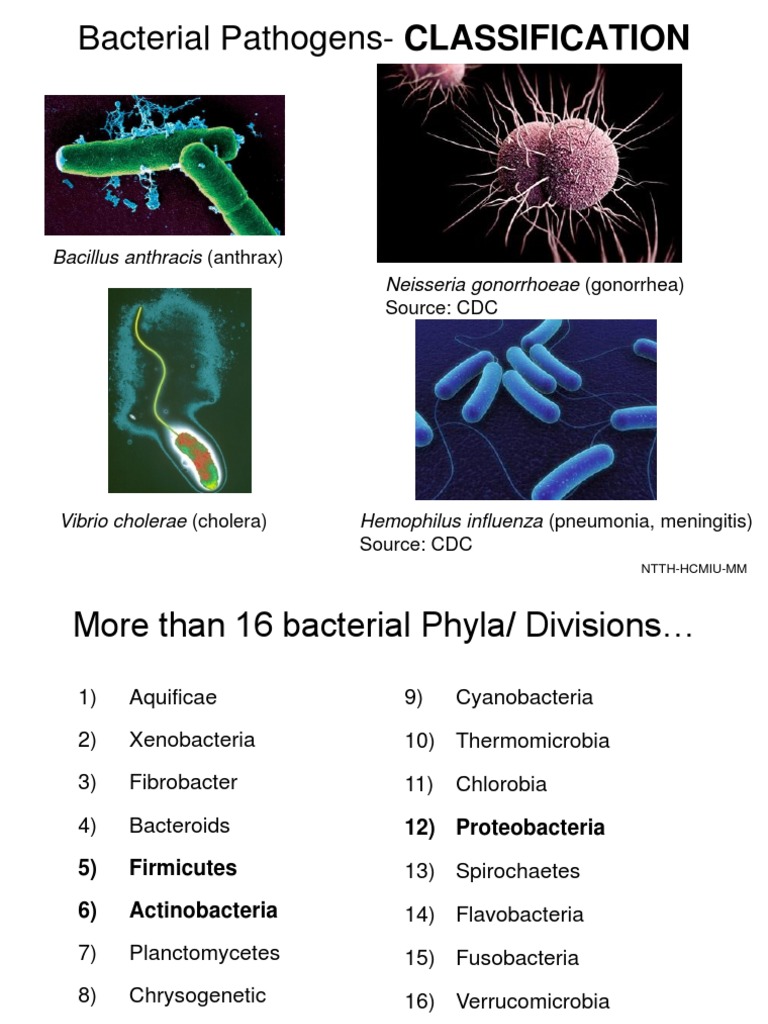
Chart Of Bacteria
Chart Of Bacteria - Web bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of earth's crust. However, they can be as tiny as 0.3 µm and as large as 0.7mm. Outer layer (cell envelope), cell interior, and additional structures. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. Web what are bacteria? There are many different types of bacteria. Discuss bacterial structure and the function of the different bacterial components 4. It has been examined that the size of bacteria has an important role in the survival of organisms. Web leukocyte levels in urine chart. Early microbial identification studies by microscopy. Outer layer (cell envelope), cell interior, and additional structures. Due to their small size, bacteria are able to exploit and thrive in various microenvironments. The limit of resolution with the unaided eye is about 200 microns, and as many bacteria are smaller. Web from identifying microbes by physical and functional characteristics to the adaptation of more modern techniques, microbiologists (and. Bacteria with a capital b refers to the. There are thousands of different kinds of bacteria, and they live in every conceivable environment all over the world. Web what are bacteria? Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms that divide by binary fission, a process by which one bacterium splits into two. Also easily determine which media should be used for each. One way of classifying them is by shape. Outer layer (cell envelope), cell interior, and additional structures. It includes the cell wall of bacteria and the plasma membrane beneath it. However, they can be as tiny as 0.3 µmeters and as large as 0.7 µm. There are three basic shapes. Based on planes of division, the coccus shape can appear in several distinct arrangements: Bacteria with a capital b refers to the. Determine the characteristics of bacteria such as shape, mobility, gram staining results, and incubation temperatures. Web from identifying microbes by physical and functional characteristics to the adaptation of more modern techniques, microbiologists (and future microbiologists) are continually building. Web on average, the size of bacteria ranges from 0.5 to 5 µm. There are three basic shapes. This classification is similar to that of plants, mammals, and other taxonomies. A visual exam to check color and clarity; Web the structure of the bacteria consists of three major parts: One way of classifying them is by shape. Web the bacteria diagram given below represents the structure of a typical bacterial cell with its different parts. Web 1 introduction 1.1 background as provided by the requestor. A dip test in which a test strip is dipped in the urine and displays color changes. However, biologists specializing in different areas have. Urine tests can detect and measure substances such as blood, cells (like white blood cells), sugar, bacteria, electrolytes, and proteins. Web the structure of the bacteria consists of three major parts: It includes the cell wall of bacteria and the plasma membrane beneath it. The cell wall, plasmid, cytoplasm and flagella are clearly marked in the diagram. Web on average,. Early microbial identification studies by microscopy. Classification on the basis of gram stain, bacterial cell wall, shape, mode of nutrition, temperature requirement, oxygen requirement, ph of growth, osmotic pressure requirement, number of flagella and spore formation. Based on planes of division, the coccus shape can appear in several distinct arrangements: Web bacterial taxonomy is the classification of strains within the. Web on average, the size of bacteria ranges from 0.5 to 5 µm. Urine is analyzed in a number of ways, including: Web on average, the size of bacteria ranges from 0.5 nanometers to 0.5 µmeters. Due to their small size, bacteria are able to exploit and thrive in various microenvironments. Bacterial shapes, arrangements, and forms. Web get the quick facts. Web on average, the size of bacteria ranges from 0.5 to 5 µm. Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms that divide by binary fission, a process by which one bacterium splits into two. Web bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of earth's crust. Since organisms are missing in such. Web the bacteria diagram given below represents the structure of a typical bacterial cell with its different parts. Web leukocyte levels in urine chart. They are among the earliest known life forms on earth. There are many different types of bacteria. It includes the cell wall of bacteria and the plasma membrane beneath it. Cocci (or coccus for a single cell) are round cells, sometimes slightly flattened when they are adjacent to one another. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. Urine tests can detect and measure substances such as blood, cells (like white blood cells), sugar, bacteria, electrolytes, and proteins. Bacterial shapes, arrangements, and forms. Recognize the shapes and arrangements of some common types of bacteria. This classification is similar to that of plants, mammals, and other taxonomies. Web bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of earth's crust. One way of classifying them is by shape. Web what are bacteria? Discuss the distinguishing characteristics of gram positive and gram negative bacteria. Determine the characteristics of bacteria such as shape, mobility, gram staining results, and incubation temperatures.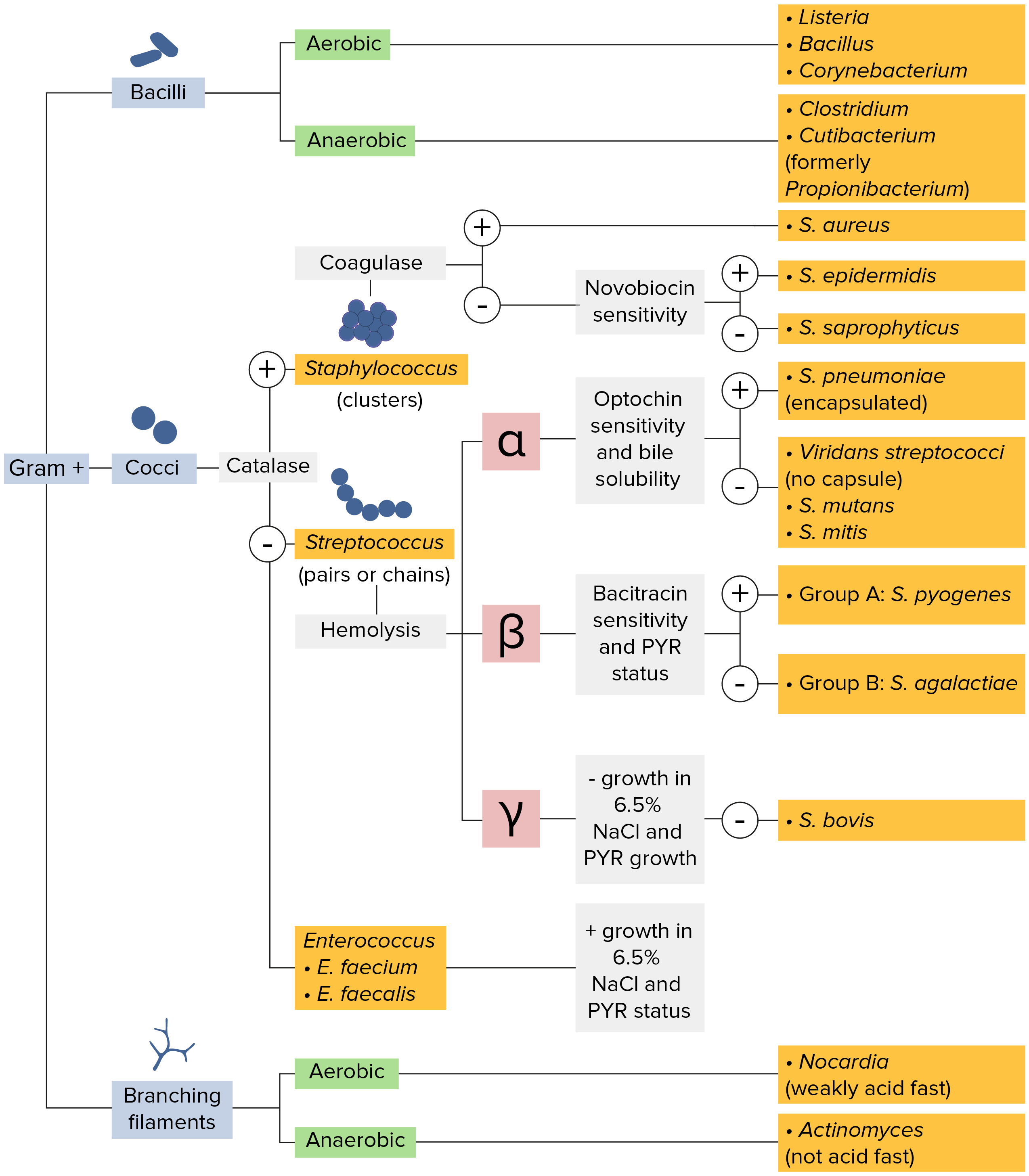
Streptococcus Concise Medical Knowledge

Bacteria Types Chart

Bacteria Identification Chart
Bacteria Types Chart

Bacteria Kingdom Classification
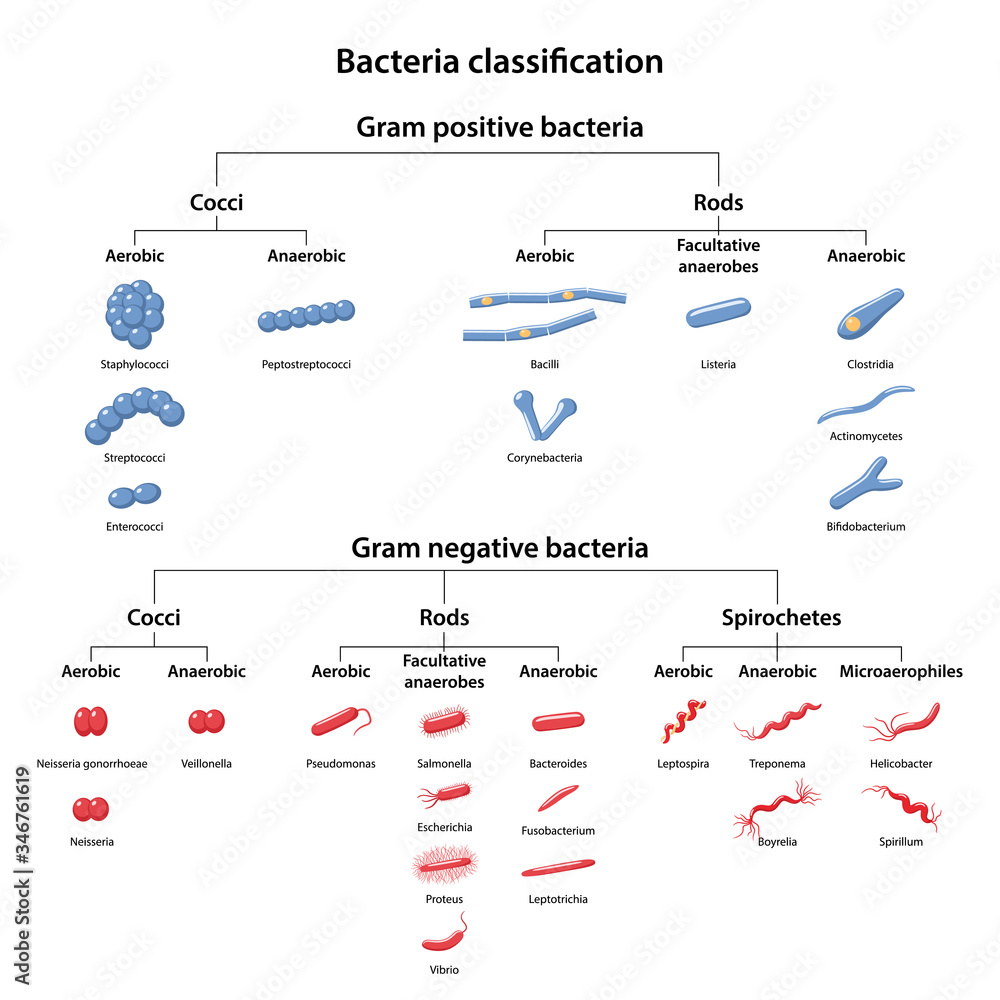
Classification of bacteria by type of respiration aerobic, anaerobic

Chart, Bacteria
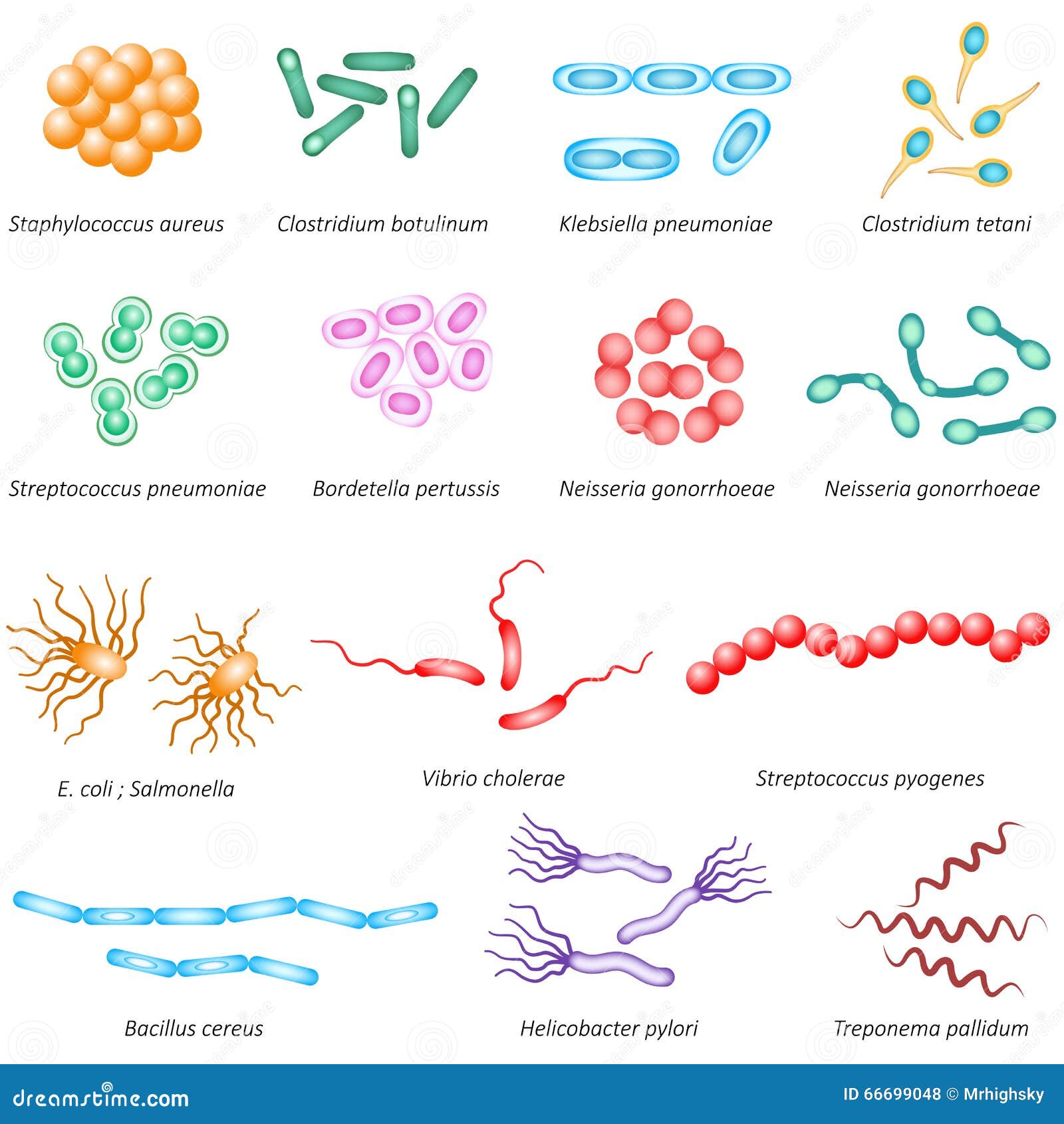
Common bacteria types stock vector. Image of education 66699048
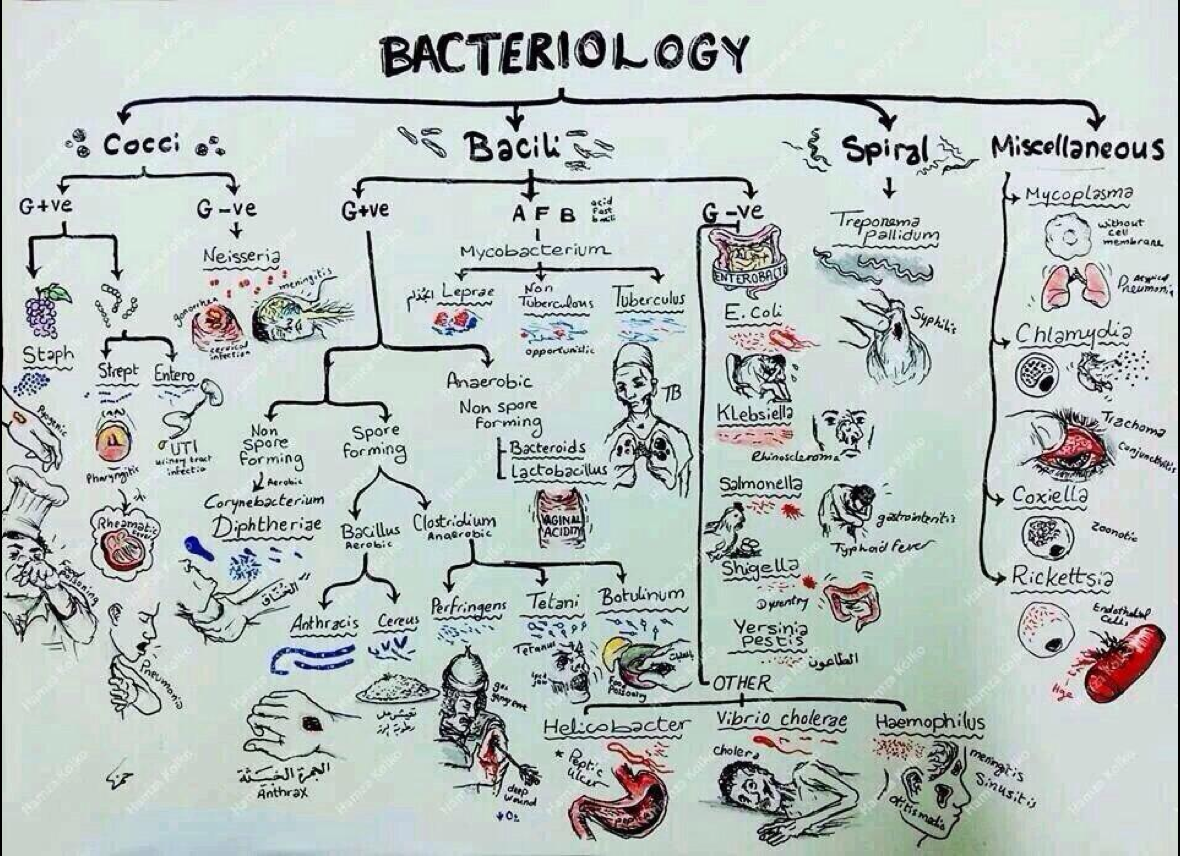
Usmle notes USMLE MICROBIOLOGY charts, tables, notes, uworld notes
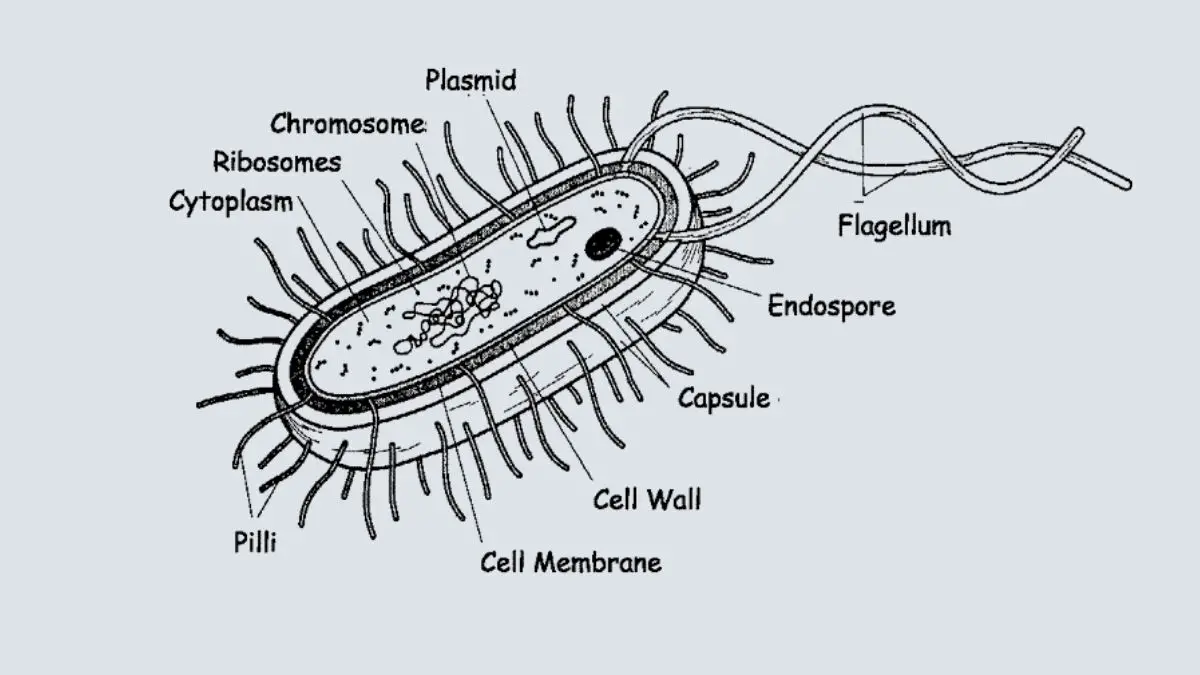
What is bacteria? Types, Structure, Shapes, Morphology, Nutrition
Early Microbial Identification Studies By Microscopy.
The Limit Of Resolution With The Unaided Eye Is About 200 Microns, And As Many Bacteria Are Smaller.
However, Biologists Specializing In Different Areas Have Developed Differing Taxonomic Conventions Over Time.
Classification On The Basis Of Gram Stain, Bacterial Cell Wall, Shape, Mode Of Nutrition, Temperature Requirement, Oxygen Requirement, Ph Of Growth, Osmotic Pressure Requirement, Number Of Flagella And Spore Formation.
Related Post: