Clumped Dispersion Pattern
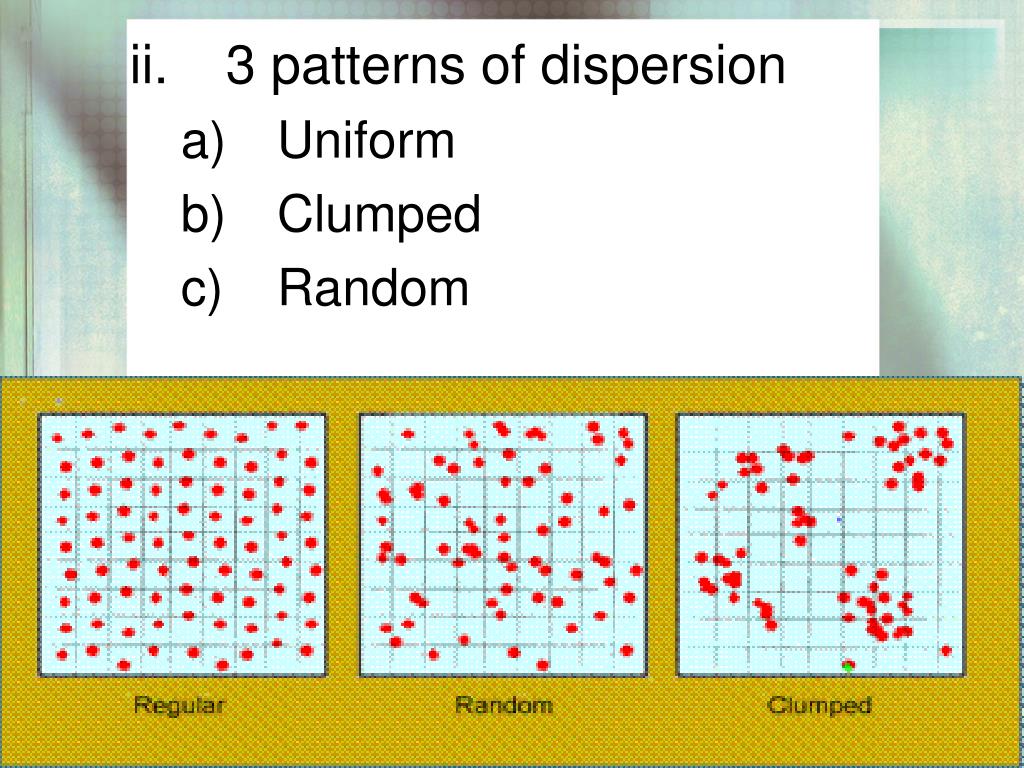
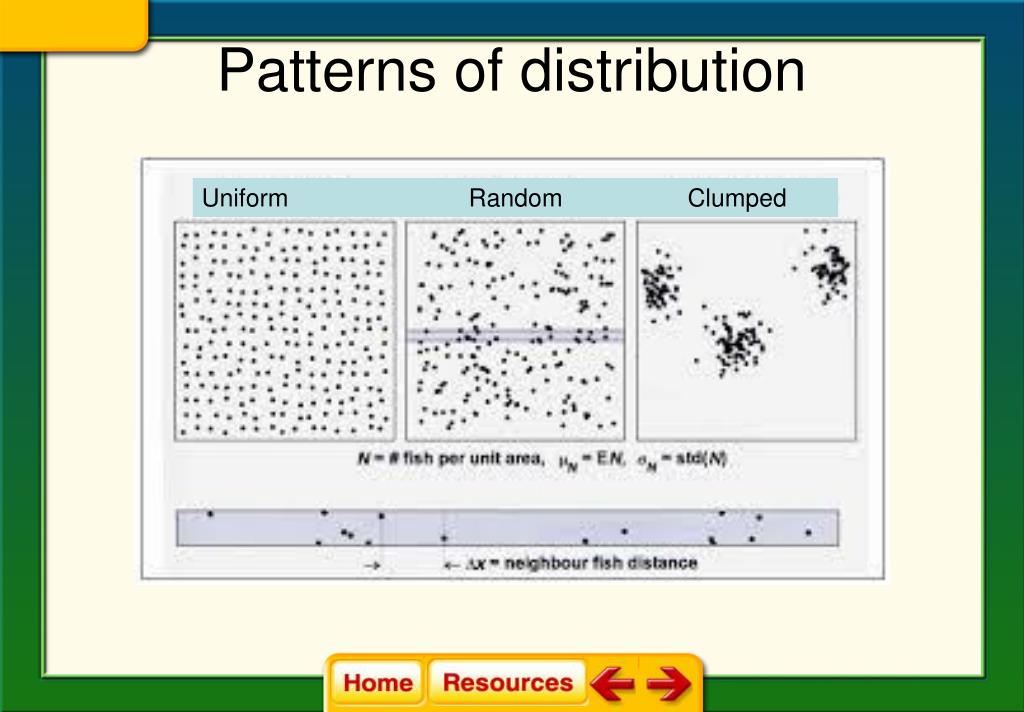
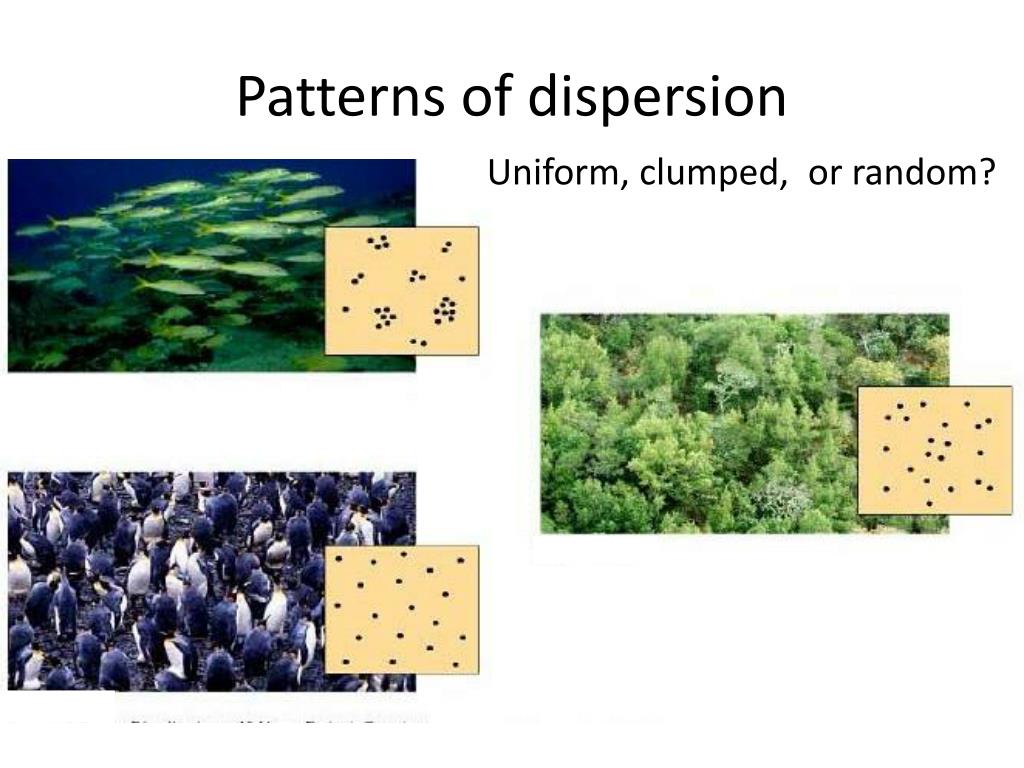
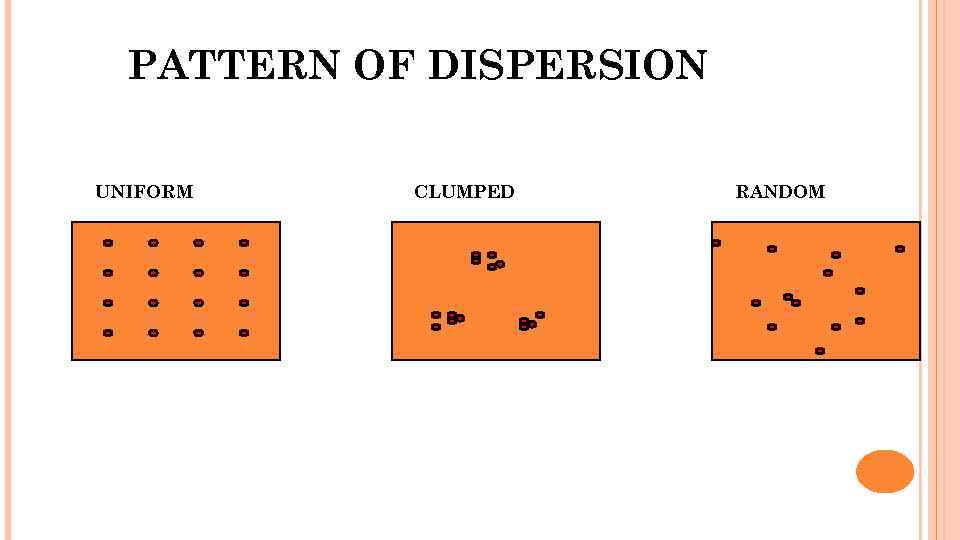
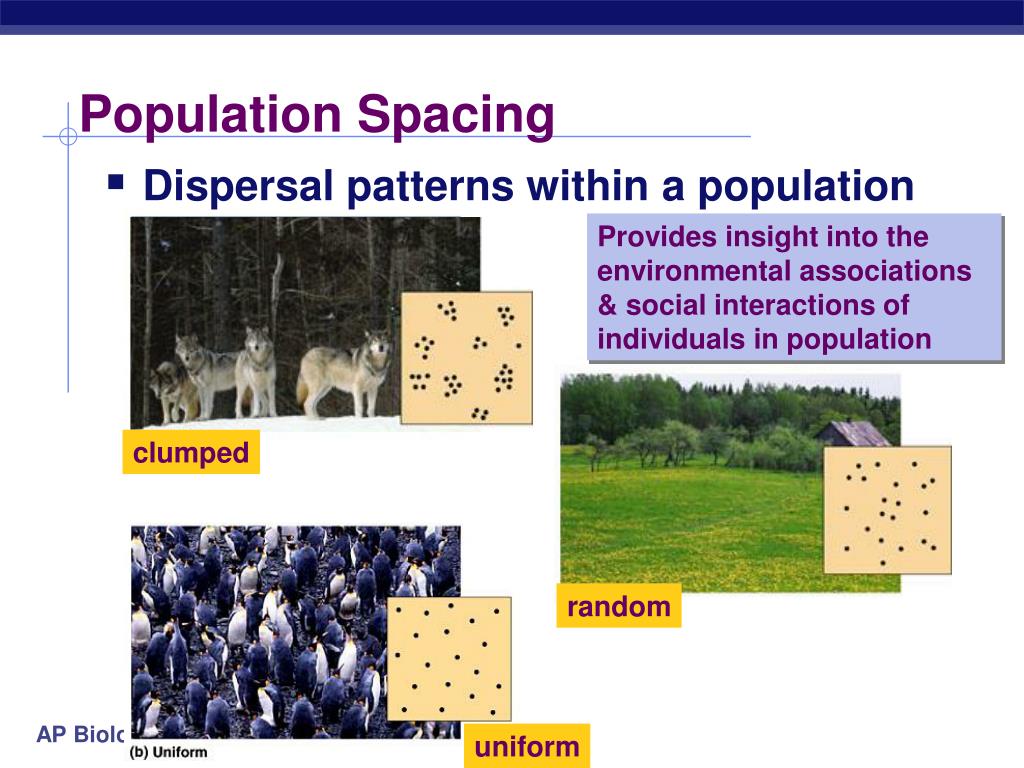
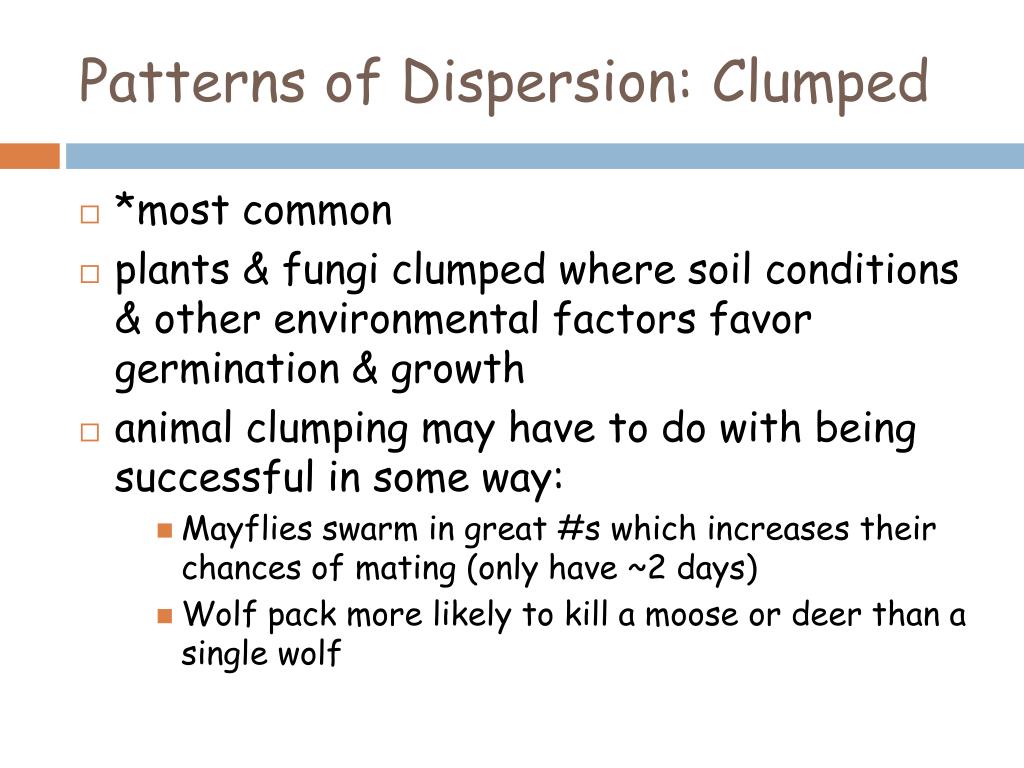
Clumped Dispersion Pattern - The three dispersion patterns are clumped, random, and uniform (figure \(\pageindex{a}\)). In a clumped dispersion, individuals are clustered in groups. Examples of clumped dispersion includes wolf packs that survive better in a clumped. They can be more or less equally spaced apart (uniform dispersion), dispersed randomly with no predictable pattern (random dispersion), or clustered in. Web clumped dispersion occurs with organisms that utilize social hierarchy or lack dispersal methods. Or a uniform pattern, with a roughly equal spacing of individuals. Web a specific type of organism can establish one of three possible patterns of dispersion in a given area: Web the dispersion pattern (distribution pattern) of a population describes the arrangement of individuals within a habitat at a particular point in time, and broad categories of patterns are used to describe them. Web the organisms in a population may be distributed in a uniform, random, or clumped pattern. In clumped distribution, the distance between neighboring individuals is minimized. Web these three figures illustrate the three different patterns of dispersion that ecologists observe. An aggregated pattern, in which organisms gather in clumps; They also affect the mathematical methods required to. Web clumped distribution, also called aggregated distribution, clumped dispersion or patchiness, is the most common type of dispersion found in nature. Web individuals of a population can be distributed. Web a specific type of organism can establish one of three possible patterns of dispersion in a given area: Web individuals in a population can be more or less equally spaced apart, dispersed randomly with no predictable pattern, or clustered in groups. Web clumped distribution, also called aggregated distribution, clumped dispersion or patchiness, is the most common type of dispersion. Web a specific type of organism can establish one of three possible patterns of dispersion in a given area: Web clumped distribution, also called aggregated distribution, clumped dispersion or patchiness, is the most common type of dispersion found in nature. In a clumped dispersion, individuals are clustered in groups. Clumped dispersion (figure 1) where individuals are aggregated in certain areas. Web individuals of a population can be distributed in one of three basic patterns: Examples of clumped dispersion includes wolf packs that survive better in a clumped. In a clumped dispersion, individuals are clustered in groups. Web these three figures illustrate the three different patterns of dispersion that ecologists observe. They can be more or less equally spaced apart (uniform. Web the dispersion pattern (distribution pattern) of a population describes the arrangement of individuals within a habitat at a particular point in time, and broad categories of patterns are used to describe them. They can be more or less equally spaced apart (uniform dispersion), dispersed randomly with no predictable pattern (random dispersion), or clustered in. The three dispersion patterns are. Or a uniform pattern, with a roughly equal spacing of individuals. Web a specific type of organism can establish one of three possible patterns of dispersion in a given area: Web clumped distribution, also called aggregated distribution, clumped dispersion or patchiness, is the most common type of dispersion found in nature. An aggregated pattern, in which organisms gather in clumps;. Web a specific type of organism can establish one of three possible patterns of dispersion in a given area: These are known as uniform, random, and clumped dispersion patterns, respectively (figure 36.5). Web individuals of a population can be distributed in one of three basic patterns: They also affect the mathematical methods required to. Web these three figures illustrate the. They also affect the mathematical methods required to. In clumped distribution, the distance between neighboring individuals is minimized. Web the dispersion pattern (distribution pattern) of a population describes the arrangement of individuals within a habitat at a particular point in time, and broad categories of patterns are used to describe them. Uniform means that the population is evenly spaced, random. Web individuals within a population can be distributed at random, in groups, or equally spaced apart (more or less). Web these three figures illustrate the three different patterns of dispersion that ecologists observe. Or a uniform pattern, with a roughly equal spacing of individuals. An aggregated pattern, in which organisms gather in clumps; They also affect the mathematical methods required. Examples of clumped dispersion includes wolf packs that survive better in a clumped. An aggregated pattern, in which organisms gather in clumps; Web these three figures illustrate the three different patterns of dispersion that ecologists observe. Or a uniform pattern, with a roughly equal spacing of individuals. A clumped dispersion may be seen in plants that drop their seeds straight. In a clumped dispersion, individuals are clustered in groups. A clumped dispersion may be seen in plants that drop their seeds straight to the ground—such as oak trees—or animals that live in groups—such as. These are known as random, clumped, and uniform distribution patterns, respectively (figure 19.3). Web clumped distribution, also called aggregated distribution, clumped dispersion or patchiness, is the most common type of dispersion found in nature. Different distributions reflect important aspects of the biology of the species; These are known as uniform, random, and clumped dispersion patterns, respectively (figure 36.5). Web individuals of a population can be distributed in one of three basic patterns: Web individuals within a population can be distributed at random, in groups, or equally spaced apart (more or less). Web individuals in a population can be more or less equally spaced apart, dispersed randomly with no predictable pattern, or clustered in groups. They can be more or less equally spaced apart (uniform dispersion), dispersed randomly with no predictable pattern (random dispersion), or clustered in. Web clumped dispersion occurs with organisms that utilize social hierarchy or lack dispersal methods. Examples of clumped dispersion includes wolf packs that survive better in a clumped. Clumped dispersion (figure 1) where individuals are aggregated in certain areas of the. Or a uniform pattern, with a roughly equal spacing of individuals. Uniform means that the population is evenly spaced, random indicates random spacing, and clumped means that the population is distributed in clusters. The three dispersion patterns are clumped, random, and uniform (figure \(\pageindex{a}\)).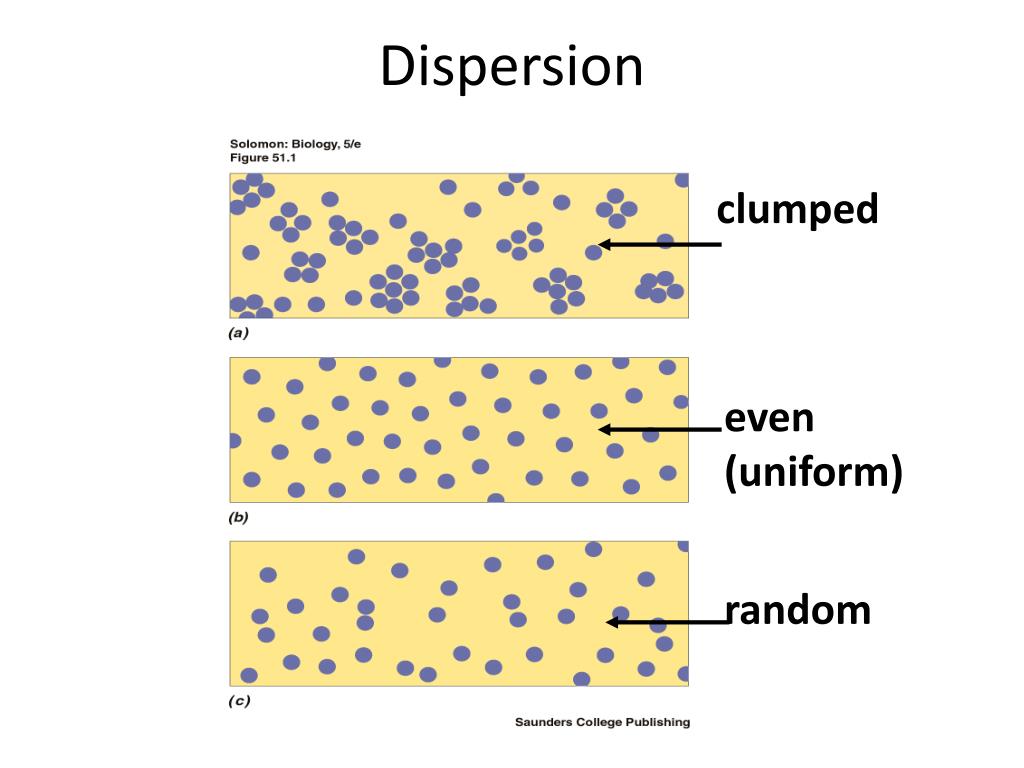
PPT Population Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2832017

Clumped Dispersion Pattern Definition & Explanation Video & Lesson
PPT Chapter 4 Population Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Chapter 4 Population Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Population Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
ECOLOGY OF INDIVIDUALS — AUTECOLOGY ORGANISM AND ENVIRONMENT

PPT Chapter 52 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID151315
PPT Population Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
PPT Population Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID

PPT Populations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2076927
Web These Three Figures Illustrate The Three Different Patterns Of Dispersion That Ecologists Observe.
In Clumped Distribution, The Distance Between Neighboring Individuals Is Minimized.
Web The Dispersion Pattern (Distribution Pattern) Of A Population Describes The Arrangement Of Individuals Within A Habitat At A Particular Point In Time, And Broad Categories Of Patterns Are Used To Describe Them.
Web A Specific Type Of Organism Can Establish One Of Three Possible Patterns Of Dispersion In A Given Area:
Related Post: