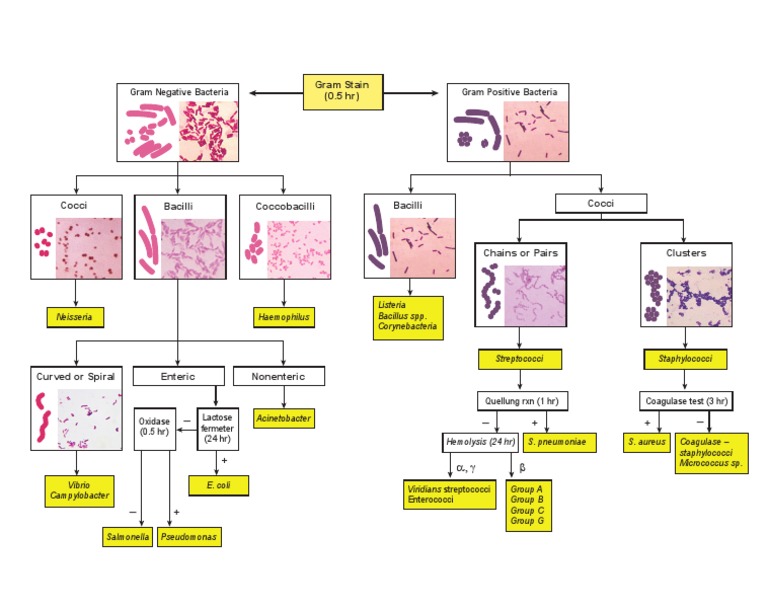
Bacteria Identification Flow Chart
Bacteria Identification Flow Chart - Web basic bacterial id from gram positive stain. Keys are charts that require decisions at branch points, much like a flow chart in computer logic: Identify different types of bacterial morphology seen on a gram stain. Web discuss the characterization of microbes based on phenotypic and genotypic methods. With improved coloring and contrast, the dyes overcome these problems by facilitating the cellular structure identification. Identify different types of colonial characteristics. Web this paper reviewed core concepts of interpreting bacterial culture results, including timing of cultures, common culture sites, potential for contamination, interpreting the gram stain, role of rapid diagnostic tests, conventional antibiotic susceptibility testing, and automated testing. Web identification flow charts manual of determinative bacteriology all of the unknowns will fall into the following groups in manual of determinative bacteriology (the pink book on the shelf in the laboratory). * = see biochemical tests for gram negative organism id job aid for positive and negative result reference. Once your bacterial species are isolated and you have good gram stain results, begin to follow the flow chart for both of your unknown bacterial species. Describe the process of pcr. Though basic identification can be carried out using a light microscope, without staining, bacteria look colorless, transparent, and are very difficult to see. Discuss how to visualize an agarose gel. Web this new key provides a broad perspective of strategies useful for the biochemical identification of bacterial fish pathogens and it will be helpful in. This labs provides an overview of identifying unknown staphs, streps, and enteric organisms through a. Web good to excellent, colorless colonies without bile precipitate indicative of proteus vulgaris, salmonella typhimurium, and shigella spp. Associate various biochemical tests with their correct applications. Samples are placed on mac conkey agar and blood agar to observe growth and colony appearance. To this end,. Though basic identification can be carried out using a light microscope, without staining, bacteria look colorless, transparent, and are very difficult to see. Use creately’s easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. Describe the process of pcr. Web good to excellent, colorless colonies without bile precipitate indicative of proteus. With improved coloring and contrast, the dyes overcome these problems by facilitating the cellular structure identification. Identify different types of bacterial morphology seen on a gram stain. Describe the process of pcr. Discuss how pcr is used to identify bacterial species. Web tmcc microbiology resource center unknown identification work flow flowchart. Identify different types of bacterial morphology seen on a gram stain. Web tmcc microbiology resource center unknown identification work flow flowchart. Associate various biochemical tests with their correct applications. Antibiotics microbiology and infectious diseas es: Once your bacterial species are isolated and you have good gram stain results, begin to follow the flow chart for both of your unknown bacterial. Associate various biochemical tests with their correct applications. Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Though basic identification can be carried out using a light microscope, without staining, bacteria look colorless, transparent, and are very difficult to see. Web bacterial flowcharts provide a visual aid to quick identification of bacterial species. This flow chart outlines the steps to identify bacteria from a. Web at the conclusion of this elearning, you should be able to: Though basic identification can be carried out using a light microscope, without staining, bacteria look colorless, transparent, and are very difficult to see. Web discuss the characterization of microbes based on phenotypic and genotypic methods. Web 1 introduction 1.1 background as provided by the requestor. Bergey’s manual of. * = see biochemical tests for gram negative organism id job aid for positive and negative result reference. Antibiotics microbiology and infectious diseas es: Web this new key provides a broad perspective of strategies useful for the biochemical identification of bacterial fish pathogens and it will be helpful in both diagnostic work and in teaching. Web tmcc microbiology resource center. Discuss how pcr is used to identify bacterial species. Web good to excellent, colorless colonies without bile precipitate indicative of proteus vulgaris, salmonella typhimurium, and shigella spp. This labs provides an overview of identifying unknown staphs, streps, and enteric organisms through a. Web at the conclusion of this elearning, you should be able to: Bacteria are identified in laboratories by. Keys are charts that require decisions at branch points, much like a flow chart in computer logic: Continuing education (ce) this course does not offer p.a.c.e ® credits. Interpret the results of biochemical methods. Web the first thing to prepare for an unknown identification exercise is to make a dichotomous key. If the answer to a question is yes, then. This flow chart outlines the steps to identify bacteria from a specimen. Web good to excellent, colorless colonies without bile precipitate indicative of proteus vulgaris, salmonella typhimurium, and shigella spp. Web identification flow charts manual of determinative bacteriology all of the unknowns will fall into the following groups in manual of determinative bacteriology (the pink book on the shelf in the laboratory). Discuss how pcr is used to identify bacterial species. Web in this study, we attempted to apply mainly saccharolytic and proteolytic enzyme tests selectively; Keys are charts that require decisions at branch points, much like a flow chart in computer logic: Web this paper reviewed core concepts of interpreting bacterial culture results, including timing of cultures, common culture sites, potential for contamination, interpreting the gram stain, role of rapid diagnostic tests, conventional antibiotic susceptibility testing, and automated testing. * = see biochemical tests for gram negative organism id job aid for positive and negative result reference. Continuing education (ce) this course does not offer p.a.c.e ® credits. Interpret the results of biochemical methods. Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. Web at the conclusion of this elearning, you should be able to: Describe the process of pcr. If the answer to a question is yes, then do x; Web bacteria identification flow chart [classic] | creately. Web discuss the characterization of microbes based on phenotypic and genotypic methods.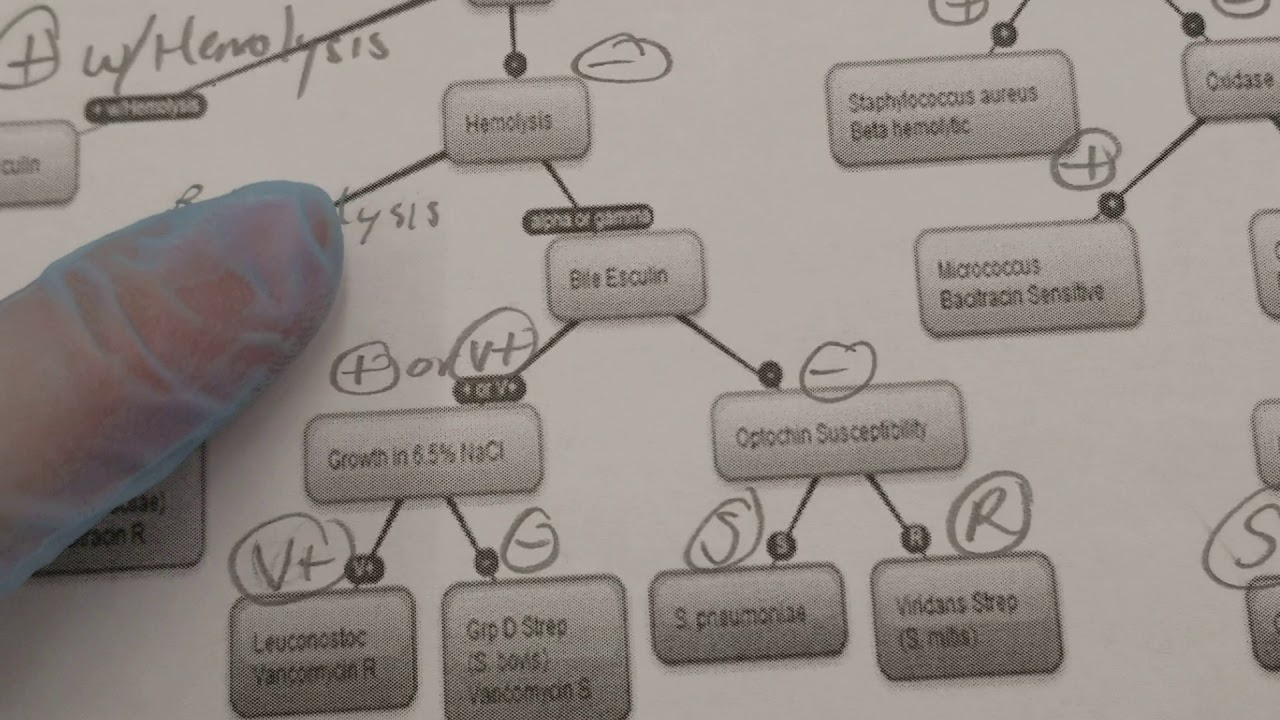
Microbiology Bacteria Identification Flowchart of Facultative

Identifying Bacteria Through Look, Growth, Stain and Strain

Microbiology Gram Positive Cocci Flow Chart Unknown Bacteria Flow Chart
Bacteroides Concise Medical Knowledge
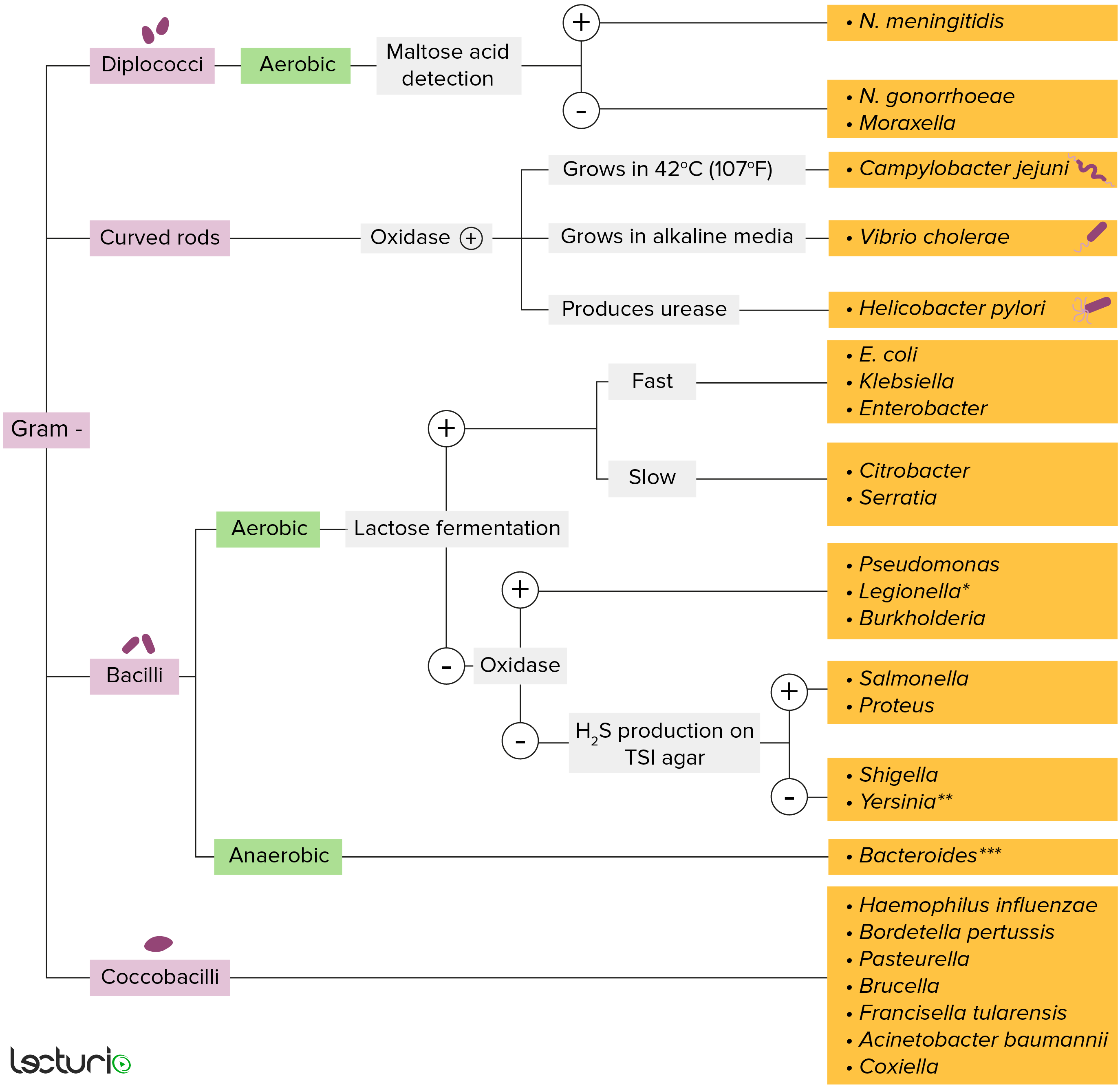
Bacteria Classification Flowchart

A field guide to dangerous bacteria Infographics

Bacteria Identification Classification Flowchart ubicaciondepersonas

Gram Positive Bacteria Overview Identification Algorithm

Organized Microbiology Gram Stain Flow Chart Unknown Bacteria Flow
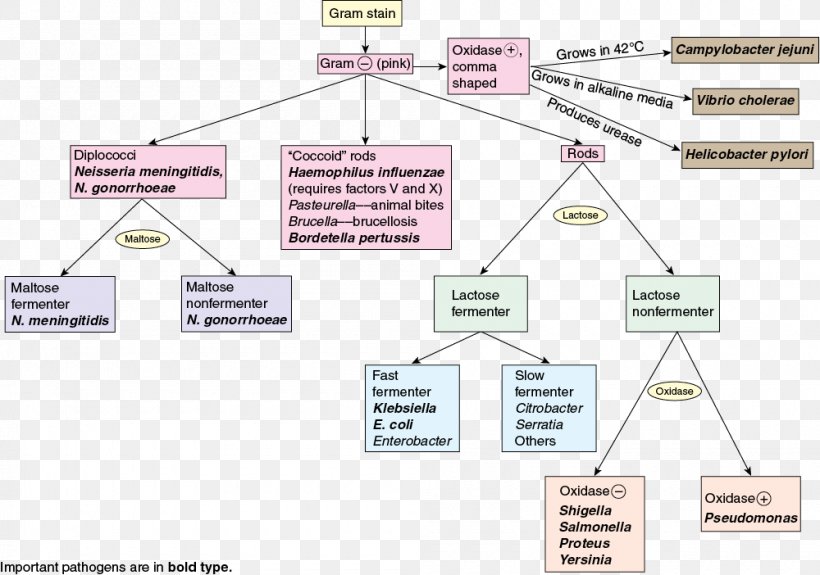
Gramnegative Bacteria Grampositive Bacteria Microbiology Flowchart
To This End, We Set Up An Accurate Identification Tree (Flow Chart) Based On Solid Identification Obtained From 16S Rrna Gene Sequencing, Rather Than Doing All The Phenotypic Tests On All Isolates.
Explain The Theory Of Pcr, Its Purpose, And Applications.
Discuss How To Visualize An Agarose Gel.
Web The First Thing To Prepare For An Unknown Identification Exercise Is To Make A Dichotomous Key.
Related Post: