Cat Bun Levels Chart
Cat Bun Levels Chart - Typically, when both bun and. Cats can develop chronic kidney disease as they age and their bun levels rise as. High levels indicate kidney failure or disease, dehydration, shock, high. Web compared with other species, cats have a high proportion of nephrons with longer loops of henle, allowing their urine specific gravity to exceed 1.080 in some cases. Find out what factors can affect these levels. Our vets help with understanding. Web this page focuses on kidney parameters (bun or urea, creatinine and sdma), potassium and sodium, magnesium, proteins in the blood (albumin and globulin) and other readings that are often out of range in ckd cats (cholesterol, alt, amylase, glucose and ck). Findings may include palpable kidney abnormalities, evidence of weight loss, dehydration, pale mucous membranes, uremic ulcers, evidence. Taken together, the blood urea nitrogen (bun) and creatinine levels can provide useful information about kidney function. Web bun stands for blood urea nitrogen and is the primary end product of protein metabolism. Web can be normal in early stage ckd. Levels that are too high may indicate excessive. Find out what factors can affect these levels. A higher reading indicates overall declining kidney health. Web the answer to both depends on the stage the disease in. Findings may include palpable kidney abnormalities, evidence of weight loss, dehydration, pale mucous membranes, uremic ulcers, evidence. High levels indicate kidney failure or disease, dehydration, shock, high. This web page does not provide a cat bun. Web this test helps indicate hydration status. Find out how creatinine and bun levels can indicate kidney failure and how to slow it. Decreased levels can be an early indicator of kidney. An increased level is called azotemia and can be caused by kidney, liver and heart disease as well as urethral. Web compared with other species, cats have a high proportion of nephrons with longer loops of henle, allowing their urine specific gravity to exceed 1.080 in some cases. High levels indicate. This web page does not provide a cat bun. Find out how creatinine and bun levels can indicate kidney failure and how to slow it. Web can be normal in early stage ckd. Typically, when both bun and. Compare the units and ranges used in different countries. Web estimates suggest one to three percent of cats will develop kidney disease during their lifetime and one in twelve geriatric cats has kidney disease. Web several compounds in your cat's blood may contain nitrogen, such as creatinine, urea, and other byproducts of protein digestion. Levels that are too high may indicate excessive. High levels indicate kidney failure or disease,. Potassium is an electrolyte lost with vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive urination. Web lowering bun levels in cats with kidney disease can be achieved through five effective steps. Find out how creatinine and bun levels can indicate kidney failure and how to slow it. Taken together, the blood urea nitrogen (bun) and creatinine levels can provide useful information about kidney function.. Web can be normal in early stage ckd. Find out how bun and creatinine levels are used to monitor kidney function and. Web a bun level of 25.3 mmol/l is on the higher side of normal but can be influenced by factors other than kidney function. Web learn about the tests, stages and symptoms of ckd in cats, and how. Typically, when both bun and. Our vets help with understanding. Web bun stands for blood urea nitrogen and is the primary end product of protein metabolism. This web page does not provide a cat bun. Web lowering bun levels in cats with kidney disease can be achieved through five effective steps. Web this page focuses on kidney parameters (bun or urea, creatinine and sdma), potassium and sodium, magnesium, proteins in the blood (albumin and globulin) and other readings that are often out of range in ckd cats (cholesterol, alt, amylase, glucose and ck). Potassium is an electrolyte lost with vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive urination. Web compared with other species, cats have. Web this page focuses on kidney parameters (bun or urea, creatinine and sdma), potassium and sodium, magnesium, proteins in the blood (albumin and globulin) and other readings that are often out of range in ckd cats (cholesterol, alt, amylase, glucose and ck). The creatinine level in the blood test is lower than 1.6, which means that less than 66% of.. Web bun stands for blood urea nitrogen and is the primary end product of protein metabolism. Web blood urea nitrogen (bun): Web this test helps indicate hydration status. This test determines kidney function. Typically, when both bun and. Web can be normal in early stage ckd. Web learn about chronic kidney disease in cats, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment. Compare the units and ranges used in different countries. Find out how creatinine and bun levels can indicate kidney failure and how to slow it. Web a bun level of 25.3 mmol/l is on the higher side of normal but can be influenced by factors other than kidney function. Decreased levels can be an early indicator of kidney. Our vets help with understanding. Findings may include palpable kidney abnormalities, evidence of weight loss, dehydration, pale mucous membranes, uremic ulcers, evidence. Find out how bun and creatinine levels are used to monitor kidney function and. The creatinine level in the blood test is lower than 1.6, which means that less than 66% of. Web learn about the factors that may affect blood test results for cats with ckd, such as fasting, fluids, stress and haemolysis.
Cat Bun Levels Chart
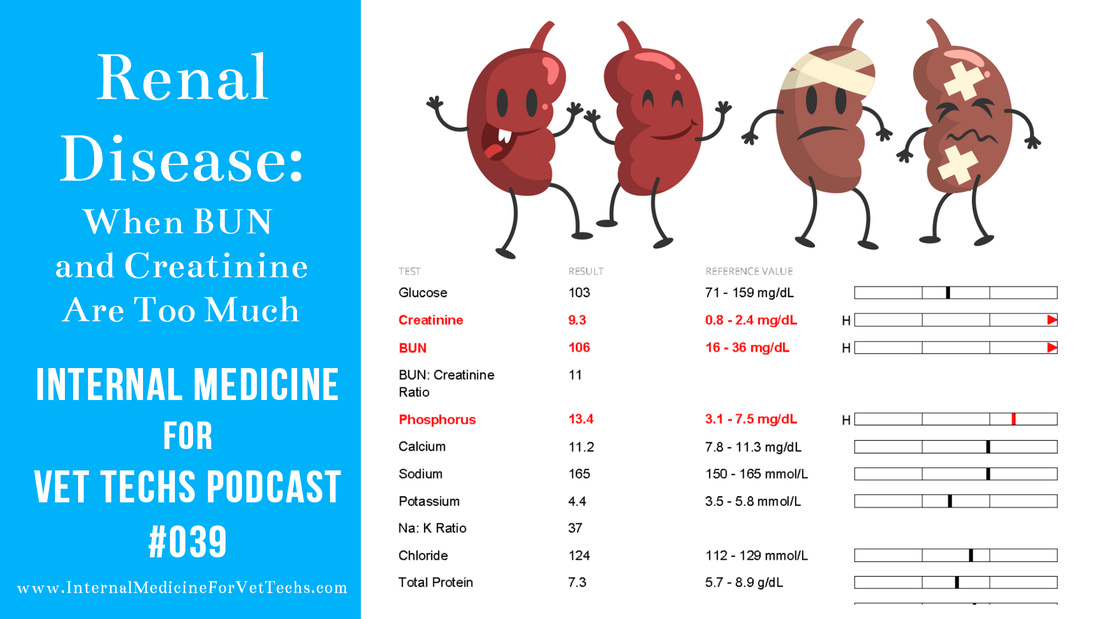
Cat Bun Levels Chart
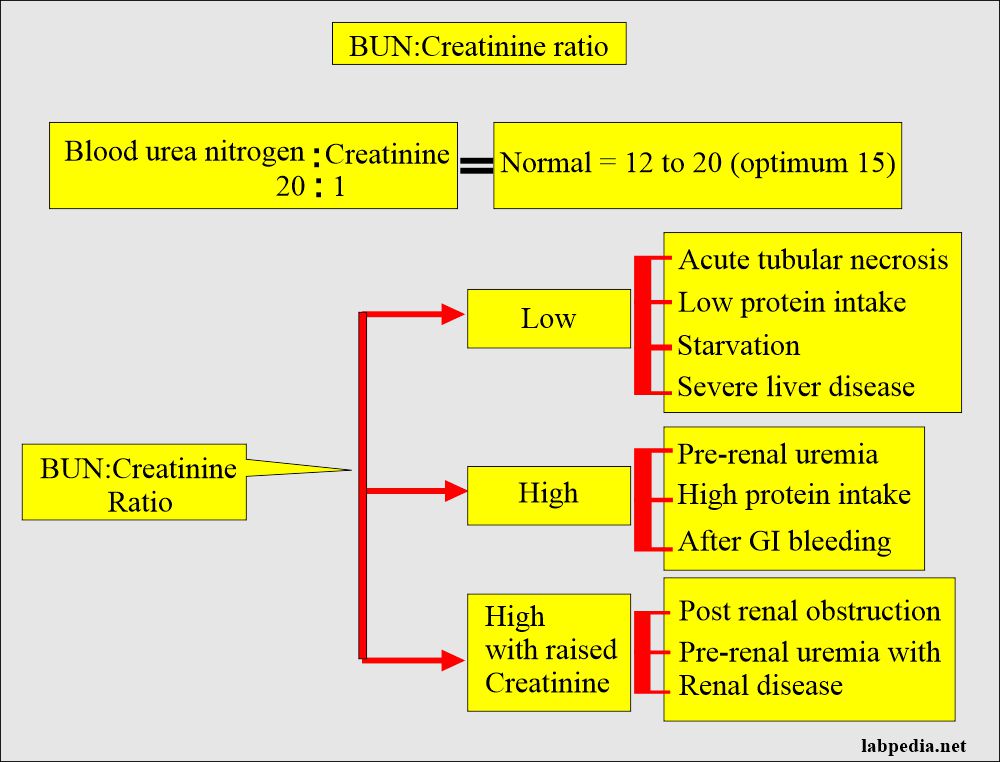
Blood Urea Nitrogen/Creatinine ratio and Interpretations

Cat Bun Levels Chart

Cat Bun Levels Chart

Cat Bun Levels Chart

Chronic Renal Disease (CRD)

Normal Bun Levels In Cats

Cat Creatinine Levels Chart

Cat Infographics CatWorld
Web Lowering Bun Levels In Cats With Kidney Disease Can Be Achieved Through Five Effective Steps.
A Higher Reading Indicates Overall Declining Kidney Health.
Levels That Are Too High May Indicate Excessive.
Web Bun/Creat Ratio Is Calculated Using The Serum Urea Nitrogen And The Serum Creatinine.
Related Post: