Anticoagulant Reversal Agents Chart
Anticoagulant Reversal Agents Chart - The following document has additional information for consideration. Web anticoagulant reversal recommendations (adults) (oral anticoagulants, parenteral anticoagulants, fibrinolytics) updated august 2022. These recommendations are meant to serve as general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Web the 2019 guideline from the anticoagulation forum provides clear instructions on how to use 2 agents for reversing the effects of direct oral anticoagulants (doacs): Web antithrombotic reversal (of anticoagulants and antiplatelets) should be limited to clinical situations (e.g. Web this fact sheet provides clinician guidance for administering anticoagulant reversal/hemostatic agents. Web overview of anticoagulant reversal. Web anticoagulant reversal outweighs the risk of thrombosis (either from the reversal agent itself or normalization of coagulation in a patient with underlying thromboembolic risk). , recombinant activated factor vii. Faster reversal (low volume of pcc allows for complete reversal in <30. Web anticoagulant reversal recommendations (adults) (oral anticoagulants, parenteral anticoagulants, fibrinolytics) updated august 2022. Faster reversal (low volume of pcc allows for complete reversal in <30. Web overview of anticoagulant reversal. These recommendations are meant to serve as general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Web the 2019 guideline from the anticoagulation forum provides clear instructions on how to use. Web this fact sheet provides clinician guidance for administering anticoagulant reversal/hemostatic agents. Faster reversal (low volume of pcc allows for complete reversal in <30. Lower volume, which reduces risk of volume overload. Pcc is the preferred agent for warfarin reversal in major bleeding. The following document has additional information for consideration. Web overview of anticoagulant reversal. , recombinant activated factor vii. Web the 2019 guideline from the anticoagulation forum provides clear instructions on how to use 2 agents for reversing the effects of direct oral anticoagulants (doacs): Web anticoagulant reversal outweighs the risk of thrombosis (either from the reversal agent itself or normalization of coagulation in a patient with underlying thromboembolic. Pcc is the preferred agent for warfarin reversal in major bleeding. Web the 2019 guideline from the anticoagulation forum provides clear instructions on how to use 2 agents for reversing the effects of direct oral anticoagulants (doacs): Web overview of anticoagulant reversal. Web anticoagulant reversal recommendations (adults) (oral anticoagulants, parenteral anticoagulants, fibrinolytics) updated august 2022. They should be used in. The following document has additional information for consideration. Web doac level that may contribute to bleeding is unknown. Web overview of anticoagulant reversal. Web antithrombotic reversal (of anticoagulants and antiplatelets) should be limited to clinical situations (e.g. Pcc is the preferred agent for warfarin reversal in major bleeding. Pcc is the preferred agent for warfarin reversal in major bleeding. The following document has additional information for consideration. These recommendations are meant to serve as general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Faster reversal (low volume of pcc allows for complete reversal in <30. Web this fact sheet provides clinician guidance for administering anticoagulant reversal/hemostatic agents. These recommendations are meant to serve as general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. Lower volume, which reduces risk of volume overload. Web this fact sheet provides clinician guidance for administering anticoagulant reversal/hemostatic agents. Web anticoagulant reversal outweighs the risk of thrombosis (either from the reversal agent itself or normalization of coagulation in a patient with underlying thromboembolic risk).. Web anticoagulant reversal outweighs the risk of thrombosis (either from the reversal agent itself or normalization of coagulation in a patient with underlying thromboembolic risk). The international society on thrombosis and haemostasis suggests consideration of doac reversal in patients with serious bleeding and a plasma doac concentration > 50 ng/ml10. They should be used in conjunction with general haemostatic measures. Web this fact sheet provides clinician guidance for administering anticoagulant reversal/hemostatic agents. Faster reversal (low volume of pcc allows for complete reversal in <30. Web anticoagulant reversal recommendations (adults) (oral anticoagulants, parenteral anticoagulants, fibrinolytics) updated august 2022. They should be used in conjunction with general haemostatic measures and definitive management of the bleeding source. Web the 2019 guideline from the. Web overview of anticoagulant reversal. Web this fact sheet provides clinician guidance for administering anticoagulant reversal/hemostatic agents. Lower volume, which reduces risk of volume overload. The international society on thrombosis and haemostasis suggests consideration of doac reversal in patients with serious bleeding and a plasma doac concentration > 50 ng/ml10. Web the 2019 guideline from the anticoagulation forum provides clear. Lower volume, which reduces risk of volume overload. These recommendations are meant to serve as general guidelines and should not replace clinical judgment. The following document has additional information for consideration. Web this fact sheet provides clinician guidance for administering anticoagulant reversal/hemostatic agents. Web the 2019 guideline from the anticoagulation forum provides clear instructions on how to use 2 agents for reversing the effects of direct oral anticoagulants (doacs): Web anticoagulant reversal outweighs the risk of thrombosis (either from the reversal agent itself or normalization of coagulation in a patient with underlying thromboembolic risk). Web doac level that may contribute to bleeding is unknown. Pcc is the preferred agent for warfarin reversal in major bleeding. , recombinant activated factor vii. Web overview of anticoagulant reversal. The international society on thrombosis and haemostasis suggests consideration of doac reversal in patients with serious bleeding and a plasma doac concentration > 50 ng/ml10. They should be used in conjunction with general haemostatic measures and definitive management of the bleeding source.
Anticoagulant Reversal Agents Chart Labb by AG

Anticoagulant Reversal Agents Chart Labb by AG

Anticoagulant Reversal Agents Chart vrogue.co

Medication Reversal Agents CheatSheet NCLEX Quiz
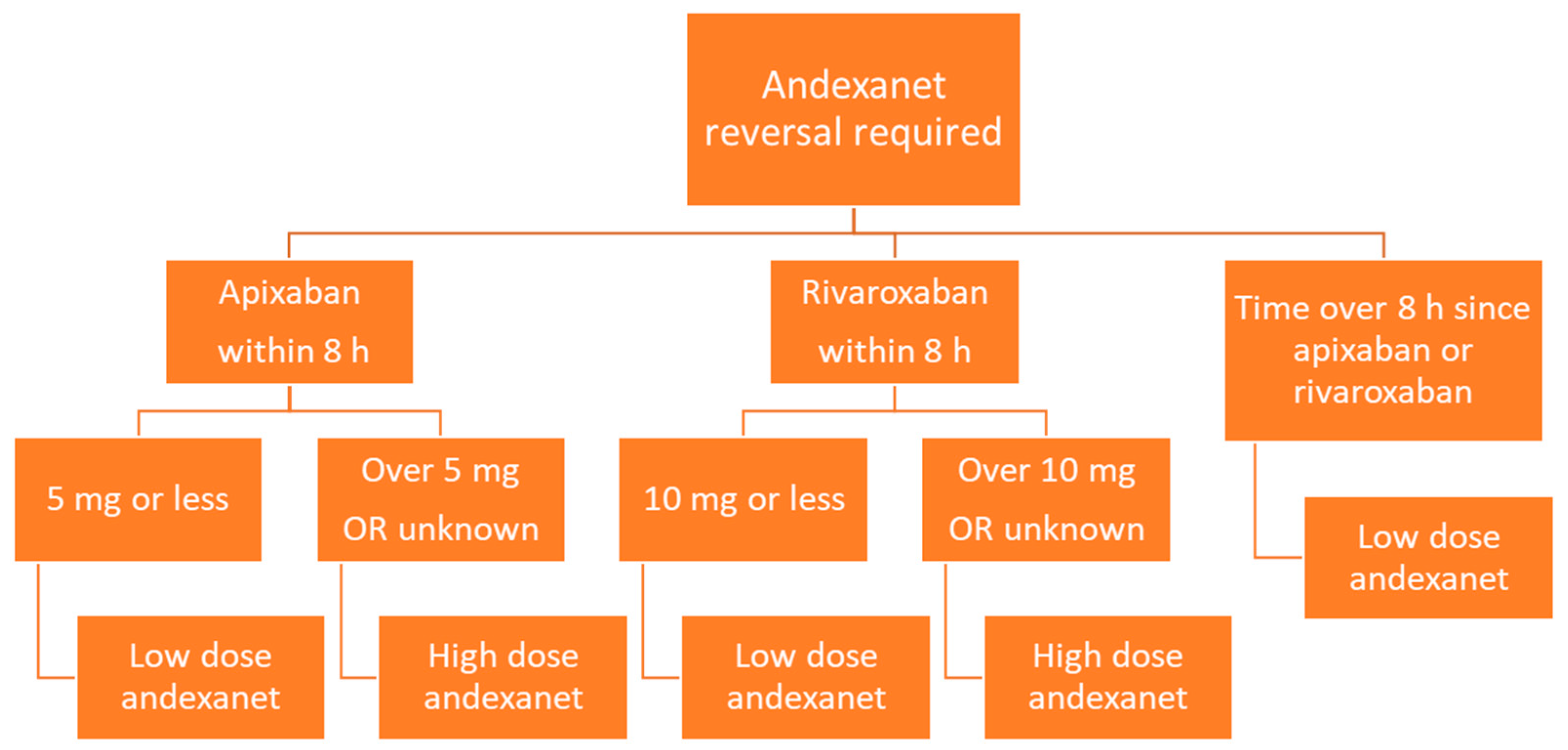
Medicines Free FullText DirectActing Oral Anticoagulants and

Anticoagulant Reversal Agents Chart Labb by AG
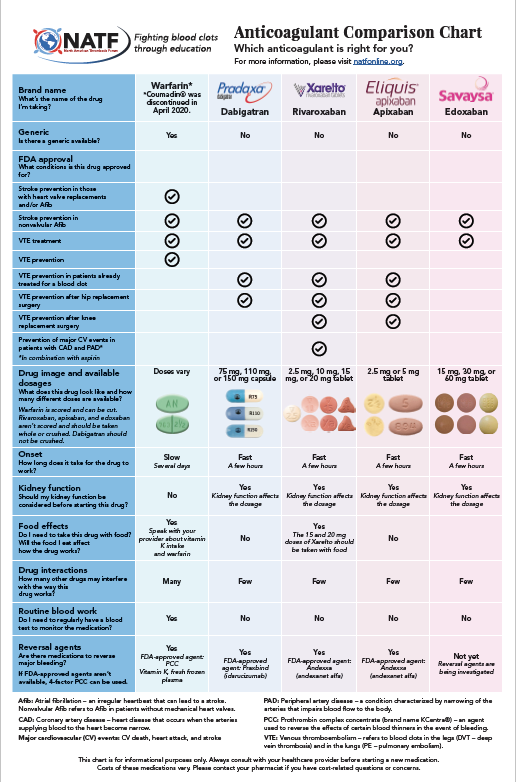
Anticoagulant Reversal Agents Chart vrogue.co

Update on Reversal Agents for Novel Oral Anticoagulants American

Anticoagulation Reversal Chart

Anticoagulant Reversal Agents Chart
Faster Reversal (Low Volume Of Pcc Allows For Complete Reversal In <30.
Web Antithrombotic Reversal (Of Anticoagulants And Antiplatelets) Should Be Limited To Clinical Situations (E.g.
Web Anticoagulant Reversal Recommendations (Adults) (Oral Anticoagulants, Parenteral Anticoagulants, Fibrinolytics) Updated August 2022.
Related Post: