Chart Of Macromolecules
Chart Of Macromolecules - These large macromolecules may consist of thousands of covalently bonded atoms, some with mass greater than 100,000 daltons. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Is a leading independent global leader in the design, engineering, and manufacturing of process technologies and equipment for gas and liquid molecule handling for the nexus. Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Web there are three main types of biological macromolecules, according to mammalian systems: Web these are often categorized into four basic types: Web for the purpose of this evaluation, the operation on the molecule was simply a 25 ms wait and the molecule was in the state j i = 1, − 1 / 2, −. Carbohydrates (or polysaccharides), lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. Principles of biology ii (biol 2108) university. (c) molal and molar concentrations of dilute aqueous solutions are approximately equal. Is a leading independent global leader in the design, engineering, and manufacturing of process technologies and equipment for gas and liquid molecule handling for the nexus. These biological macromolecules are essential for life and include proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Unit 4 elements of life. Web chart industries, inc., a global leader in the design, engineering, and manufacturing of. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. In order to function in the cell, barnase has to be folded from a nonfunctional conformation into a functional conformation. While they have different structures and functions, they are all composed of long complex chains of. Web a macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biological processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. Web these are often categorized into four basic types: The image below depicts how the bacterial protein barnase undergoes modifications that involve changing its conformation, or shape. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. Web there are three main types of biological macromolecules,. These large macromolecules may consist of thousands of covalently bonded atoms, some with mass greater than 100,000 daltons. Is a leading independent global leader in the design, engineering, and manufacturing of process technologies and equipment for gas and liquid molecule handling for the nexus. Carbohydrates (or polysaccharides), lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. Unit 4 elements of life. Many macromolecules are. Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: As surprising as it seems, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is technically a set of macromolecules. Unit 8 membranes and transport. (c) molal and molar concentrations of dilute aqueous solutions are approximately equal. Web a macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biological processes, such as a protein or. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); Unit 6 structure of a cell. Web for the purpose of this evaluation, the operation on the molecule was simply a 25. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. The results are summarized in fig. Unit 7 more about cells. Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web explain each of the following statements: Each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Unit 8 membranes and transport. (b) carbon dioxide escapes from the solution when the cap is removed from a carbonated softdrink bottle. Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: The image below depicts how the bacterial protein barnase undergoes modifications that involve changing its conformation, or shape. In order to function in the cell, barnase has to be folded from. This document has been uploaded by a student, just like you, who decided to remain anonymous. They can have very different shapes, although the most common structure involves a long chain. Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. The four major. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Unit 8 membranes and transport. Different types of biological macromolecules. Macromolecules are made up of single units known as monomers that are joined by covalent bonds to form larger polymers. The four major classes of biological macromolecules are. Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. These large macromolecules may consist of thousands of covalently bonded atoms, some with mass greater than 100,000 daltons. Web chart industries, inc., a global leader in the design, engineering, and manufacturing of process technologies and equipment for gas and liquid molecule handling, has released its financial results for the second quarter of 2024. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules. Principles of biology ii (biol 2108) university. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); Perimeter college at georgia state university. Web explain each of the following statements: Unit 4 elements of life.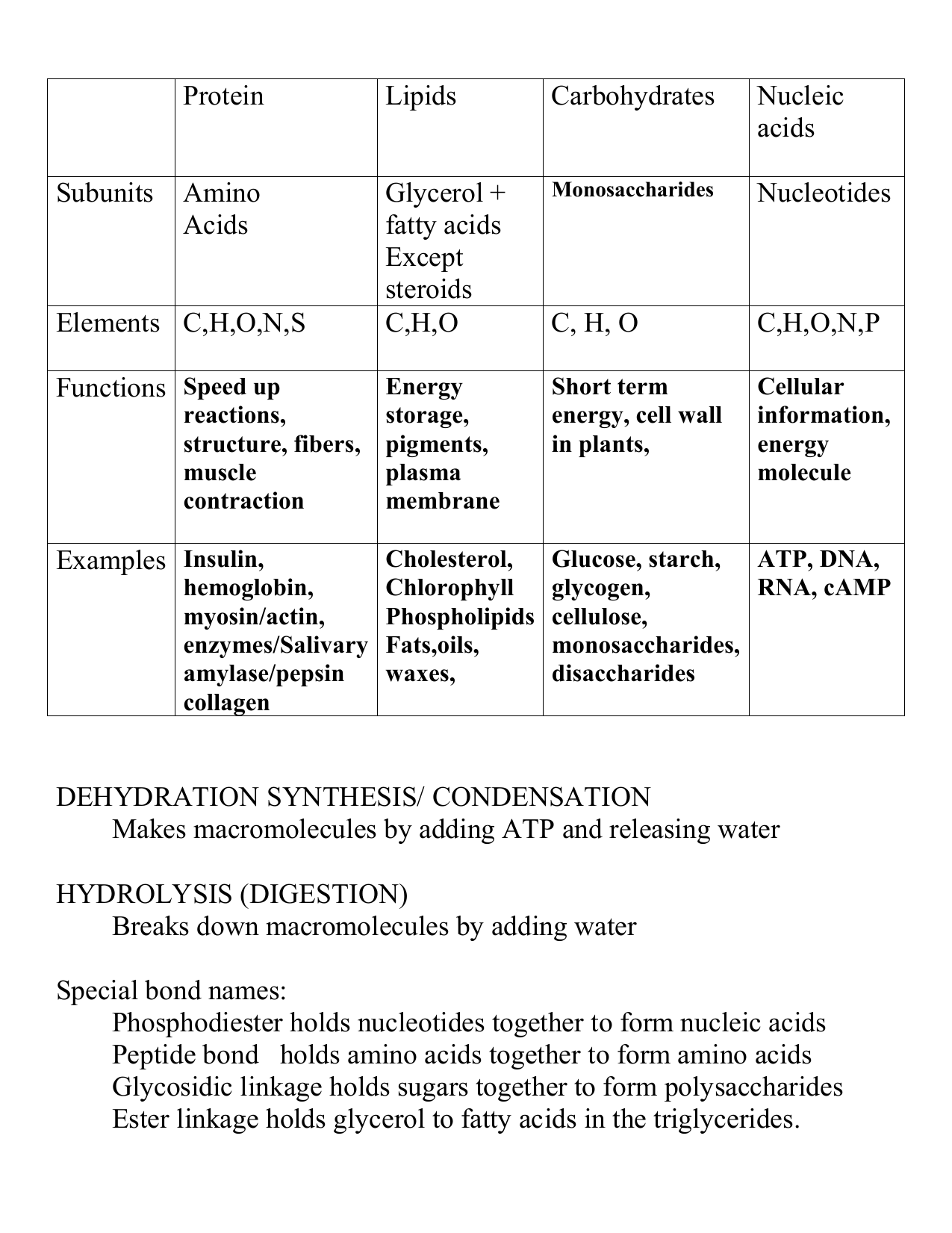
Biochemistry Macromolecules Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart

2.3 Biologically Important Macromolecules Biology LibreTexts
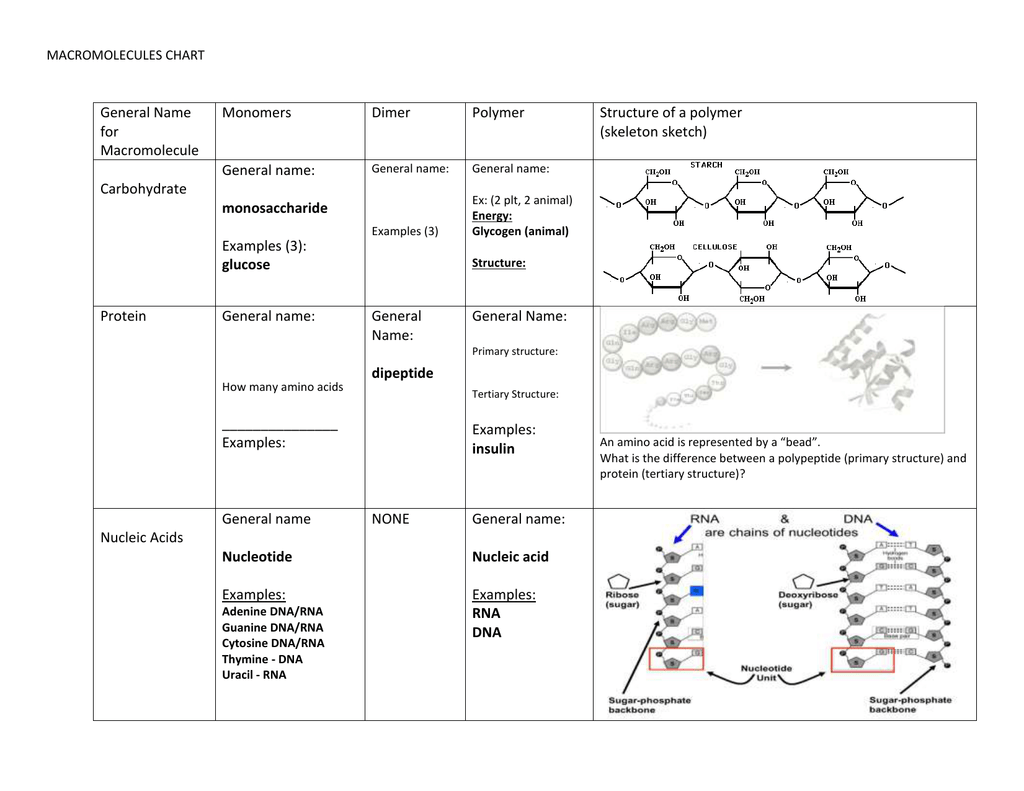
MACROMOLECULES CHART General Name for Macromolecule
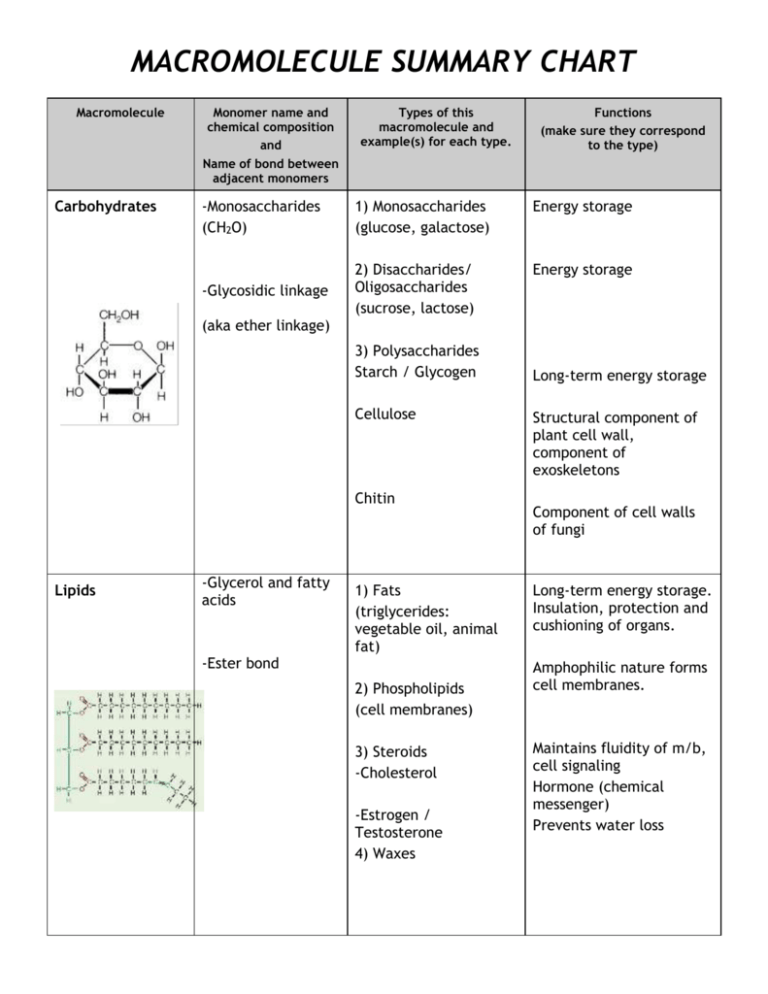
macromolecule summary chart
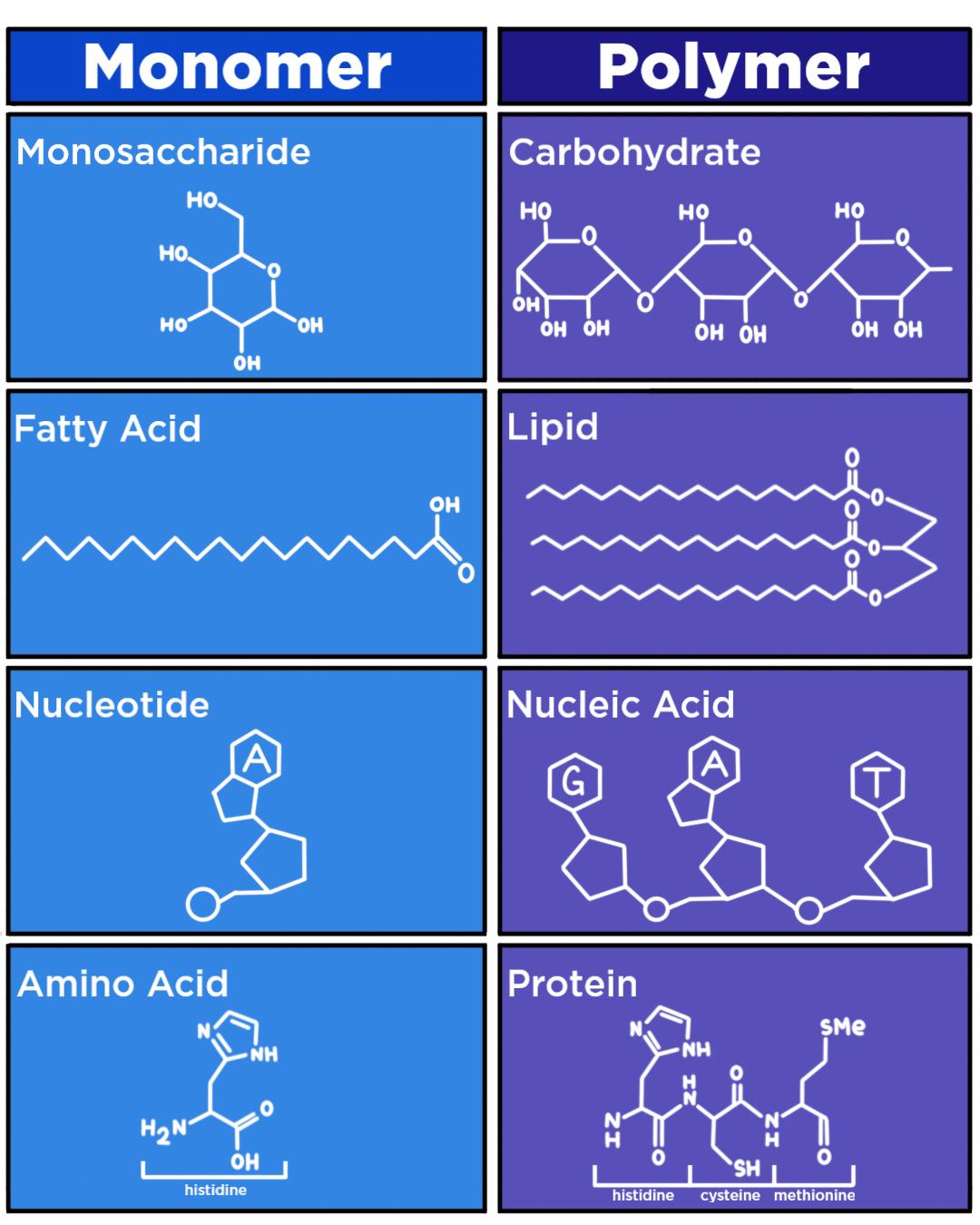
Macromolecules Monomers And Polymers Chart

Macromolecules Teaching biology, Biology lessons, Science biology
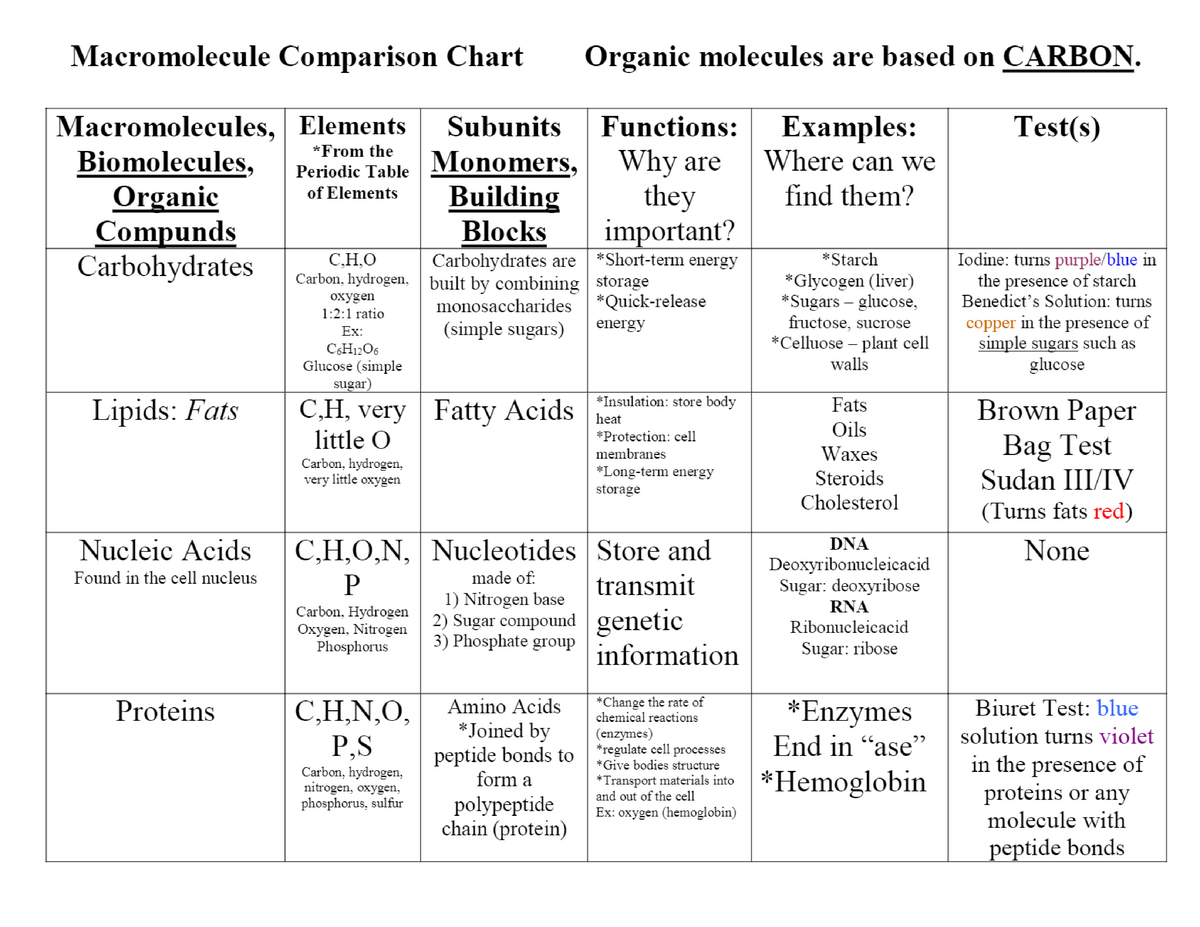
Macromolecule Comparison Chart Organic Bio201 Studocu
Macromolecules Chart Rae Rocks Teaching

simple diagram of macromolecules, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and

Pre IB/GT Biology 1 Macromolecules Chart Diagram Quizlet
These Are Classified Separately In Different Segments Of A Course.
The Results Are Summarized In Fig.
Web Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like What Are The Four Macromolecules?, The Monomer Of Carbohydrates, The Monomer Of Proteins And More.
Carbohydrates (Or Polysaccharides), Lipids, Proteins And Nucleic Acids.
Related Post: