Brugada Pattern Vs Syndrome
Brugada Pattern Vs Syndrome - Correct recognition of the diagnostic brugada syndrome ecg pattern. Two others may suggest the disease. Coved st elevations greater than 2 mm accompanied with an inverted t wave. Web brugada syndrome (brs) is an “inherited” condition characterized by predisposition to syncope and cardiac arrest, predominantly during sleep. Web the electrical abnormality caused by brugada syndrome can produce a characteristic pattern on the electrocardiogram (ecg), a pattern that is actually called. Web the brugada ecg pattern is usually more pronounced at night or at rest 22 and after large meals, 23 when most vf episodes and sudden deaths in the brugada. Web people with brugada syndrome often have a recognizable pattern (brugada pattern) on the ekg printout. Web brugada syndrome (brs) is an inherited ion channel channelopathy predisposing to ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Web brugada syndrome is an ecg abnormality with a high incidence of sudden death in patients with structurally normal hearts. Web brugada syndrome vs pattern: Web the brugada syndrome may present with three different ecg patterns, referred to as type 1, type 2, and type 2 brugada syndrome ecg. Web brugada syndrome is an ecg abnormality with a high incidence of sudden death in patients with structurally normal hearts. Web the brugada pattern, which occurs in asymptomatic individuals without any other clinical criteria, has an. Web the electrical abnormality caused by brugada syndrome can produce a characteristic pattern on the electrocardiogram (ecg), a pattern that is actually called. First described in 1992 by the brugada brothers, the disease has since had an exponential rise in the numbers of cases reported. Web the brugada syndrome (brs) is a hereditary arrhythmic syndrome manifesting as syncope or sudden. Web the electrical abnormality caused by brugada syndrome can produce a characteristic pattern on the electrocardiogram (ecg), a pattern that is actually called. Coved st elevations greater than 2 mm accompanied with an inverted t wave. 1) there is one true diagnostic of the brugada pattern; Watch a video by mayo. Web three different ecg patterns have been described in. Correct recognition of the diagnostic brugada syndrome ecg pattern. Web three different ecg patterns have been described in brugada syndrome patients: Web the brugada pattern, which occurs in asymptomatic individuals without any other clinical criteria, has an estimated prevalence of between 0.1% and 1%. Web the brugada syndrome may present with three different ecg patterns, referred to as type 1,. Correct recognition of the diagnostic brugada syndrome ecg pattern. Web brugada syndrome (brs) is an “inherited” condition characterized by predisposition to syncope and cardiac arrest, predominantly during sleep. Web brugada syndrome vs pattern: First described in 1992 by the brugada brothers, the disease has since had an exponential rise in the numbers of cases reported. Web the brugada ecg pattern. Brugada syndrome is a genetic disorder that can cause a dangerous irregular heartbeat. Web brugada pattern without symptoms was present in 62% (n=40) while brugada syndrome was revealed in 38% (n=25) of the patients. Web brugada syndrome (brs) is an “inherited” condition characterized by predisposition to syncope and cardiac arrest, predominantly during sleep. First described in 1992 by the brugada. Coved st elevations greater than 2 mm accompanied with an inverted t wave. The most typical, and diagnostic, is type. 1) there is one true diagnostic of the brugada pattern; Web the brugada syndrome (brs) is a hereditary arrhythmic syndrome manifesting as syncope or sudden cardiac death (scd) in individuals without overt. First described in 1992 by the brugada brothers,. Brugada syndrome is a genetic disorder that can cause a dangerous irregular heartbeat. Web three different ecg patterns have been described in brugada syndrome patients: Web brugada syndrome is an ecg abnormality with a high incidence of sudden death in patients with structurally normal hearts. Web brugada syndrome vs pattern: Web brugada syndrome is an ecg abnormality with a high. Web brugada syndrome is an ecg abnormality with a high incidence of sudden death in patients with structurally normal hearts. Web three different ecg patterns have been described in brugada syndrome patients: Web the brugada syndrome may present with three different ecg patterns, referred to as type 1, type 2, and type 2 brugada syndrome ecg. Web the electrical abnormality. Web the brugada pattern, which occurs in asymptomatic individuals without any other clinical criteria, has an estimated prevalence of between 0.1% and 1%. Web the brugada syndrome (brs) is a hereditary arrhythmic syndrome manifesting as syncope or sudden cardiac death (scd) in individuals without overt. Web three different ecg patterns have been described in brugada syndrome patients: Web people with. Correct recognition of the diagnostic brugada syndrome ecg pattern. Web the brugada ecg pattern is usually more pronounced at night or at rest 22 and after large meals, 23 when most vf episodes and sudden deaths in the brugada. Web brugada syndrome (brs) is an inherited ion channel channelopathy predisposing to ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Web people with brugada syndrome often have a recognizable pattern (brugada pattern) on the ekg printout. Web the brugada syndrome (brs) is a hereditary arrhythmic syndrome manifesting as syncope or sudden cardiac death (scd) in individuals without overt. Web the electrical abnormality caused by brugada syndrome can produce a characteristic pattern on the electrocardiogram (ecg), a pattern that is actually called. Coved st elevations greater than 2 mm accompanied with an inverted t wave. Brugada syndrome is a genetic disorder that can cause a dangerous irregular heartbeat. Web brugada syndrome is an ecg abnormality with a high incidence of sudden death in patients with structurally normal hearts. Web brugada syndrome (brs) is an “inherited” condition characterized by predisposition to syncope and cardiac arrest, predominantly during sleep. Web the brugada pattern, which occurs in asymptomatic individuals without any other clinical criteria, has an estimated prevalence of between 0.1% and 1%. The most typical, and diagnostic, is type. 1) there is one true diagnostic of the brugada pattern; Web brugada syndrome vs pattern: Web learn the difference between brugada syndrome and brugada pattern, two conditions that affect the electrical activity of the heart. Web brugada syndrome is an ecg abnormality with a high incidence of sudden death in patients with structurally normal hearts.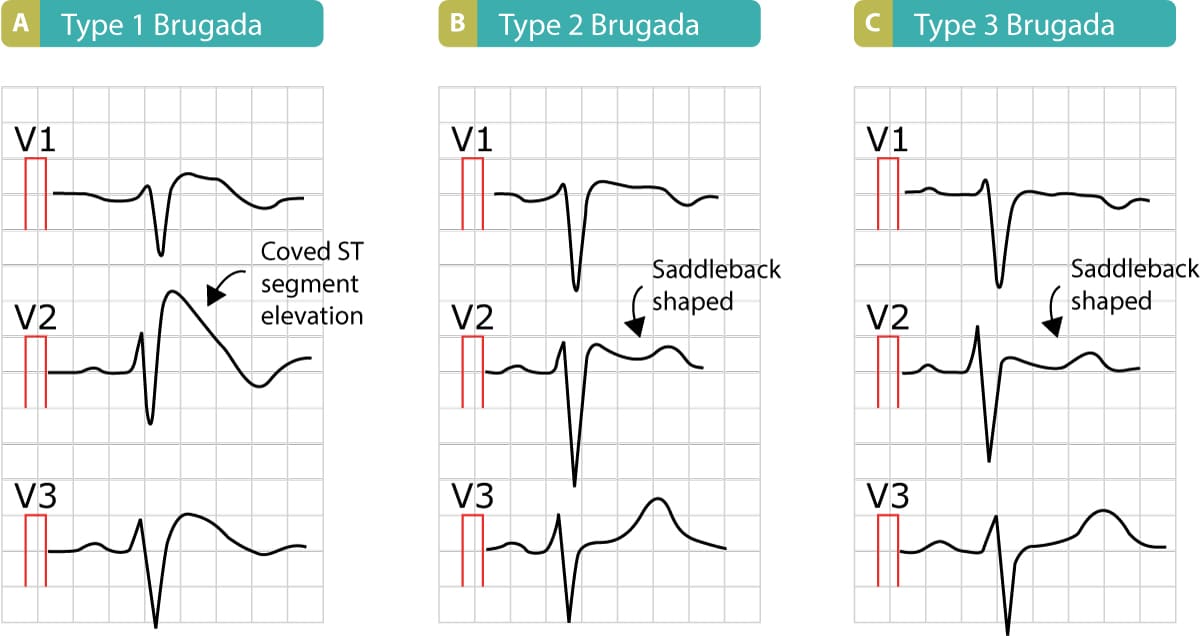
Brugada syndrome ECG, clinical features and management

Brugada Syndrome Causes, ECG, Symptoms, Treatment
Brugada Syndrome • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis

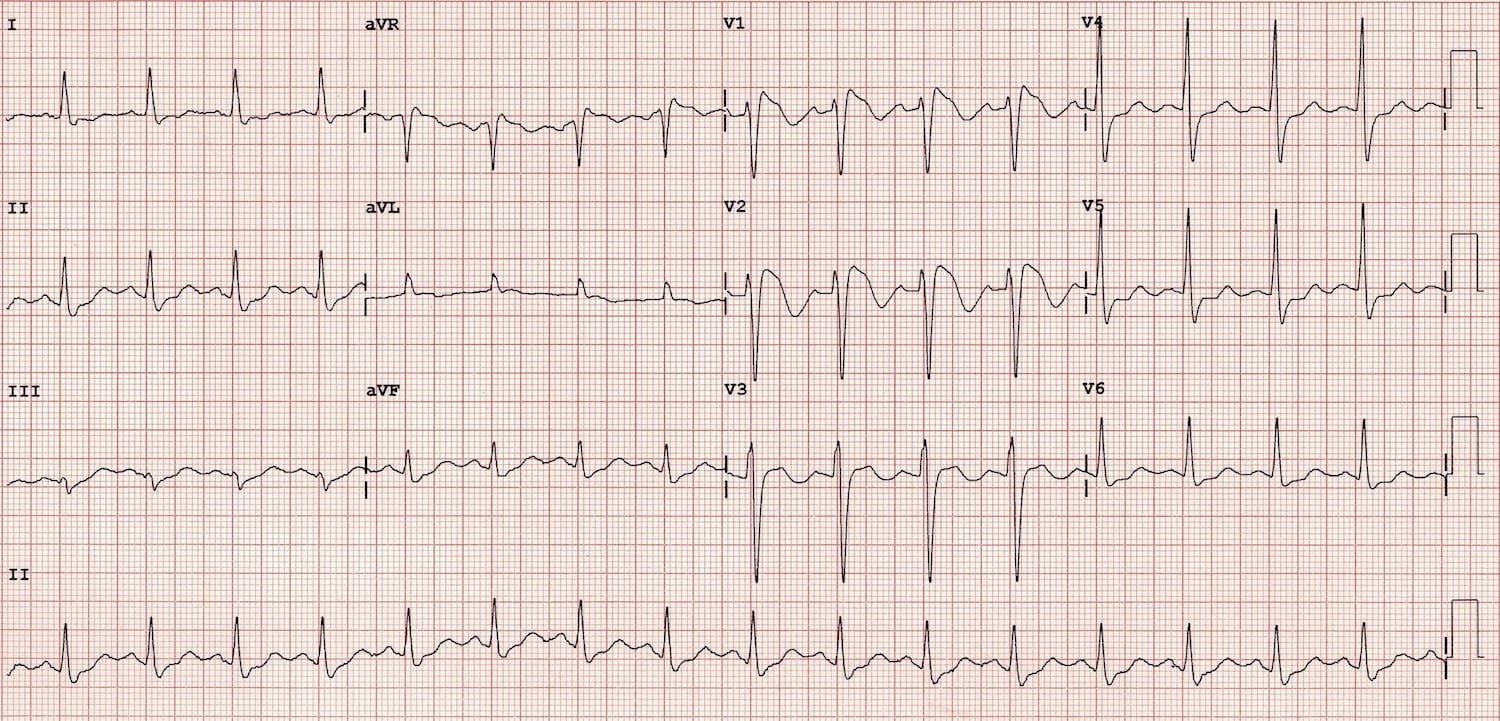
ECG interpretation in Brugada syndrome Nishizaki 2013 Journal of
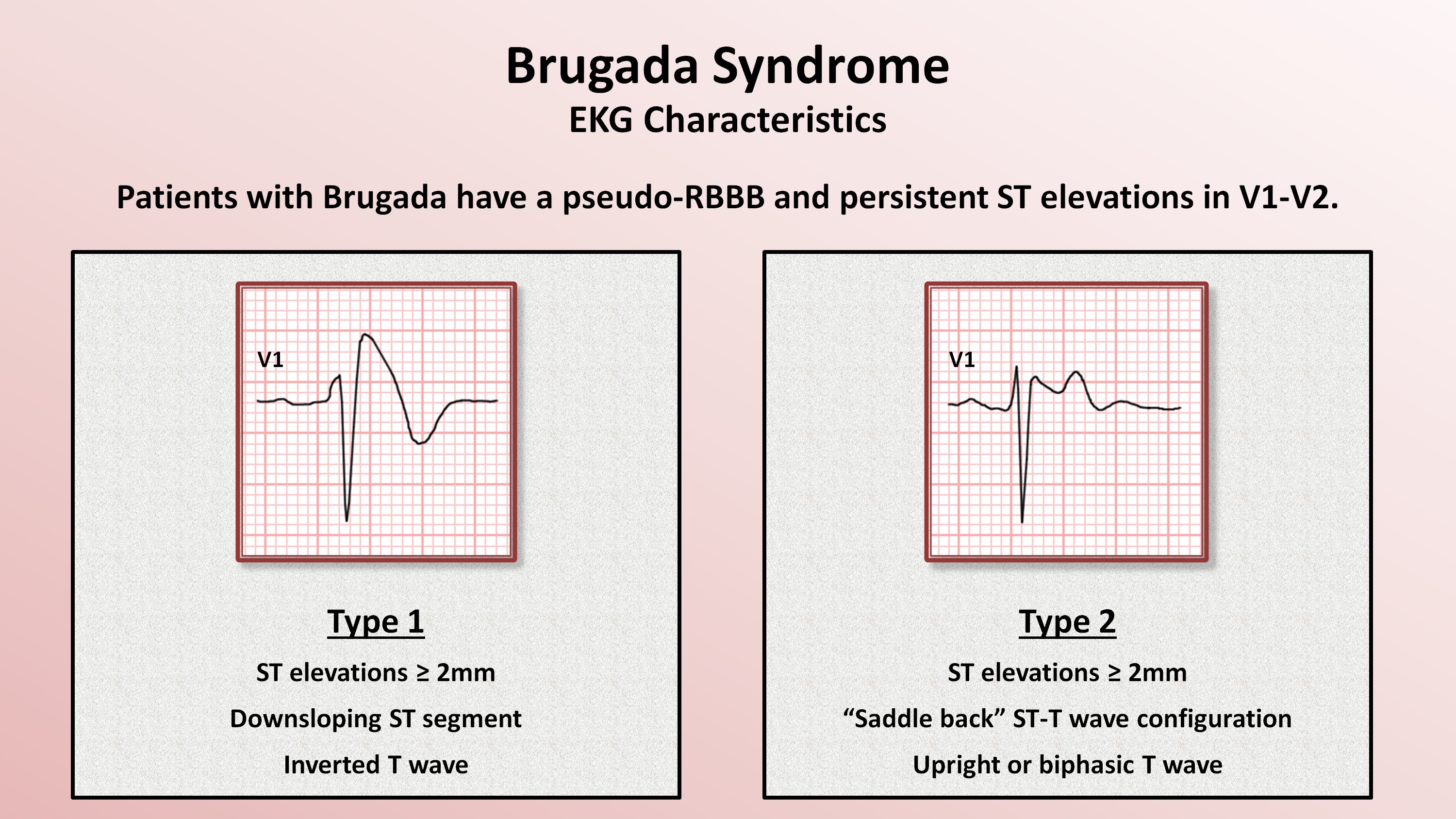
Brugada Syndrome

Brugada Syndrome Causes, ECG, Symptoms, Treatment
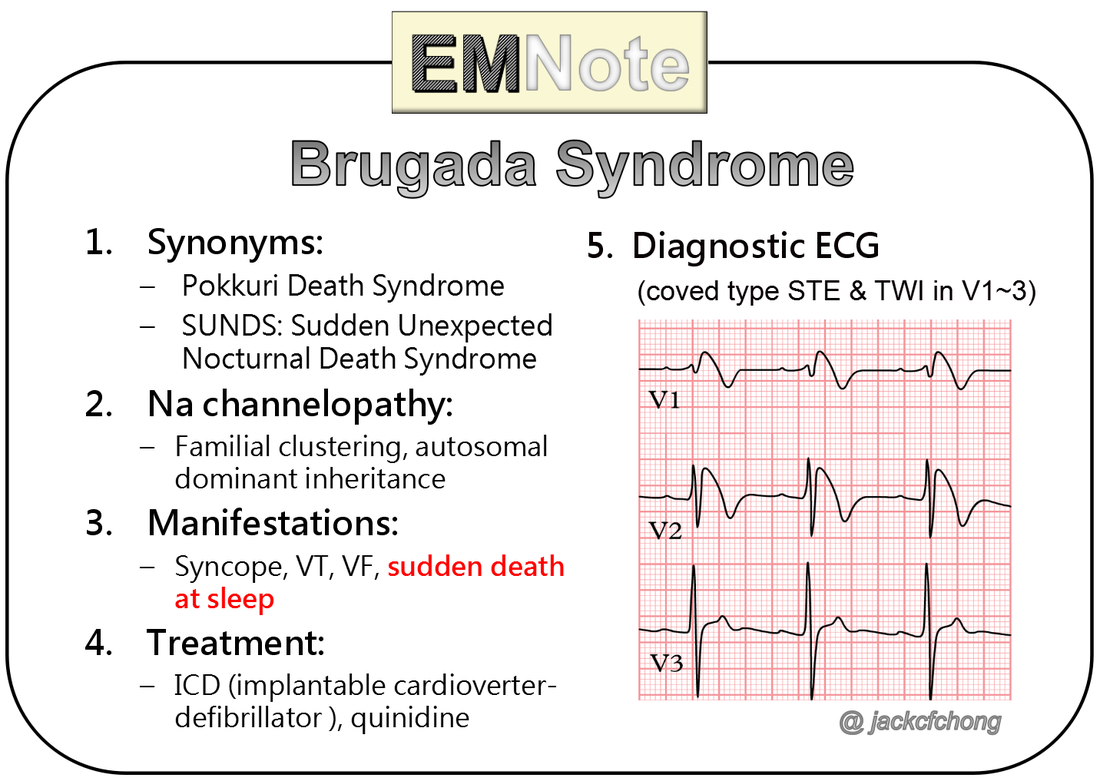
Brugada syndrome,what to know?

PPT EKG Rounds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4792132

Brugada Syndrome ECGpedia
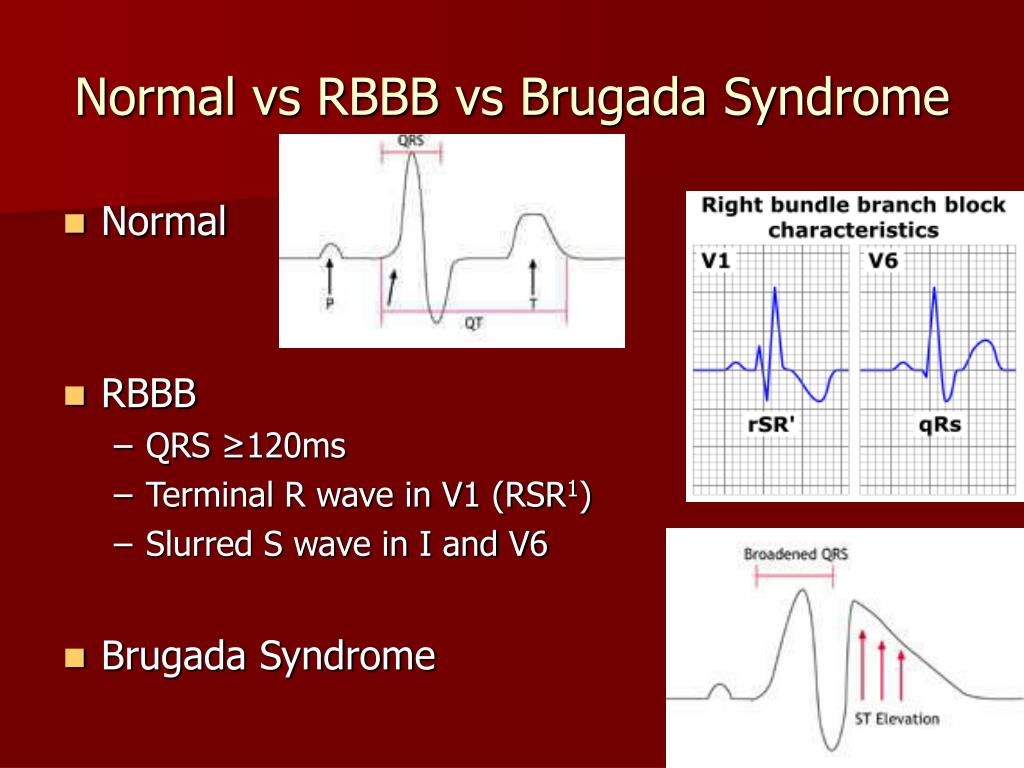
PPT Brugada Syndrome PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6925466
First Described In 1992 By The Brugada Brothers, The Disease Has Since Had An Exponential Rise In The Numbers Of Cases Reported.
Watch A Video By Mayo.
Web Brugada Pattern Without Symptoms Was Present In 62% (N=40) While Brugada Syndrome Was Revealed In 38% (N=25) Of The Patients.
Two Others May Suggest The Disease.
Related Post: