Chart Of Electron Affinity
Chart Of Electron Affinity - The figure below shows electron affinities in \(\ce{kj/mol}\) for the representative elements. Web electron affinity can be defined in two equivalent ways. Web electron affinity chart for all the elements are given below. Web explore how electron affinity changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. You can also get the periodic table labeled with electron affinity values of elements. Web the electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released per mole when an electron is added to a neutral atom. Web the electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form a negative ion. X(g) + e − → x − (g) + energy In other words, the neutral atom's likelihood of gaining an electron. Electron affinity also applies to molecules, in some cases. Adding an electron to a metal requires energy. In other words, the neutral atom's likelihood of gaining an electron. Web the electron affinity is the potential energy change of the atom when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atom to form a negative ion. Web halogens have the greatest electron affinity, and this can be easily explained by. The figure below shows electron affinities in \(\ce{kj/mol}\) for the representative elements. Web table shows electron affinity (i.e. E(g) +e− → e−(g) energy change=ea (4.5.1) (4.5.1) e ( g) + e − → e ( g) − energy change= e a. Web electron affinity is defined as the change in energy (in kj/mole) of a neutral atom (in the gaseous. In general, elements with the most negative electron affinities (the highest affinity for an added electron) are those with the smallest size and highest ionization energies and are located in the upper right. Electron affinity is the energy change when an atom gains an electron. Electron affinities decrease from top to bottom down groups. In other words, the neutral atom's. Adding an electron to a metal requires energy. The equivalent more common definition is the energy released (e initial + e final) when an additional electron is attached to a neutral atom or molecule. The figure below shows electron affinities in \(\ce{kj/mol}\) for the representative elements. Web the electron affinity (ea) is the energy released to add an electron to. By convention, the negative sign shows a release of energy. First, as the energy that is released by adding an electron to an isolated gaseous atom. In other words, the neutral atom's likelihood of gaining an electron. As discussed, electron affinities increase from left to right across periods; Web halogens have the greatest electron affinity, and this can be easily. For most elements, except noble gases, this is an exothermic process. Web the energy change that occurs when a neutral atom gains an electron is called its electron affinity. Web halogens have the greatest electron affinity, and this can be easily explained by looking at their valence shell electron configuration: The figure below shows electron affinities in \(\ce{kj/mol}\) for the. The electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule to form a negative ion. The first electron affinities of the group 7 elements. The tendency of an atom or. Web the electron affinity (ea) of an element is the energy change that. What does electron affinity determine? When energy is released in a chemical reaction or process, that energy is expressed as a negative number. X(g) +e− → x−(g) + energy (a7.1) (a7.1) x ( g) + e − → x ( g) − + e n e r g y. As discussed, electron affinities increase from left to right across periods;. First electron affinities have negative values. Web the electron affinity ( ea e a) of an element e e is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: The figure below shows electron affinities in \(\ce{kj/mol}\) for the representative elements. As discussed, electron affinities increase from left to right across. Web the electron affinity ( ea e a) of an element e e is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: The second (reverse) definition is that electron affinity is the energy required to remove an electron from a singly charged gaseous negative ion. Electron affinities decrease from top. Web the electron affinity (ea) is the energy released to add an electron to an elements in the gaseous state. The equivalent more common definition is the energy released (e initial + e final) when an additional electron is attached to a neutral atom or molecule. In other words, the neutral atom's likelihood of gaining an electron. For most elements, except noble gases, this is an exothermic process. The amount of energy released when an electron is added to atom) for most of chemical elements. Web the energy change that occurs when a neutral atom gains an electron is called its electron affinity. How to find electron affinity By convention, the negative sign shows a release of energy. Web the electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released per mole when an electron is added to a neutral atom. When energy is released in a chemical reaction or process, that energy is expressed as a negative number. Web explore how electron affinity changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. The first electron affinities of the group 7 elements. X(g) +e− → x−(g) + energy (a7.1) (a7.1) x ( g) + e − → x ( g) − + e n e r g y. First, as the energy that is released by adding an electron to an isolated gaseous atom. So the more negative the electron affinity the more favourable the electron addition process is. As discussed, electron affinities increase from left to right across periods;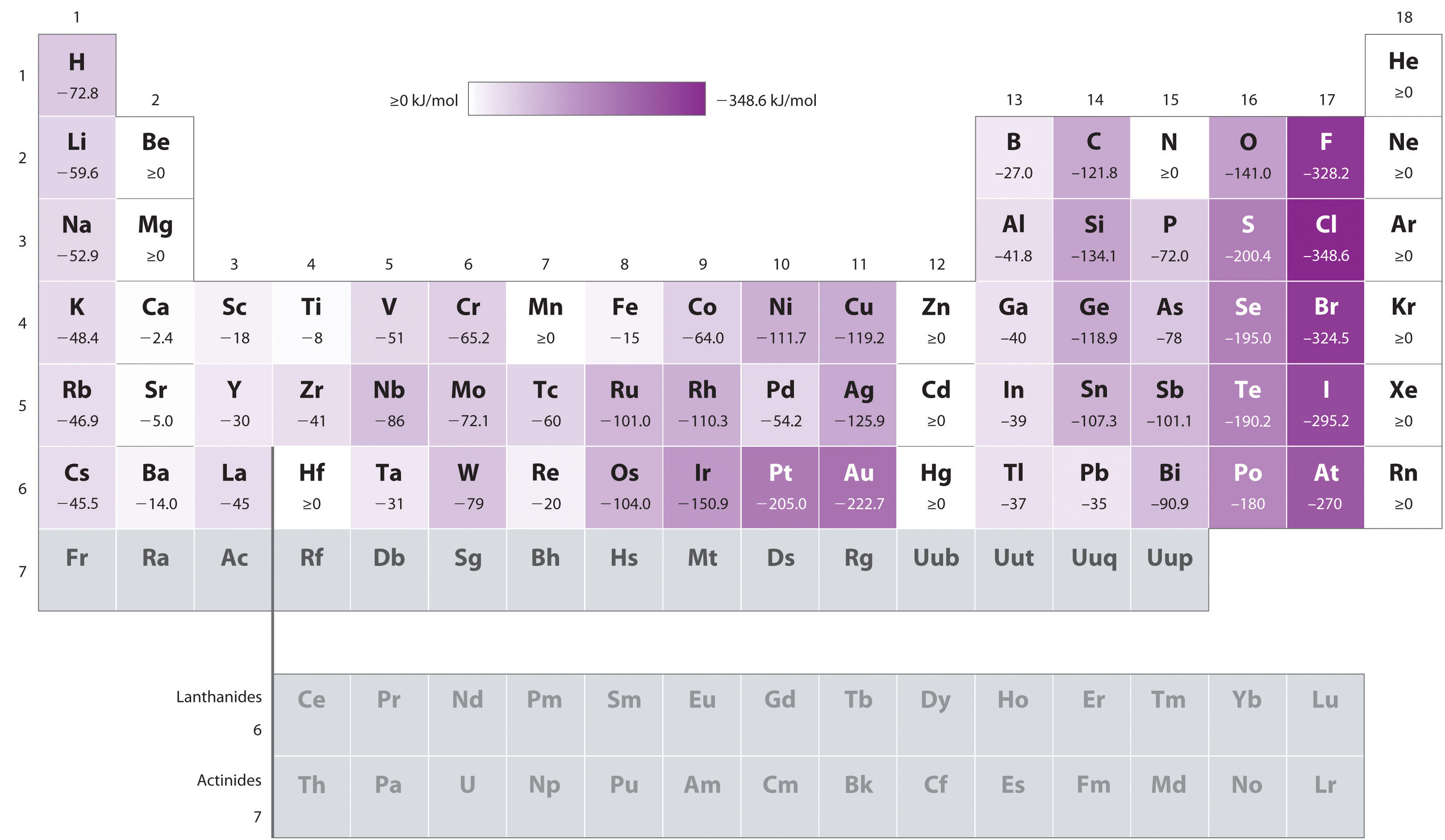
7.5 Electron Affinities Chemistry LibreTexts
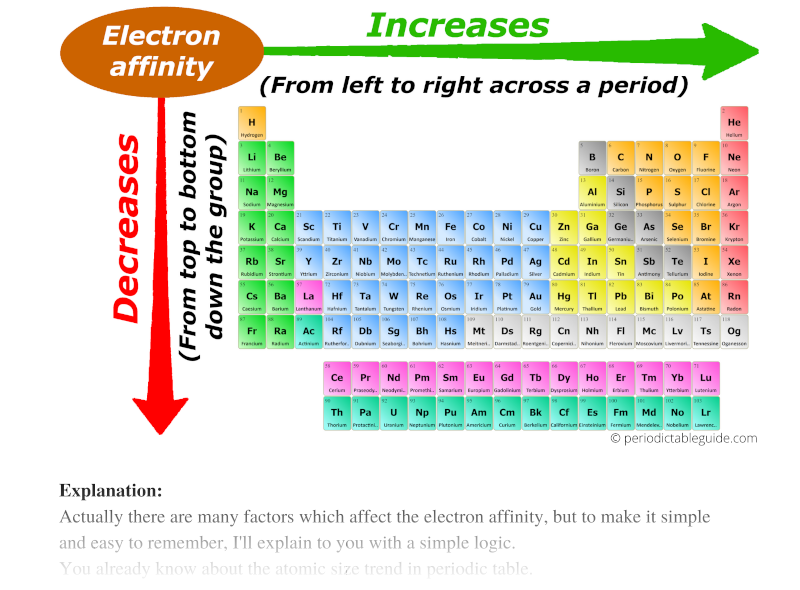
All Periodic Trends in Periodic Table (Explained with Image)
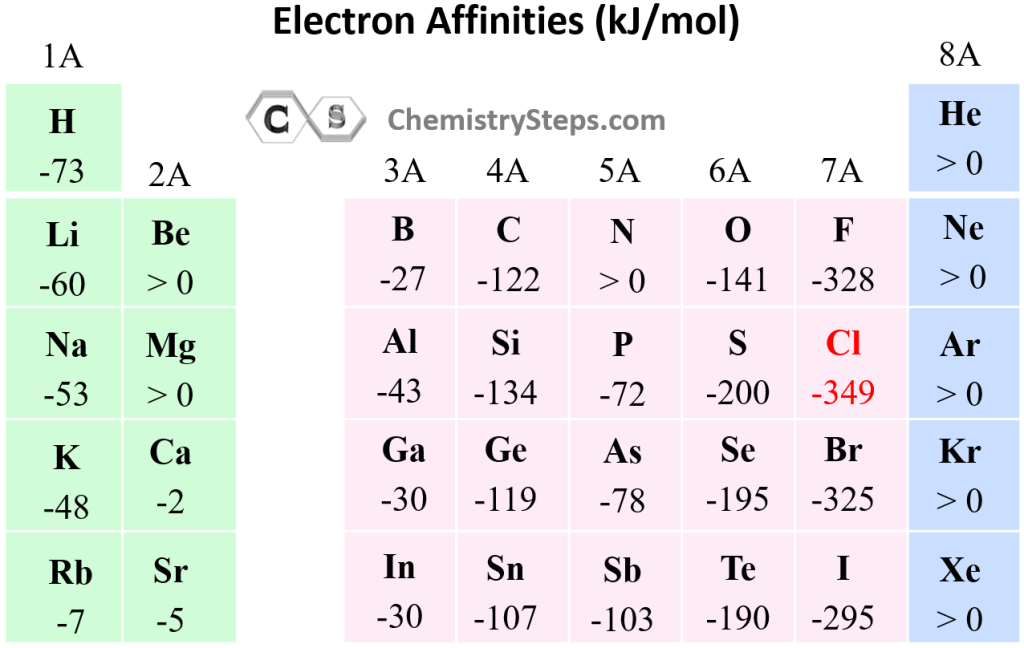
Electron Affinity Chemistry Steps
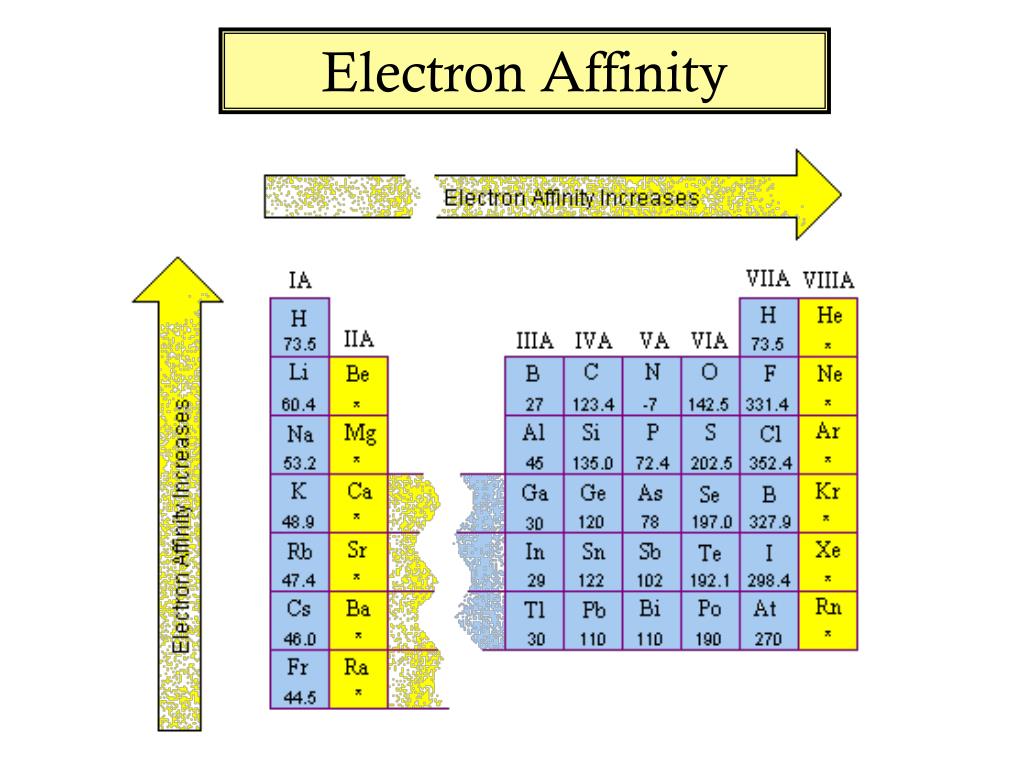
PPT Chapter 4 The Periodic Table PowerPoint Presentation, free
Periodic Behavior Presentation Chemistry
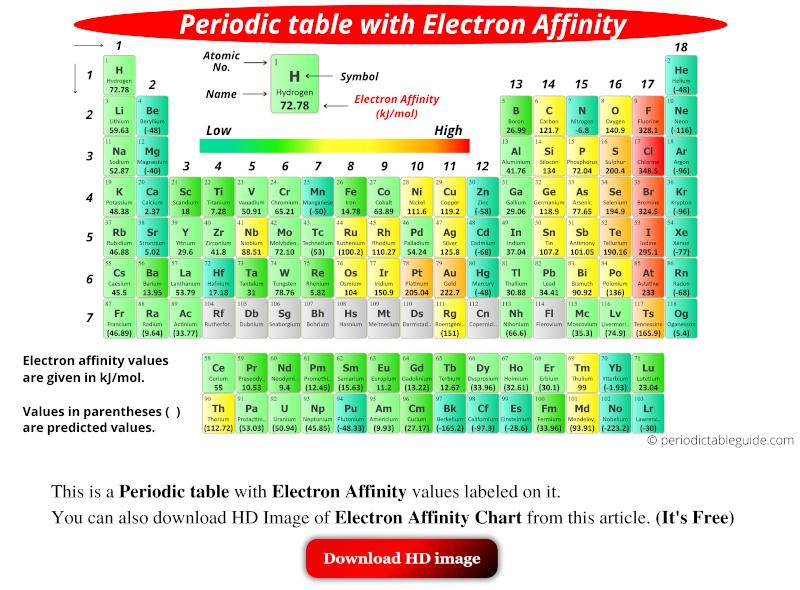
Electron Affinity Chart (Labeled Periodic table + List)
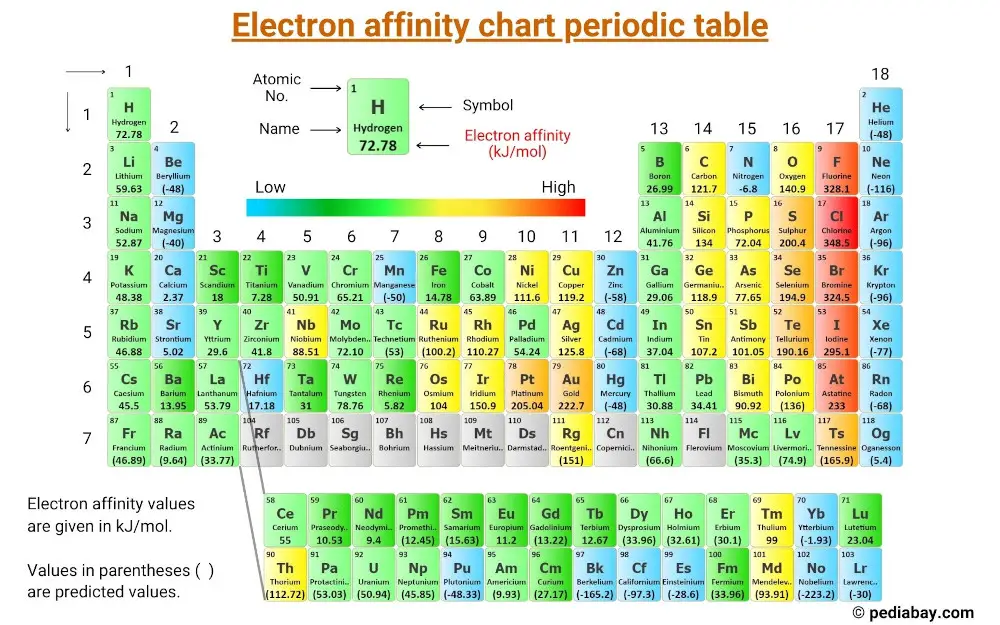
Electron Affinity Chart of Elements (With Periodic Table) Pediabay

Electron Affinity Trend and Definition

Electron Affinity Definition, Chart & Trend in Periodic Table

FileElectron affinity periodic table.svg Wikipedia
In General Successive Electron Affinity Increase In Magnitude Ea 1 < Ea 2 < Ea 3 And So On.
The Tendency Of An Atom Or.
The Electron Affinity Of An Atom Or Molecule Is Defined As The Amount Of Energy Released When An Electron Is Added To A Neutral Atom Or Molecule To Form A Negative Ion.
Electron Affinity Is The Energy Change When An Atom Gains An Electron.
Related Post:
.PNG)