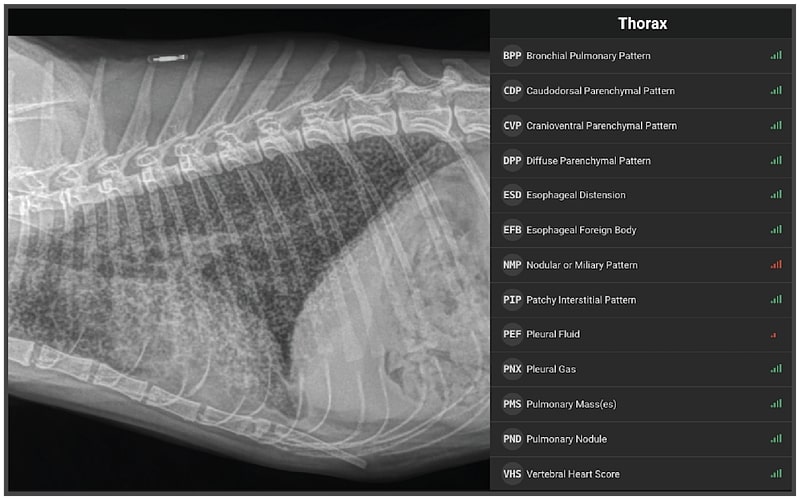
Bronchial Pattern Cat
Bronchial Pattern Cat - 58.3%), moderate (n = 6; It is discussed later in this chapter as part of tracheobronchitis. Also see professional content regarding tracheobronchitis. Web tracheobronchitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the trachea and bronchial airways; Tram tracks often are best seen overlying the diaphragm or heart, where the summation effect makes them more apparent (image 2). The walls are thickened due to a combination of smooth muscle hypertrophy, mucus production, cellular infiltrate, and in come cases (feline asthma), bronchoconstriction. The inflammation of the bronchi causes the walls of the airways to become thickened and swollen, along with excessive mucus production, with secretions gathering in the airways. Managing dogs and cats in respiratory distress is a multifaceted effort that involves stabilizing patients prior to determining a definitive diagnosis. The bronchioles end in the small sacs called alveoli, where the barrier between the air and the blood is a thin membrane. Bsc, bvms (hons), ms, dacvecc. A micronodular pattern was observed in cat 5. Web when a cat breathes air in through its nose or mouth, the air travels down the trachea, which divides into the tubes known as the right and left bronchi, then into the smaller airways called bronchioles in the lungs. Web allergic disease most often presents with a bronchial pattern with or. However, bronchointerstitial, alveolar, and more structured pseudonodular patterns can occur. The inflammation of the bronchi causes the walls of the airways to become thickened and swollen, along with excessive mucus production, with secretions gathering in the airways. Web cat 2 was tested for feline immunodeficiency virus and feline leukemia virus; As well as sometimes right middle lung lobe atelectasis. Air. As well as sometimes right middle lung lobe atelectasis. It is more likely to occur in cats already affected by respiratory disease or a disorder of the lungs or airways. Air trapping may also be evident (increased lucency and flattening of the diaphragm); Web all 24 cats showed a bronchial pattern on day 0, which was classified as mild (n. Managing dogs and cats in respiratory distress is a multifaceted effort that involves stabilizing patients prior to determining a definitive diagnosis. Bsc, bvms (hons), ms, dacvecc. A micronodular pattern was observed in cat 5. Tram tracks often are best seen overlying the diaphragm or heart, where the summation effect makes them more apparent (image 2). An interstitial pattern reflects increased. Bronchial pattern is caused by thickening and increased prominence of the bronchial walls, usually secondary to chronic inflammation. Web when a cat breathes air in through its nose or mouth, the air travels down the trachea, which divides into the tubes known as the right and left bronchi, then into the smaller airways called bronchioles in the lungs. As well. Web the bronchial pattern is most common in cats with chronic lower airway disease. As well as sometimes right middle lung lobe atelectasis. Air trapping may also be evident (increased lucency and flattening of the diaphragm); In severe cases alveolar consolidation may be present. Web tracheobronchitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the trachea and bronchial airways; Web a recent study confirmed that the most common radiographic abnormality is a bronchial pattern, but an unstructured interstitial pattern can be present in many cats. Fortunately, respiratory distress—no matter what the cause—requires somewhat standardized interventions during initial stabilization. Managing dogs and cats in respiratory distress is a multifaceted effort that involves stabilizing patients prior to determining a definitive diagnosis.. Web bronchitis in cats is a term that refers broadly to the inflammation of the bronchial tubes in your cat’s respiratory system. 25.0%) or severe (n = 4; In severe cases alveolar consolidation may be present. Web in cats, feline bronchial disease (including 'asthma') is the most common cause for coughing. Ratios of lung inflation on ventrodorsal views were significantly. The inflammation of the bronchi causes the walls of the airways to become thickened and swollen, along with excessive mucus production, with secretions gathering in the airways. 58.3%), moderate (n = 6; Bronchial pattern is caused by thickening and increased prominence of the bronchial walls, usually secondary to chronic inflammation. Ratios of lung inflation on ventrodorsal views were significantly higher. A micronodular pattern was observed in cat 5. Tram tracks often are best seen overlying the diaphragm or heart, where the summation effect makes them more apparent (image 2). This pattern comes closest to helping shed light on what disease the pet is suffering from. 2 bronchiectasis can be identified in a smaller number of cats. A bronchial pattern is. Web in cats, feline bronchial disease (including 'asthma') is the most common cause for coughing. 58.3%), moderate (n = 6; It is more likely to occur in cats already affected by respiratory disease or a disorder of the lungs or airways. Fortunately, respiratory distress—no matter what the cause—requires somewhat standardized interventions during initial stabilization. Also see professional content regarding tracheobronchitis. An interstitial pattern reflects increased opacity of the pulmonary interstitium. Web when a cat breathes air in through its nose or mouth, the air travels down the trachea, which divides into the tubes known as the right and left bronchi, then into the smaller airways called bronchioles in the lungs. Air trapping may also be evident (increased lucency and flattening of the diaphragm); Web results of the present study suggested that a bronchial pattern was the most common radiographic abnormality in cats with fbd, followed by an unstructured interstitial pattern and signs of lung hyperinflation. Bacterial infection often follows primary lung disease such as hemorrhage, viral infection or chronic bronchitis with superinfection. 2 bronchiectasis can be identified in a smaller number of cats. Web cat 2 was tested for feline immunodeficiency virus and feline leukemia virus; Web feline bronchitis describes a group of common inflammatory airway diseases of cats that include feline asthma. It is discussed later in this chapter as part of tracheobronchitis. Web all 24 cats showed a bronchial pattern on day 0, which was classified as mild (n = 14; Web the classic pattern includes evidence of bronchial wall thickening (doughnuts or railroad tracks);
Perspectives in veterinary medicine Description and classification of
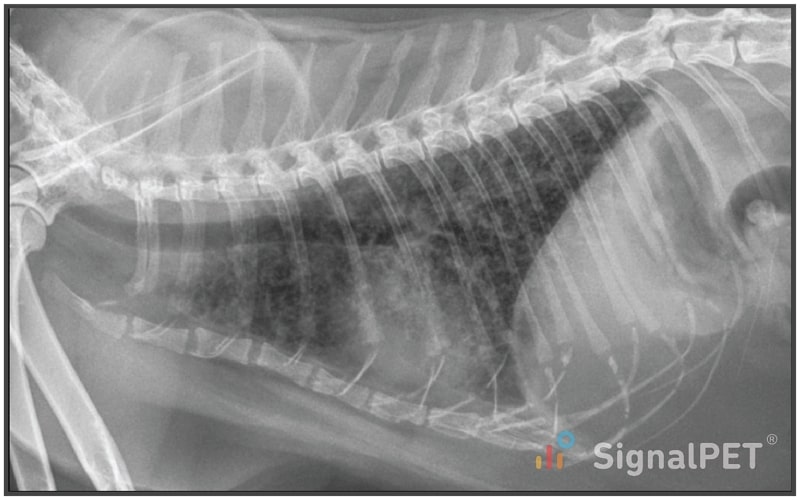
Radiology Case of the Week Feline Miliary Pulmonary Pattern

Lung; cat No. 1. Diffuse, severe bronchointerstitial pattern

Plain lateral thoracic radiograph of the cat showing a mild bronchial

Common Pulmonary Diseases in Cats Clinician's Brief

Figure 3 from Radiographic abnormalities in cats with feline bronchial

Radiographic abnormalities in cats with feline bronchial disease and

Feline Asthma Clinician's Brief
Radiology Case of the Week Feline Miliary Pulmonary Pattern
Right lateral radiograph of a sixmonthold cat infected with
Web • Radiographic Changes In Asthmatic Cats Often Include A Prominent Bronchial Pattern (Tram Lines And Donuts) Or A Mixed Pattern Of Bronchial, Alveolar, Or Interstitial Changes.
This Pattern Comes Closest To Helping Shed Light On What Disease The Pet Is Suffering From.
However, Bronchointerstitial, Alveolar, And More Structured Pseudonodular Patterns Can Occur.
25.0%) Or Severe (N = 4;
Related Post: