Antiderivative Chart
Antiderivative Chart - Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Find the general antiderivative of a given function. Type in any integral to get the solution, steps and graph. Listed are some common derivatives and antiderivatives. Let f and g be two functions defined on an interval i. The answer to an indefinite integral is a function plus c. Knowing the power rule of differentiation, we conclude that f(x) = x2 is an antiderivative of f since f′ (x) = 2x. State the power rule for integrals. Web basic antiderivatives these are the antiderivative formulas you should memorize for math 3b. Web the fundamental theorem of calculus connects differential and integral calculus by showing that the definite integral of a function can be found using its antiderivative. The antiderivative of a function ƒ is a function whose derivative is ƒ. If we know f(x) is the integral of f(x), then f(x) is the derivative of f(x). Find the general antiderivative of a given function. Explain the terms and notation used for an indefinite integral. Let's learn how to draw these functions. Web 4.10.1 find the general antiderivative of a given function. As you can see, integration reverses differentiation, returning the function to its original state, up to a constant c. Listed are some common derivatives and antiderivatives. Consider the function f(x) = 2x. Web these antiderivative rules help us to find the antiderivative of sum or difference of functions, product and. In addition, sketch the graph of two additional antiderivatives of the given function, and state the corresponding initial conditions that each of them satisfy. The fundamental theorem of calculus states the relation between differentiation and integration. Let f and g be two functions defined on an interval i. List of general antiderivatives function antiderivative f(x) = xn (n 6= −1). Web in order to find an antiderivative for \(f(x)=\frac{1}{x}\) we need to remember that \(\dfrac{d}{dx}\log x = \frac{1}{x}\text{,}\) and more generally that \(\dfrac{d}{dx}\log |x| = \frac{1}{x}\text{.}\) Type in any integral to get the solution, steps and graph. In addition, sketch the graph of two additional antiderivatives of the given function, and state the corresponding initial conditions that each of them. The answer to an indefinite integral is a function plus c. The antiderivative of a function ƒ is a function whose derivative is ƒ. 4.10.2 explain the terms and notation used for an indefinite integral. In addition, sketch the graph of two additional antiderivatives of the given function, and state the corresponding initial conditions that each of them satisfy. State. Web the fundamental theorem of calculus connects differential and integral calculus by showing that the definite integral of a function can be found using its antiderivative. Consider the function f(x) = 2x. The antiderivative of a function ƒ is a function whose derivative is ƒ. In addition, sketch the graph of two additional antiderivatives of the given function, and state. If we know f(x) is the integral of f(x), then f(x) is the derivative of f(x). Find the general antiderivative of a given function. An indefinite integral gives you the family of antiderivatives of a function. Find the general antiderivative of a given function. Let k be a constant. Web the fundamental theorem of calculus connects differential and integral calculus by showing that the definite integral of a function can be found using its antiderivative. Let f and g be respectively antiderivatives of f and g on i. Web in order to find an antiderivative for \(f(x)=\frac{1}{x}\) we need to remember that \(\dfrac{d}{dx}\log x = \frac{1}{x}\text{,}\) and more generally. Let f and g be two functions defined on an interval i. Knowing the power rule of differentiation, we conclude that f(x) = x2 is an antiderivative of f since f′ (x) = 2x. As you can see, integration reverses differentiation, returning the function to its original state, up to a constant c. A function f is an antiderivative of. As you can see, integration reverses differentiation, returning the function to its original state, up to a constant c. Knowing the power rule of differentiation, we conclude that f(x) = x2 is an antiderivative of f since f′ (x) = 2x. Web 4.10.1 find the general antiderivative of a given function. Web given the graph of a function, can you. Web the table below shows you how to differentiate and integrate 18 of the most common functions. The fundamental theorem of calculus states the relation between differentiation and integration. Find the general antiderivative of a given function. The antiderivative of a function ƒ is a function whose derivative is ƒ. Let f and g be respectively antiderivatives of f and g on i. Web in order to find an antiderivative for \(f(x)=\frac{1}{x}\) we need to remember that \(\dfrac{d}{dx}\log x = \frac{1}{x}\text{,}\) and more generally that \(\dfrac{d}{dx}\log |x| = \frac{1}{x}\text{.}\) 1 a+1 xa+1 a6= 1 logjxj a= 1 x logx ( +1+1) 1x+1 logx ( +1) 2x exponents e xe ax (loga) 1ax xex (x 1)ex e xe trigonometric functions cosx sinx sinx cosx tanx logjcosxj cotx logjsinxj sec2 x tanx csc2 x cotx hyperbolic functions coshx sinhx The antiderivative of a function ƒ is a function whose derivative is ƒ. Web the fundamental theorem of calculus connects differential and integral calculus by showing that the definite integral of a function can be found using its antiderivative. State the power rule for integrals. State the power rule for integrals. Web the answer to a definite integral is a number. Web given the graph of a function, can you identify the graph of its antiderivative? Definite and indefinite integrals are connected by the fundamental theorem of calculus. List of general antiderivatives function antiderivative f(x) = xn (n 6= −1) f(x) = 1 n+1 xn+1 +c f(x) = x−1 = 1 x f(x) = ln|x|+ c f(x) = ex f(x) = ex + c f(x. Explain the terms and notation used for an indefinite integral.
antiderivative calculator ti 84
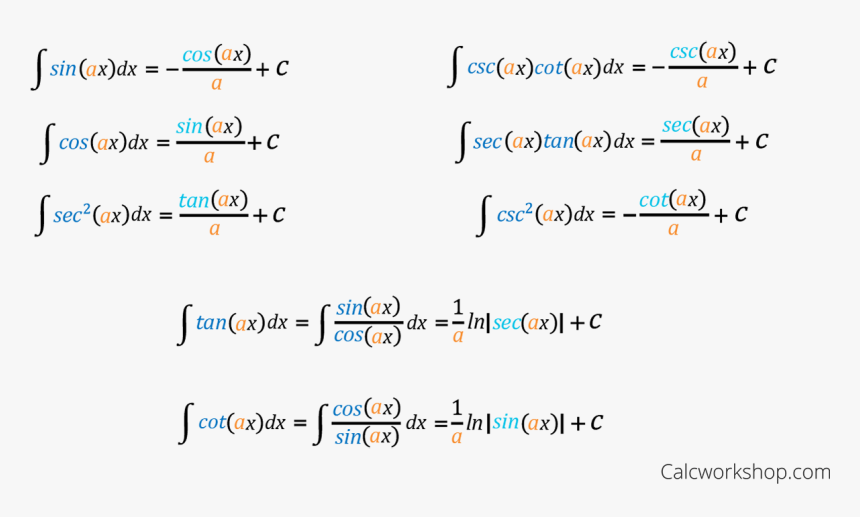
Rules For Integrating Trig Functions Antiderivative Trig Chart, HD
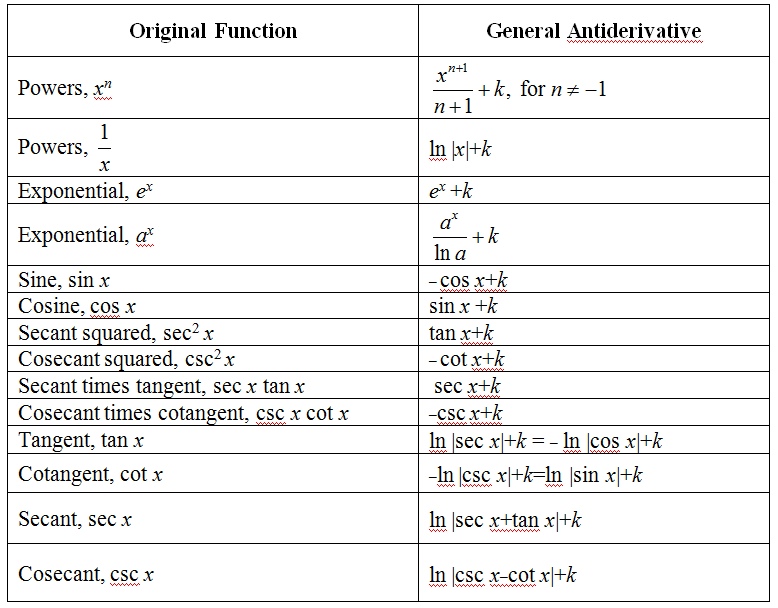
Antiderivatives Of Trig Functions slidesharetrick

Introduction to antiderivatives StudyPug
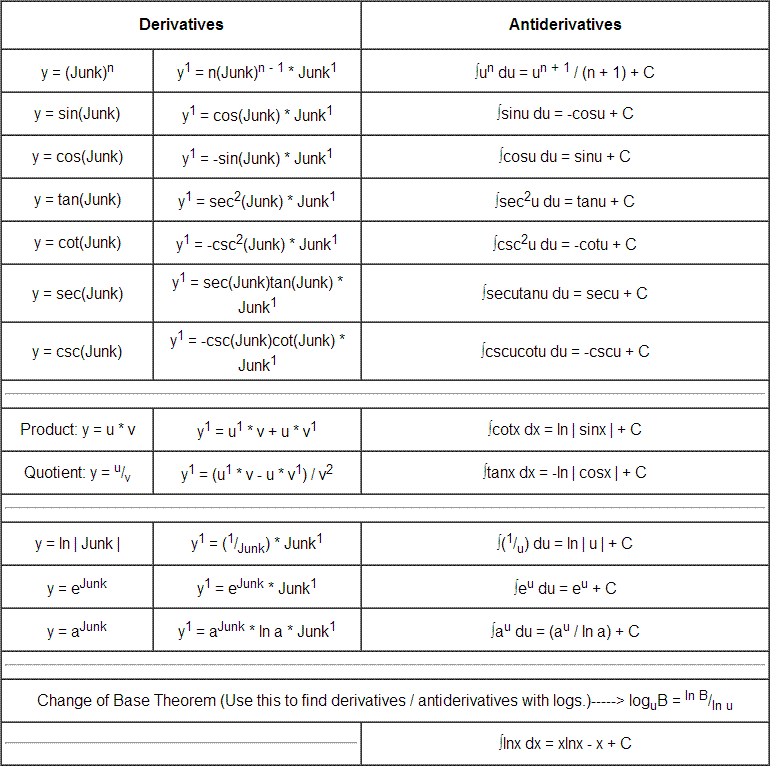
Table of Derivatives/ Antiderivatives

Introduction to antiderivatives StudyPug

Common Antiderivatives Diagram Quizlet

Antiderivative Formula
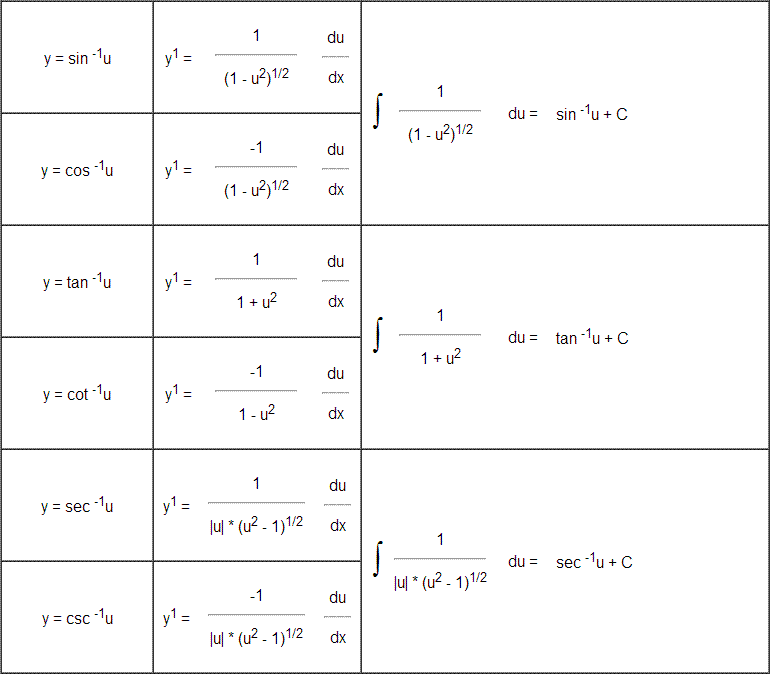
Table of Derivatives/ Antiderivatives
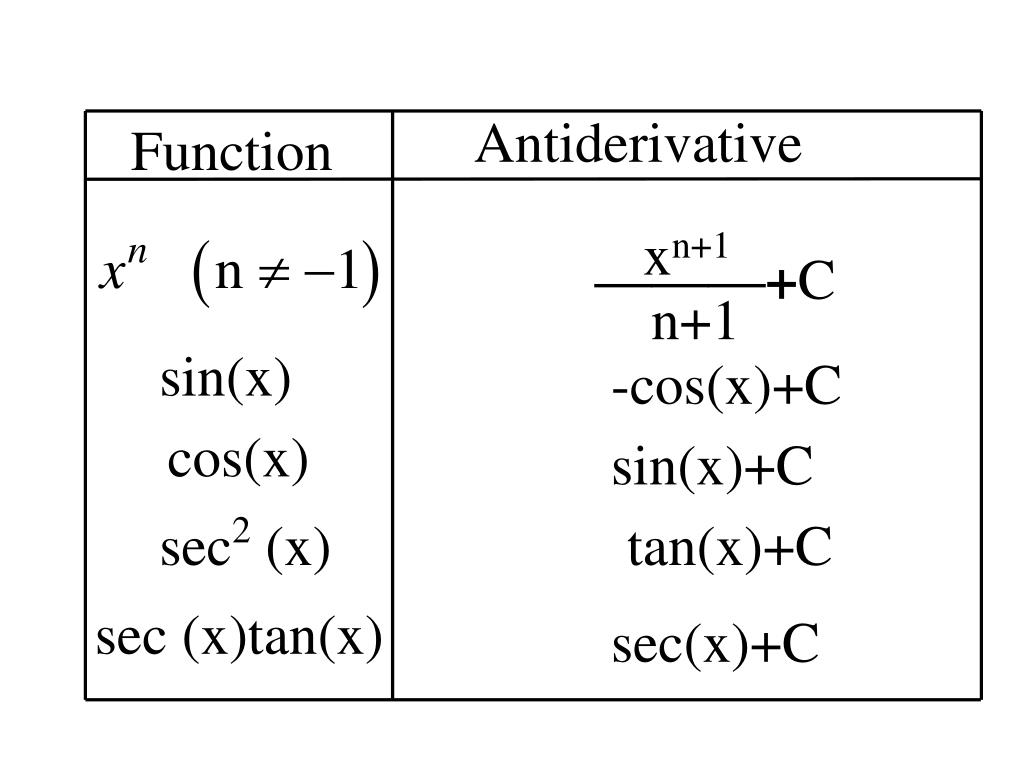
PPT 4 .9 Antiderivatives PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web These Antiderivative Rules Help Us To Find The Antiderivative Of Sum Or Difference Of Functions, Product And Quotient Of Functions, Scalar Multiple Of A Function And Constant Function, And Composition Of Functions.
4.10.3 State The Power Rule For Integrals.
Graph Functions, Plot Points, Visualize Algebraic Equations, Add Sliders, Animate Graphs, And More.
Web Given The Graph Of A Function \(F\), We Can Construct The Graph Of Its Antiderivative \(F\) Provided That \((A)\) We Know A Starting Value Of \(F\), Say \(F(A)\), And \((B)\) We Can Evaluate The Integral \(\Int^b_A F (X).
Related Post: