other is unharmed. Inquilinism is a type of commensalism where one of the species uses the body or a cavity with the body of the other organisms as a living.
Commensalism Drawing
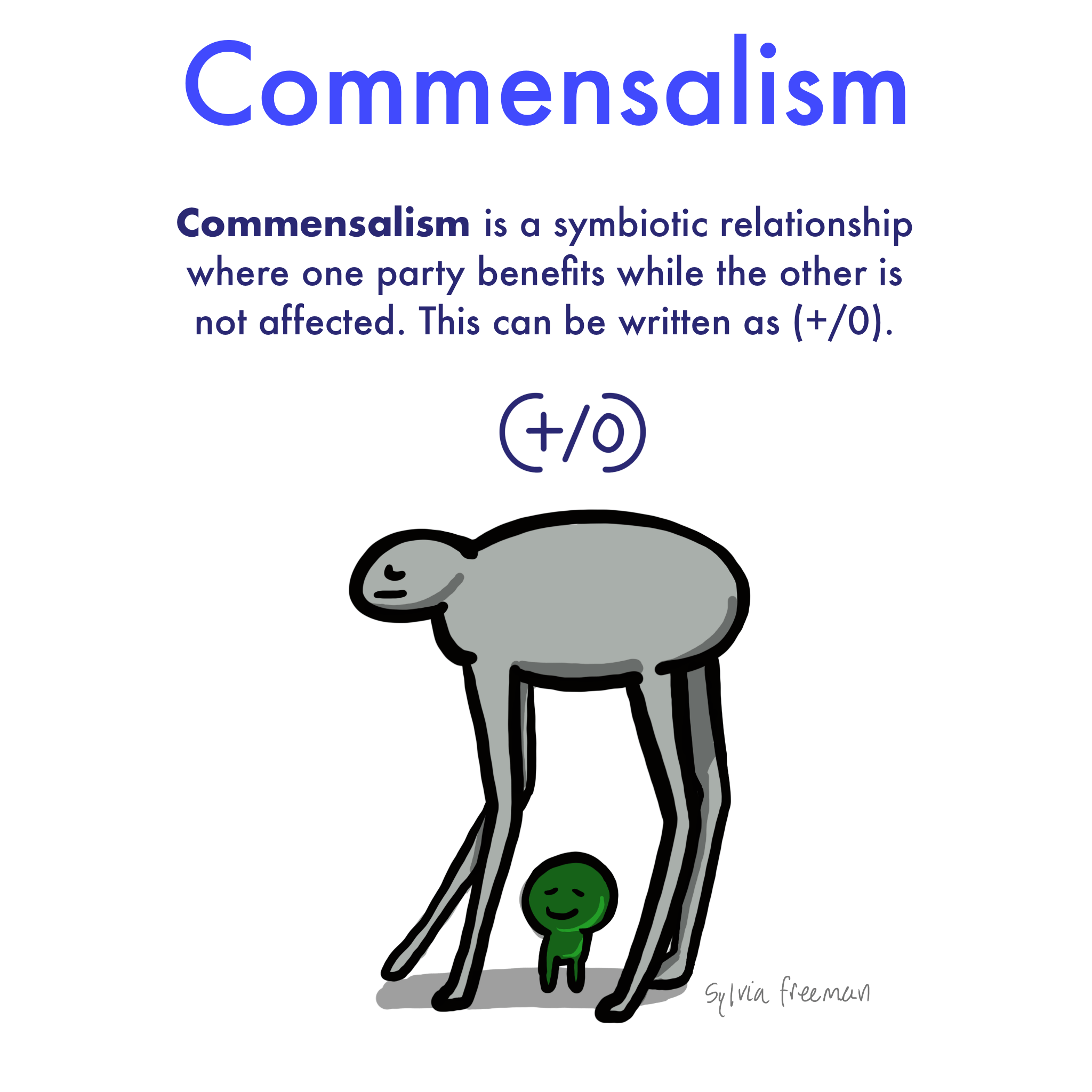
Commensalism — Definition & Examples Expii

Commensalism Definition, Types, Examples, and Diagram

Commensalism Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
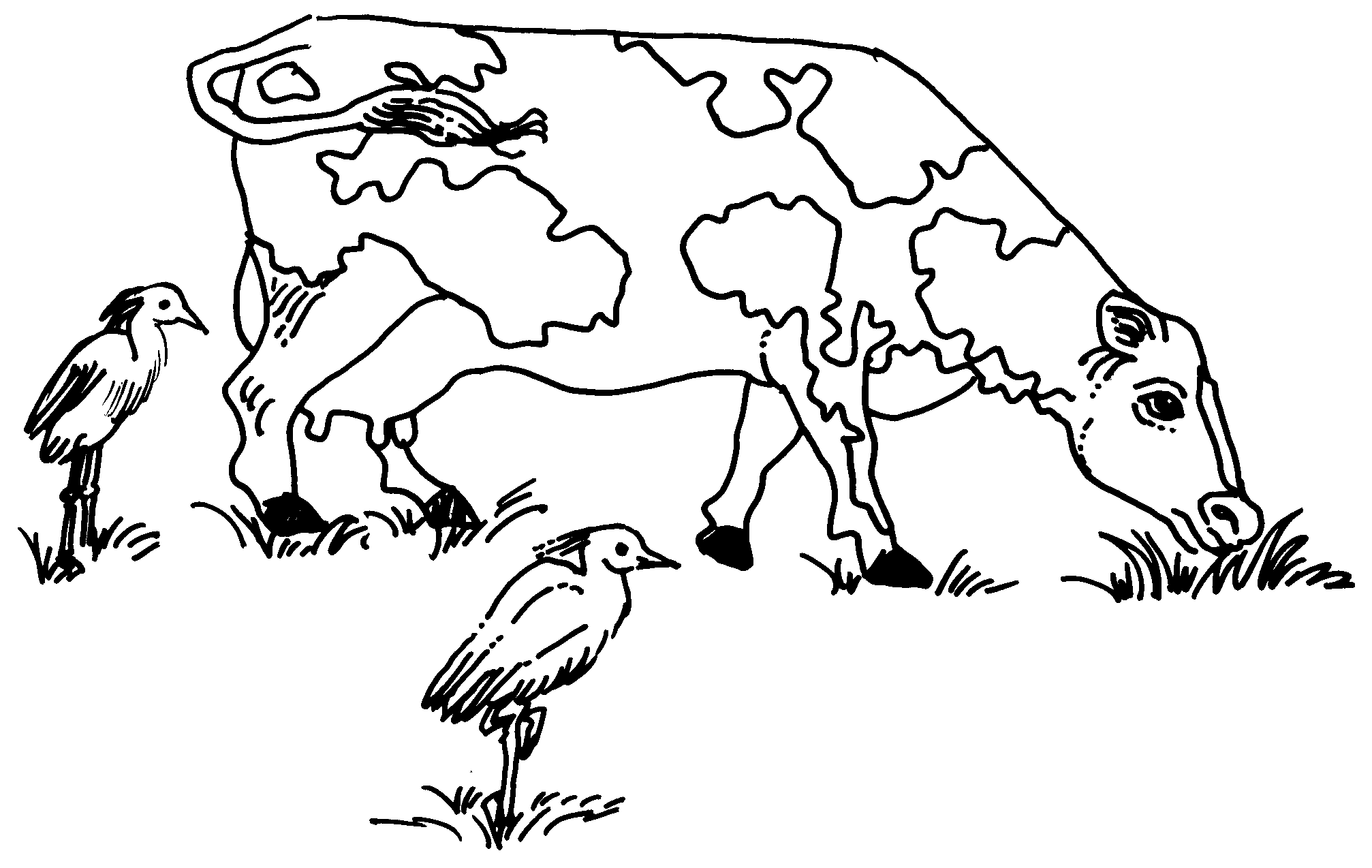
Example Of A Commensalism Relationship drawing free image download
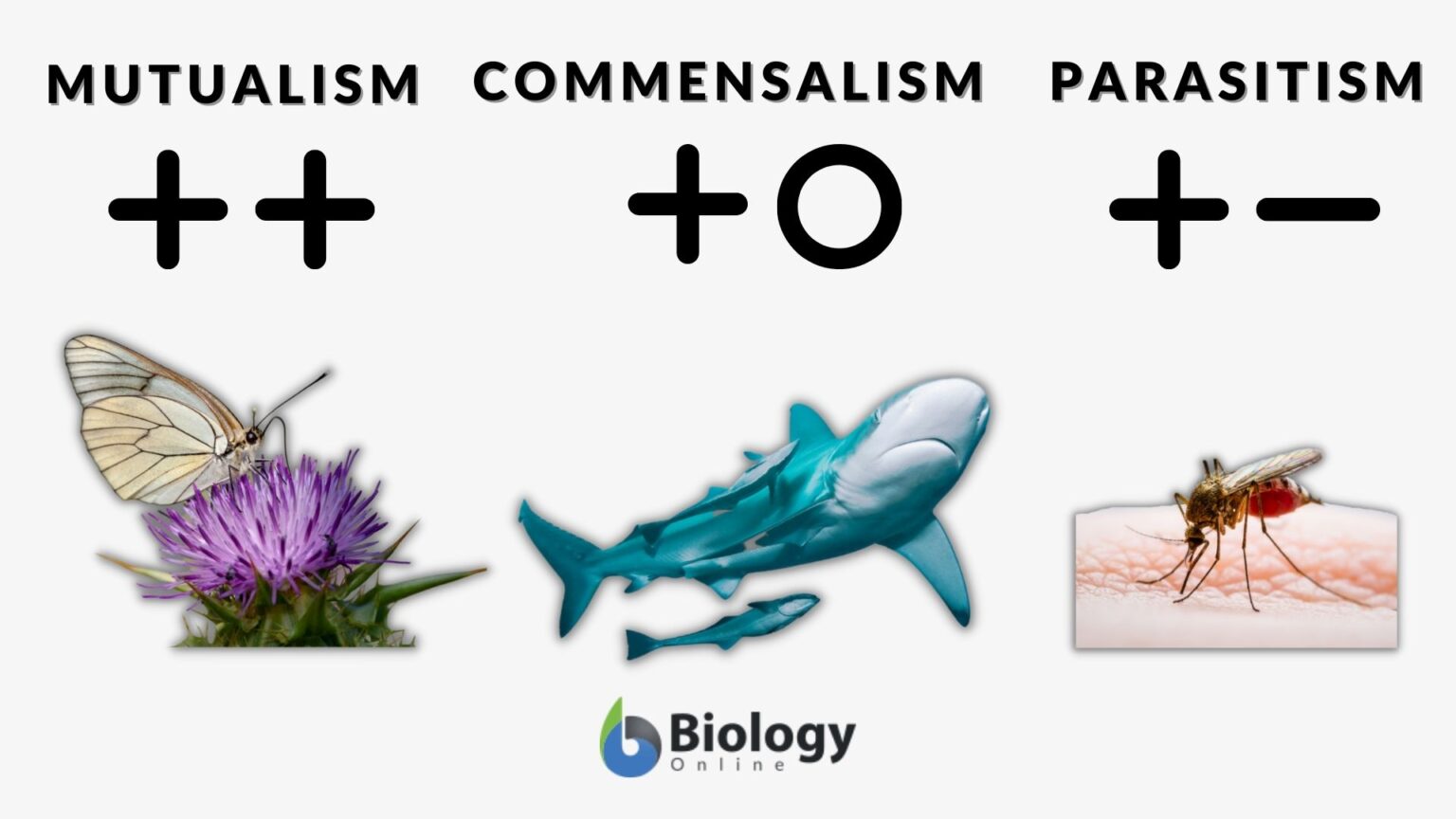
Commensalism Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary

Commensalism Stock Illustrations, Images & Vectors Shutterstock
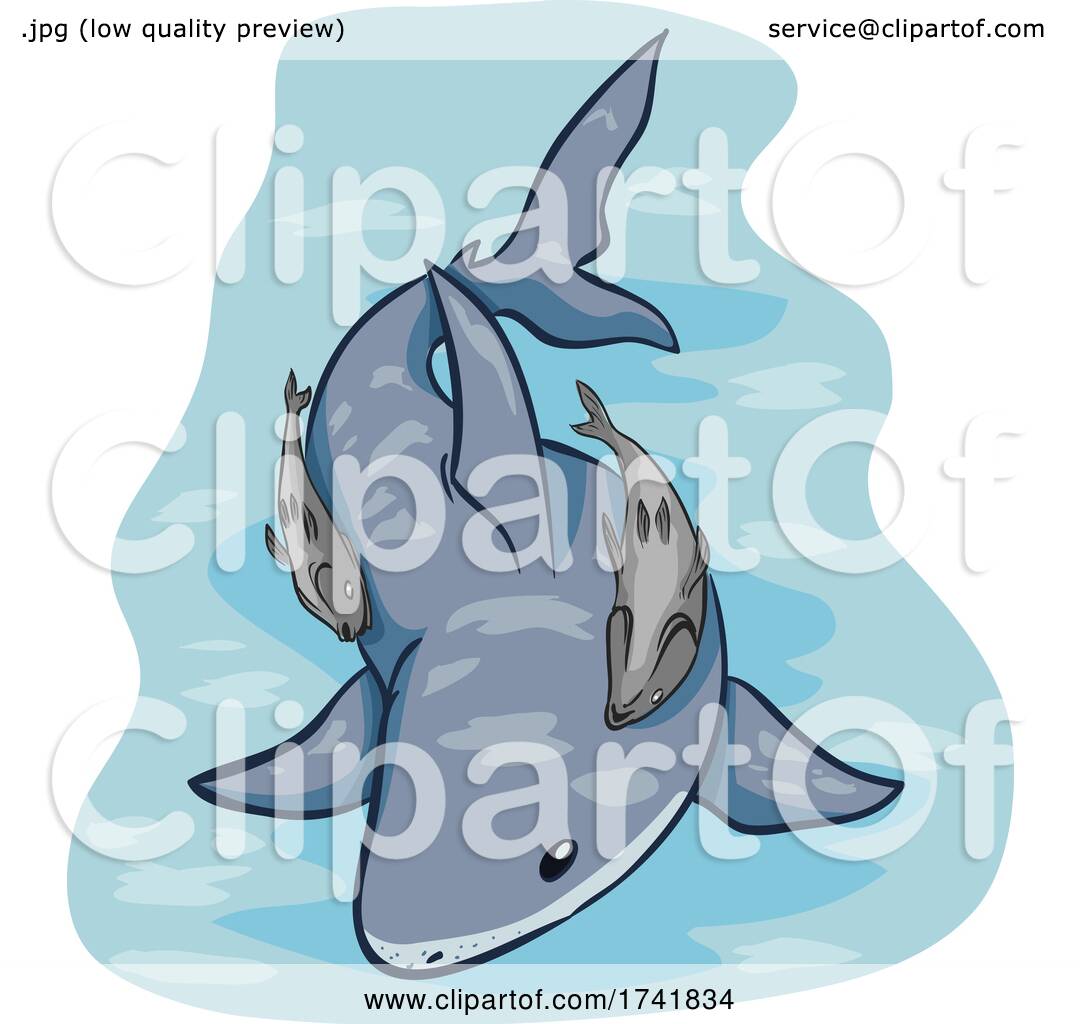

Commensalism Drawing
/commensalism-definition-and-examples-4114713-v2-706cadecce404b008d6620bb061841cc.png)
Commensalism Definition, Examples, and Relationships

Commensalism Drawing
Web Commensalism Is A Type Of Symbiotic Relationship Between Two Species, Where One Species Benefits Without Harming Or Benefiting The Other.
The Commensal Relation Is Often Between A Larger Host And A Smaller Commensal.
Web The Commensal—The Species That Benefits From The Association—May Obtain Nutrients, Shelter, Support, Or Locomotion From The Host Species, Which Is Unaffected.
Web Commensalism Is A Type Of Symbiotic Relationship Between Different Species Of Organisms In Which One Species Benefits From The Relationship While The Other Species Is Neither Harmed Nor Benefits.
Related Post: