Canine Lung Patterns
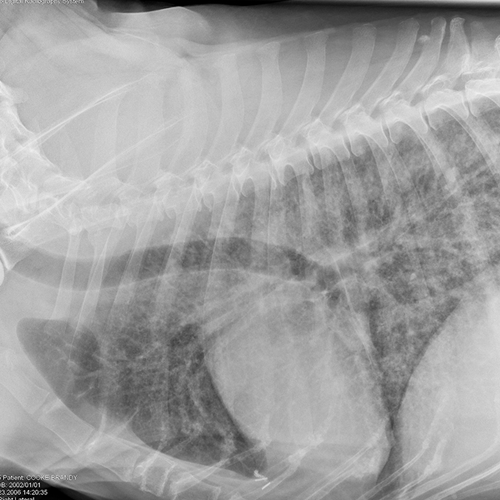
Canine Lung Patterns - Tumors of the larynx and trachea |. Lung diseases can be complex, and a variety of patterns (mixed patterns) can be present. Trauma (such as being hit by a car) may. Identification of the lung pattern is helpful, as a list of differential diagnoses can be determined for that particular lung pattern. Web pathologic interstitial patterns are due to increased opacity in the interstitium, resulting from abnormal cellular or fluid accumulation. Clinically when faced with a mixed pattern, identify the most severe ( i.e. Web there are 4 pulmonary patterns described. For reasons of simplicity we will not discuss mixed patterns. They can thus avoid symptomatic obstruction unless forced to increase ventilation by the demands of activity or environment (by inducing panting from heat. Web many dogs seem to be able to prevent this for long periods by adopting an inspiratory pattern that is slow in frequency with a relatively prolonged inspiration and large tidal volume. They can thus avoid symptomatic obstruction unless forced to increase ventilation by the demands of activity or environment (by inducing panting from heat. An alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Lung diseases can be complex, and a variety of patterns (mixed patterns) can be present. Identification of the. Web if the lungs are too radiopaque, and artifacts and extrapulmonary disease have been ruled out as a cause, the type of opacification using pulmonary patterns, and most importantly the distribution (focal, lobar, multifocal or diffuse) and the location (cranioventral, caudodorsal etc.) should be noted. Web the available lateral and dorsoventral (dv)/ventrodorsal (vd) thoracic radiographs for each dog were examined. Web there are 4 pulmonary patterns described. Web in this article, we will review some of the common radiographic lung patterns and distributions identified in coughing dogs while putting the clinical picture together. Web the invasion of the respiratory tract by deleterious pathogens is normally prevented by physical, chemical, and immunologic mechanisms including mucus and mucociliary clearance, various innate antimicrobial. Six total lung lobes were scored: Web the available lateral and dorsoventral (dv)/ventrodorsal (vd) thoracic radiographs for each dog were examined and scored based on a modified lung congestion score developed for this study. Web pathologic interstitial patterns are due to increased opacity in the interstitium, resulting from abnormal cellular or fluid accumulation. Metastatic tumors of the lungs |. The. A bronchial and bronchointerstitial pattern are the most common radiographic lung patterns seen in canine eosinophilic bronchopneumopathy with these patterns most frequently topographically distributed to at least the caudodorsal lung field. Web there are 4 pulmonary patterns described. Normal variants causing increased lung opacity. Underinflation (expiration) can also cause interstitial pattern in a normal patient because the components of the. Matthew winter, dacvr will review the radiographic features of lung patterns in dogs and cats as well as the keys to interpreting the meaning of these patterns. Examples of interstitial, alveolar, bronchial, and vascular lung patterns will be illustrated. An alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Lung diseases. Web pathologic interstitial patterns are due to increased opacity in the interstitium, resulting from abnormal cellular or fluid accumulation. Normal variants causing increased lung opacity. The right cranial, right middle, right caudal, accessory, left cranial, and left caudal. Web •review of lung patterns. Matthew winter, dacvr will review the radiographic features of lung patterns in dogs and cats as well. The pattern approach to interpreting lung lesions simplifies your life. Web pathologic interstitial patterns are due to increased opacity in the interstitium, resulting from abnormal cellular or fluid accumulation. For reasons of simplicity we will not discuss mixed patterns. Voice change (hoarse bark or loss of voice); A bronchial and bronchointerstitial pattern are the most common radiographic lung patterns seen. The altered opacity of the lung may be either increased (more opaque) or decreased (more lucent), but the majority of pulmonary diseases in dogs and cats produce an increased opacity. The pattern approach to interpreting lung lesions simplifies your life. Web there is a wide variation in how the lung appears based on age and body condition in normal animals.. Web there are 4 pulmonary patterns described. Matthew winter, dacvr will review the radiographic features of lung patterns in dogs and cats as well as the keys to interpreting the meaning of these patterns. Web in this article, we will review some of the common radiographic lung patterns and distributions identified in coughing dogs while putting the clinical picture together.. Web these characteristic opacity changes are called lung patterns. Examples of interstitial, alveolar, bronchial, and vascular lung patterns will be illustrated. Underinflation (expiration) can also cause interstitial pattern in a normal patient because the components of the interstitium are less widely separated by aerated lung. Web many dogs seem to be able to prevent this for long periods by adopting an inspiratory pattern that is slow in frequency with a relatively prolonged inspiration and large tidal volume. Common pulmonary patterns include mass, alveolar, bronchial, vascular, structured interstitial, and. The pattern approach to interpreting lung lesions simplifies your life. Lung diseases can be complex, and a variety of patterns (mixed patterns) can be present. For reasons of simplicity we will not discuss mixed patterns. Six total lung lobes were scored: Trauma (such as being hit by a car) may. Web with increased opacity, many diseases will present with a mixed pulmonary pattern, so the dominant pattern should be identified to formulate an appropriate differential list (figure 5). Web the invasion of the respiratory tract by deleterious pathogens is normally prevented by physical, chemical, and immunologic mechanisms including mucus and mucociliary clearance, various innate antimicrobial factors, alveolar macrophages, and the pulmonary immune response. Identification of the lung pattern is helpful, as a list of differential diagnoses can be determined for that particular lung pattern. Voice change (hoarse bark or loss of voice); Web what is the pulmonary pattern? Web there are 4 pulmonary patterns described.
Canine Thorax Radiograph
Common Pulmonary Diseases in Dogs Clinician's Brief

Figure 1 from Topographical distribution and radiographic pattern of
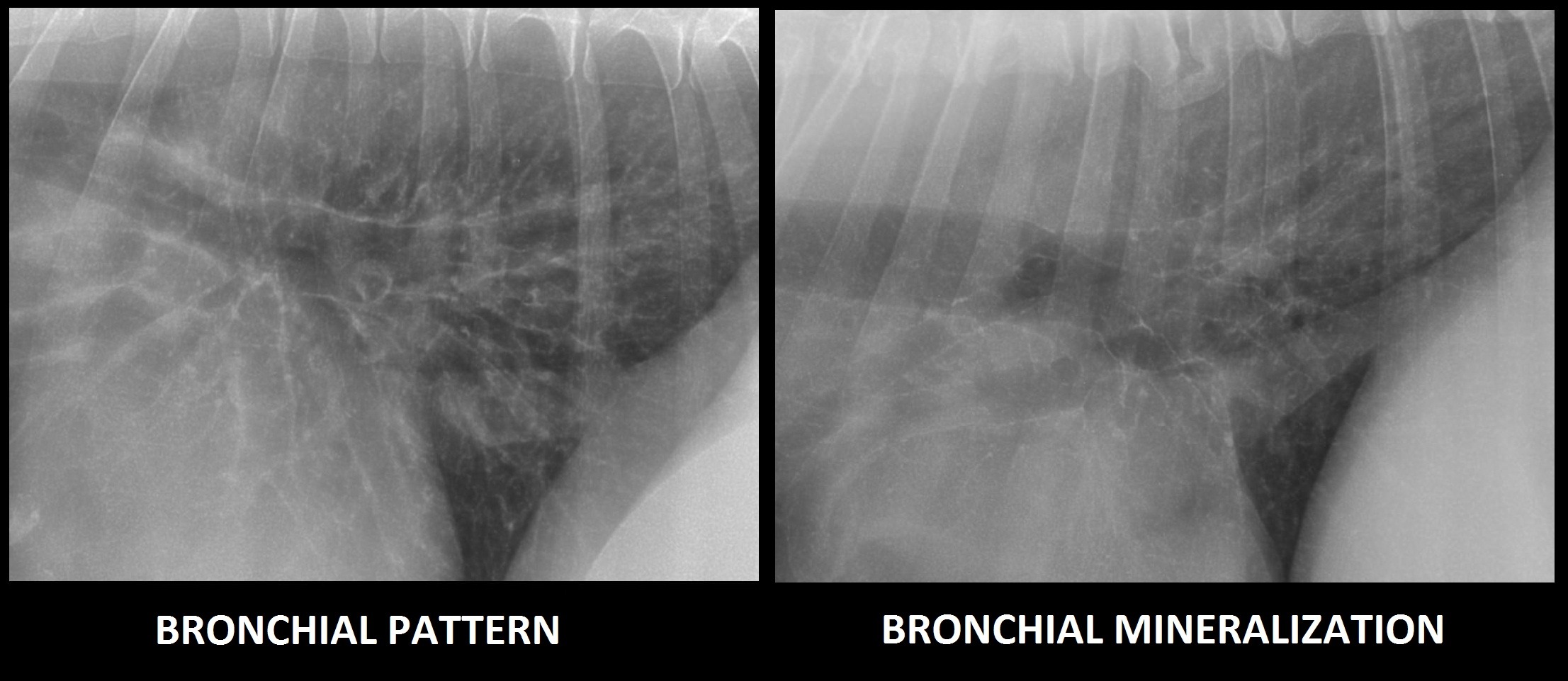
Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell
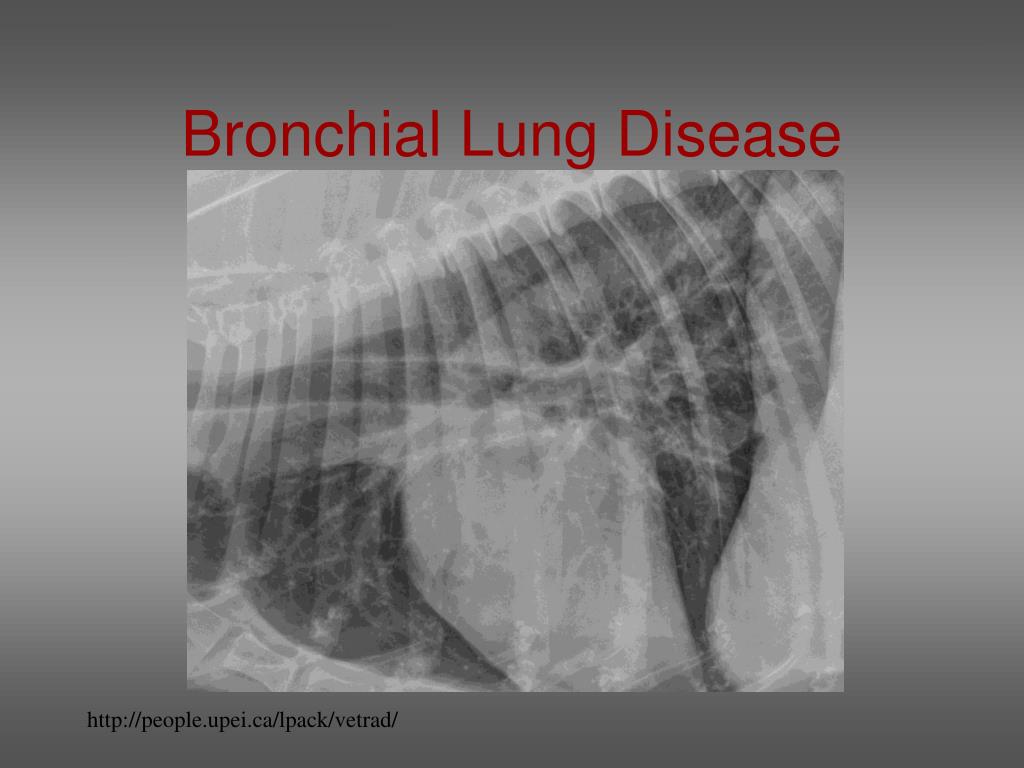
PPT Thoracic Radiology of the Dog PowerPoint Presentation, free

Topographical distribution and radiographic pattern of lung lesions in

Imaging the Coughing Dog

Imaging the Coughing Dog

Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell
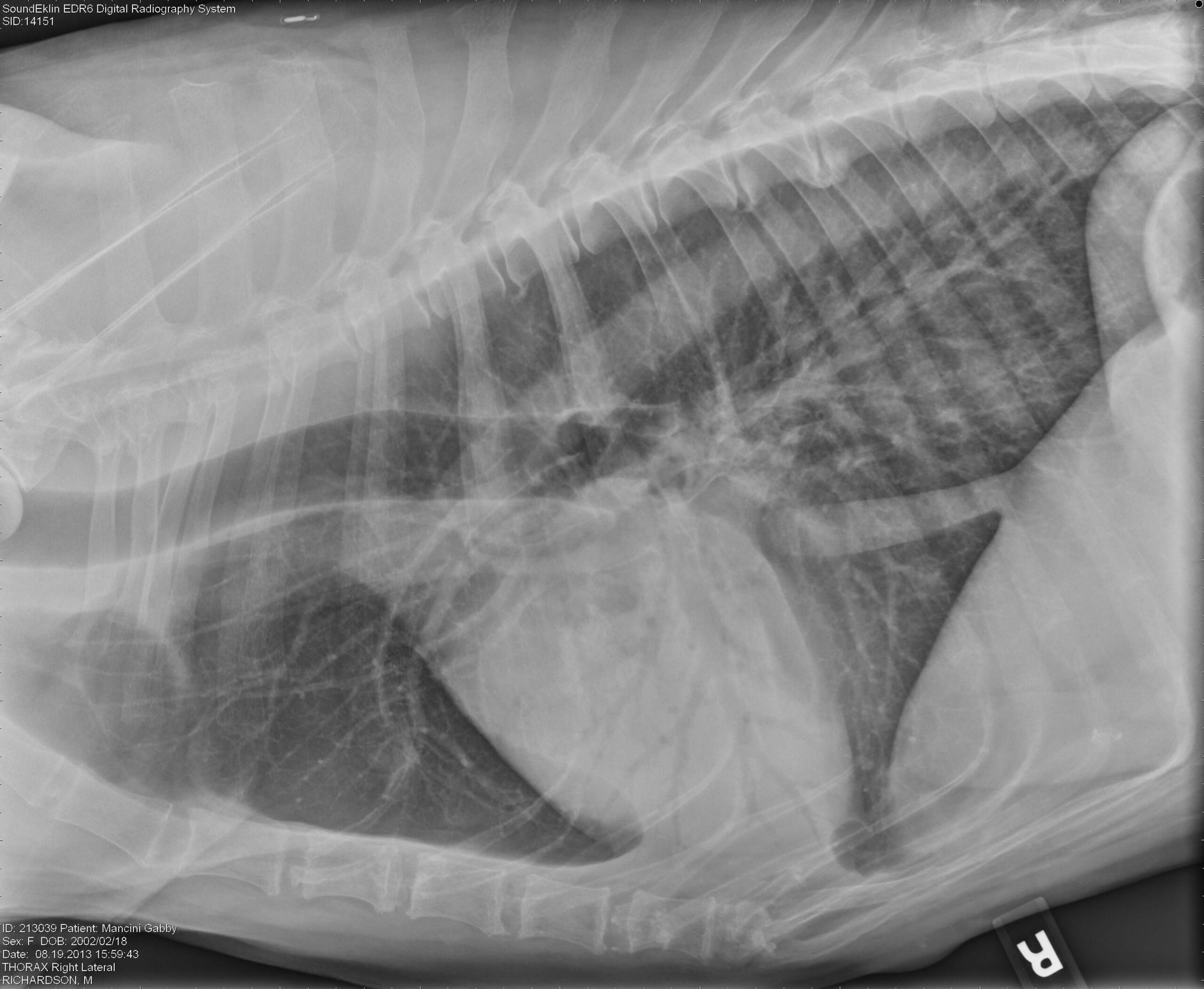
Interpreting thoracic radiograph lung patterns VETgirl Veterinary
Web Learn About Radiographic Lung Patterns, Distributions, And Differenital Diagnosis Of Common Pulmonary Diseases In Dogs And Cats.
Web •Review Of Lung Patterns.
Web The Available Lateral And Dorsoventral (Dv)/Ventrodorsal (Vd) Thoracic Radiographs For Each Dog Were Examined And Scored Based On A Modified Lung Congestion Score Developed For This Study.
•Application Of Lung Patterns To Common Clinical Presentations Will Be Discussed.
Related Post: