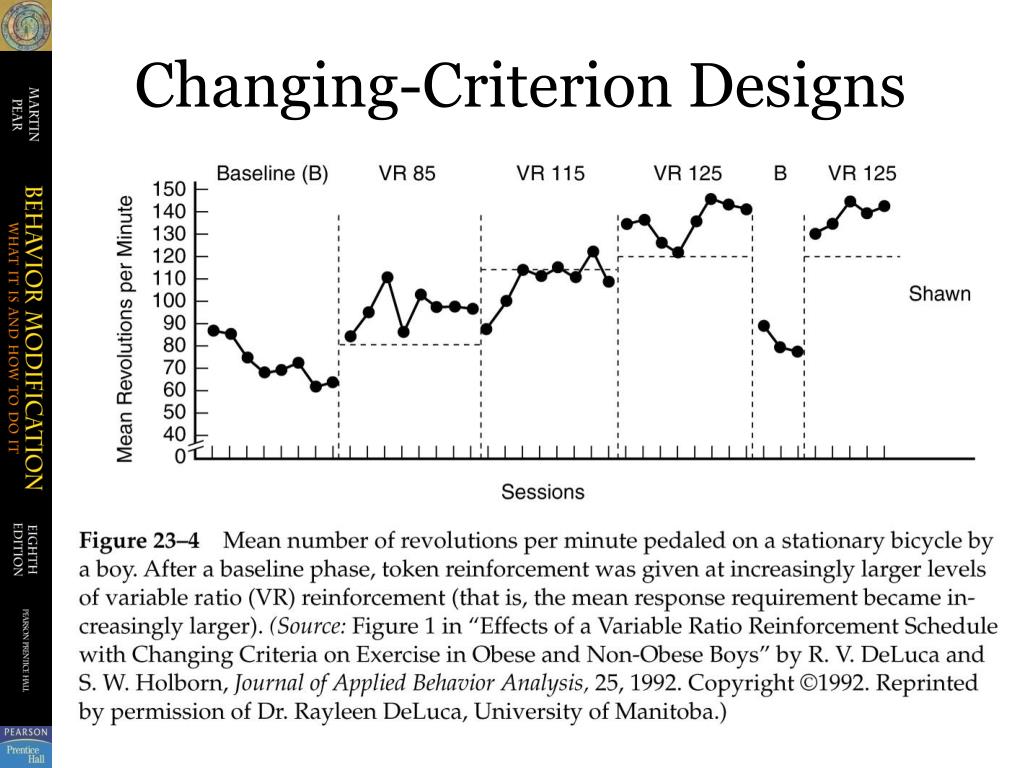
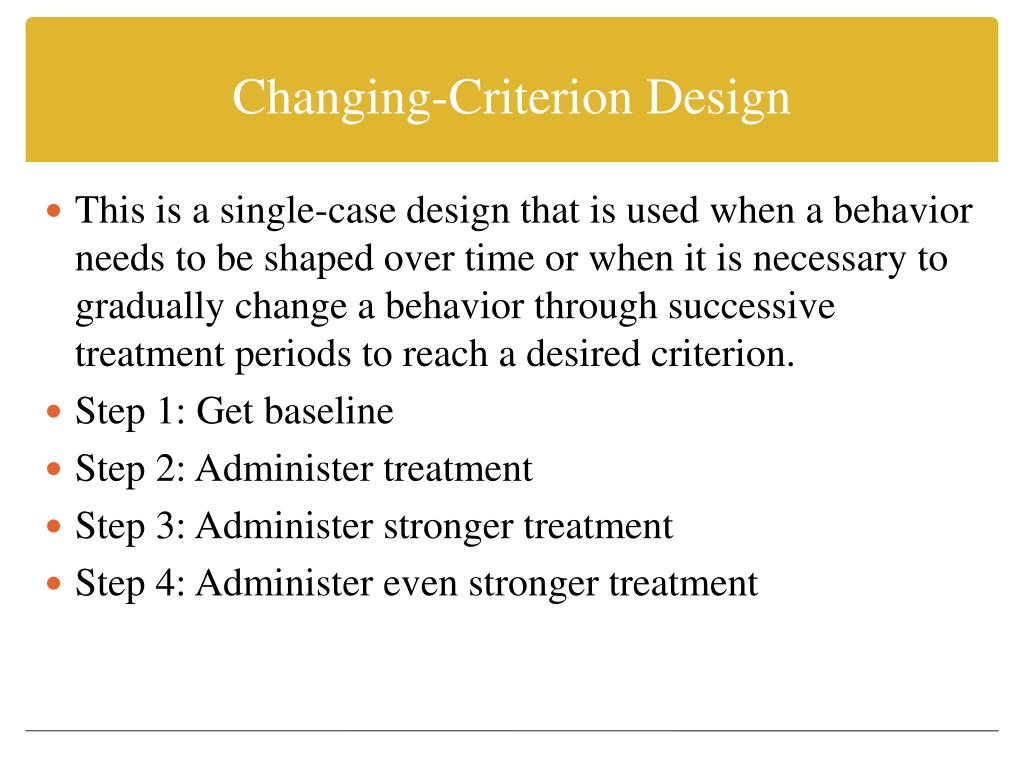
Changing Criterion Design Example
Changing Criterion Design Example - Web an overview of the changing criterion design, how to determine a functional relation, and pros/cons of the design. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. Any researcher, in the course of investigating the effects of a particular set of independent variables, must demonstrate that the observed changes in behavior are functionally related to the presence of those variables. Once stabilized, the treatment serves as a baseline for increased criterion of the next phase. Is a variation of the multiple baseline design. Approximation to the final level desired for a target behavior. Hallie steinberg & grete christianson limitations/concerns what we like/don't like about the design discussion rationale for the use of this design explanation no need to withhold intervention helps distinguish if intervention is working Web this article illustrates (a) 2 recent innovations in the changing criterion research design, (b) how these innovations apply to research and practice in special education, and (c) how clinical needs influence design features of the changing criterion design. Reducing smoking or increasing exercise are two common examples of the changing criterion design. The behavior should already be in the subject’s repertoire when using changing criterion designs. Reducing smoking or increasing exercise are two common examples of the changing criterion design. The changing criterion design is great for reducing or increasing behaviors. Web an overview of the changing criterion design, how to determine a functional relation, and pros/cons of the design. Published examples of the ccd have been limited and the structure of the design used in. Approximation to the final level desired for a target behavior. An experimental design where the initial baseline phases are followed by a series of treatment phases consisting of successive and gradual changing criteria for reinforcement or punishment. Web an overview of the changing criterion design, how to determine a functional relation, and pros/cons of the design. It also presents the. The changing criterion design is great for reducing or increasing behaviors. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. Used to evaluate effects of a treatment that is applied in a graduated fashion to a single target behavior. The behavior should already be in the subject’s repertoire when. Once stabilized, the treatment serves as a baseline for increased criterion of the next phase. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. Web this article illustrates (a) 2 recent innovations in the changing criterion research design, (b) how these innovations apply to research and practice in special. Any researcher, in the course of investigating the effects of a particular set of independent variables, must demonstrate that the observed changes in behavior are functionally related to the presence of those variables. An experimental design where the initial baseline phases are followed by a series of treatment phases consisting of successive and gradual changing criteria for reinforcement or punishment.. Web an overview of the changing criterion design, how to determine a functional relation, and pros/cons of the design. Baseline is followed by treatment phase. An experimental design where the initial baseline phases are followed by a series of treatment phases consisting of successive and gradual changing criteria for reinforcement or punishment. Length of baseline and treatment phases, magnitude of. Once stabilized, the treatment serves as a baseline for increased criterion of the next phase. The changing criterion design is great for reducing or increasing behaviors. Approximation to the final level desired for a target behavior. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. Length of baseline and. Once stabilized, the treatment serves as a baseline for increased criterion of the next phase. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. Length of baseline and treatment phases, magnitude of changes in the criterion, and number of treatment phases or changes in criterion. Hallie steinberg & grete. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. Used to evaluate effects of a treatment that is applied in a graduated fashion to a single target behavior. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. Web. Any researcher, in the course of investigating the effects of a particular set of independent variables, must demonstrate that the observed changes in behavior are functionally related to the presence of those variables. Approximation to the final level desired for a target behavior. Is a variation of the multiple baseline design. Hallie steinberg & grete christianson limitations/concerns what we like/don't. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. Published examples of the ccd have been limited and the structure of the design used in the literature has varied to a degree that might engender confusion. Used to evaluate effects of a treatment that is applied in a graduated fashion to a single target behavior. Web an overview of the changing criterion design, how to determine a functional relation, and pros/cons of the design. Reducing smoking or increasing exercise are two common examples of the changing criterion design. Web this article illustrates (a) 2 recent innovations in the changing criterion research design, (b) how these innovations apply to research and practice in special education, and (c) how clinical needs influence design features of the changing criterion design. Is a variation of the multiple baseline design. Length of baseline and treatment phases, magnitude of changes in the criterion, and number of treatment phases or changes in criterion. Approximation to the final level desired for a target behavior. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. Web successful implementation of the changing criterion design requires particular attention to three design factors: The behavior should already be in the subject’s repertoire when using changing criterion designs. An experimental design where the initial baseline phases are followed by a series of treatment phases consisting of successive and gradual changing criteria for reinforcement or punishment. It also presents the design's formal requirements, and suggests target behaviors and circumstances for which the design might be useful. The changing criterion design is great for reducing or increasing behaviors. Published examples of the ccd have been limited and the structure of the design used in the literature has varied to a.
Figure 3 from The changing criterion design. Semantic Scholar

Changing Criterion Design Graph Excel
PPT Doing Research in Behavior Modification PowerPoint Presentation

PPT SingleCase Experimental Designs PowerPoint Presentation ID2377744
D5 Use singlesubject experimental designs (e.g., Reversal, Multiple

Changing Criterion Design Aba therapy activities, Behavior analysis

Chapter 7 Changing Conditions and Changing Criterion Designs

Masked Visual Analysis (MVA) ppt download

PPT Changing Criterion Designs PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Chapter 12 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3864090
Hallie Steinberg & Grete Christianson Limitations/Concerns What We Like/Don't Like About The Design Discussion Rationale For The Use Of This Design Explanation No Need To Withhold Intervention Helps Distinguish If Intervention Is Working
Baseline Is Followed By Treatment Phase.
Once Stabilized, The Treatment Serves As A Baseline For Increased Criterion Of The Next Phase.
Published Examples Of The Ccd Have Been Limited And The Structure Of The Design Used In The Literature Has Varied To A Degree That Might Engender Confusion.
Related Post: