Amino Acid Chart With Pka
Amino Acid Chart With Pka - Web table of pk a and pi values. Web amino acid reference charts. The side chains of acid and basic amino acids, and some polar amino acids can also be titrated: Web the r group for each of the amino acids will differ in structure, electrical charge, and polarity. Web most biochemistry courses will require you to know the following: For example, the pi of the amino acid glycine is around 5.97, while the pi of lysine, with a basic side chain, is approximately 9.74. Titration curves show the neutralization of these acids by added base, and the change in ph during the titration. If a molecule is a base or an acid, depends on their functional groups. That is a daunting task for 20 amino acids. Most amino acids have a chiral carbon, which allows them to rotate polarized light. Web the r group, which differs for each amino acid, will determine its structure, polarity and ph. For example, the pi of the amino acid glycine is around 5.97, while the pi of lysine, with a basic side chain, is approximately 9.74. At neutral ph the amino group is protonated, and the carboxyl group is deprotonated. Web there are three. Web most biochemistry courses will require you to know the following: Web amino acid structure (video) | khan academy. These are arginine (arg), lysine (lys), and histidine (his). Certain functional groups give away (carbonic acid functional group) or gain protons (amide functional group) at specific pka's. Their pka's are high enough that they tend to bind protons, gaining a positive. Glycine alanine valine leucine isoleucine proline serine threonine cysteine methionine asparagine glutamine phenylalanine tyrosine tryptophan lysine arginine histidine aspartate glutamate 2.4 2.4 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.0 2.2 2.1 1.9 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.5 2.2 1.8 1.8 2.0 Web most biochemistry courses will require you to know the following: See if you can calculate the isoelectric points. The side. At neutral ph the amino group is protonated, and the carboxyl group is deprotonated. Web table of pk a and pi values. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Web each amino acid has its own pi value based on the properties of the amino acid. Their side chains contain nitrogen and resemble ammonia, which is a base. You will learn how to calculate the isoelectric point, and the effects of ph on the amino acid's overall charge. Web the pka is a measure of the strength of an acid, i.e., the lower the pk a stronger the acid. Their pka's are high enough that they tend to bind protons, gaining a positive charge in the process. Web. Web for amino acids with only one ionizable acidic group (carboxyl group) and one ionizable basic group (amino group), the pi can be calculated as the average of the two pka values. Web the pka is a measure of the strength of an acid, i.e., the lower the pk a stronger the acid. Their side chains contain nitrogen and resemble. The isoelectric points range from 5.5 to 6.2. Web each amino acid has its own pi value based on the properties of the amino acid. Amino acid pka c pka n pka r pi; Web most biochemistry courses will require you to know the following: Titration curves show the neutralization of these acids by added base, and the change in. Web for amino acids with only one ionizable acidic group (carboxyl group) and one ionizable basic group (amino group), the pi can be calculated as the average of the two pka values. Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, which is shown in figure 2.1. Web amino acid pka and pi values. Web the r group for each. They contain an amino group, carboxylic acid group, alpha carbon, and side chain. Includes amino acid structures, peptide bond formation depictions, amino acid abbreviations and molecular weights, the genetic code table. Web here is a table with some structures and pk a values for amino acids. Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, which is shown in figure. Web amino acid structure (video) | khan academy. They contain an amino group, carboxylic acid group, alpha carbon, and side chain. Basic molecules gain protons and acidic molecules donate protons. For example, the pi of the amino acid glycine is around 5.97, while the pi of lysine, with a basic side chain, is approximately 9.74. Titration curves show the neutralization. Most amino acids have a chiral carbon, which allows them to rotate polarized light. At neutral ph the amino group is protonated, and the carboxyl group is deprotonated. Web the isoelectric point of an amino acid is the ph at which the amino acid has a neutral charge. Web most biochemistry courses will require you to know the following: Includes amino acid structures, peptide bond formation depictions, amino acid abbreviations and molecular weights, the genetic code table. This table omits the amino acids with acidic and basic side chains, in addition to cysteine and tyrosine (all of which have 3 pk a values!). Web amino acid structure (video) | khan academy. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Refer to the charts and structures below to explore amino acid properties, types, applications, and availability. Web for amino acids with only one ionizable acidic group (carboxyl group) and one ionizable basic group (amino group), the pi can be calculated as the average of the two pka values. Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, which is shown in figure 2.1. Thus, amino acids with (chemically) similar side groups can be expected to function in similar ways, for example, during protein folding. Web there are three amino acids that have basic side chains at neutral ph. We will also discuss zwitterions, or the forms of amino acids that dominate at the isoelectric point. Glycine alanine valine leucine isoleucine proline serine threonine cysteine methionine asparagine glutamine phenylalanine tyrosine tryptophan lysine arginine histidine aspartate glutamate 2.4 2.4 2.3 2.3 2.3 2.0 2.2 2.1 1.9 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.2 2.5 2.2 1.8 1.8 2.0 Web the pka is a measure of the strength of an acid, i.e., the lower the pk a stronger the acid.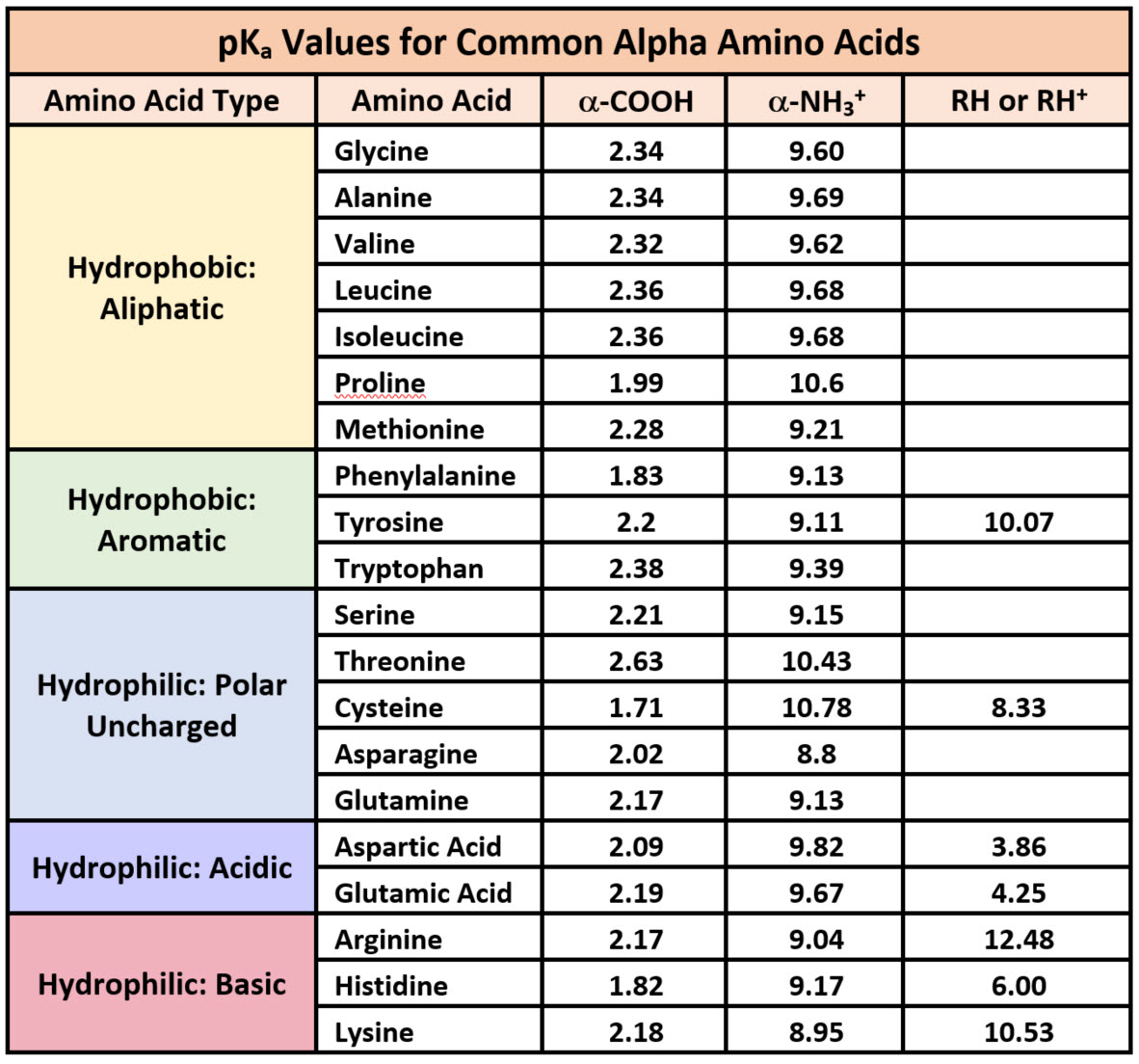
3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides Biology LibreTexts
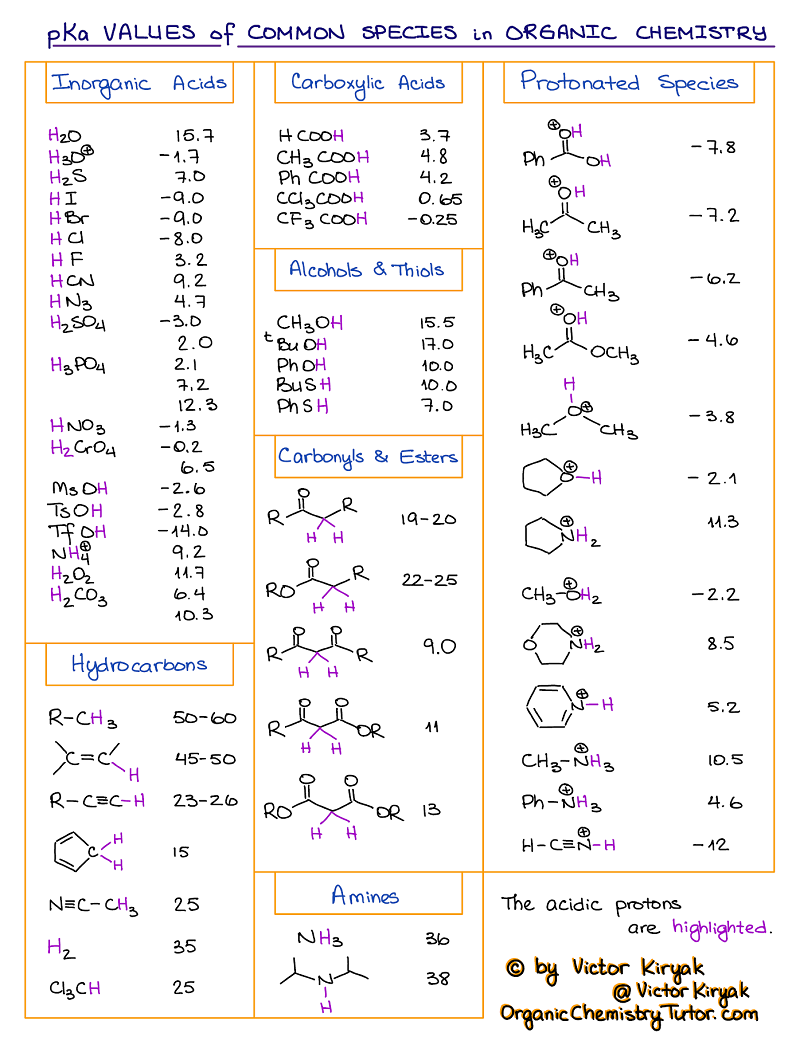
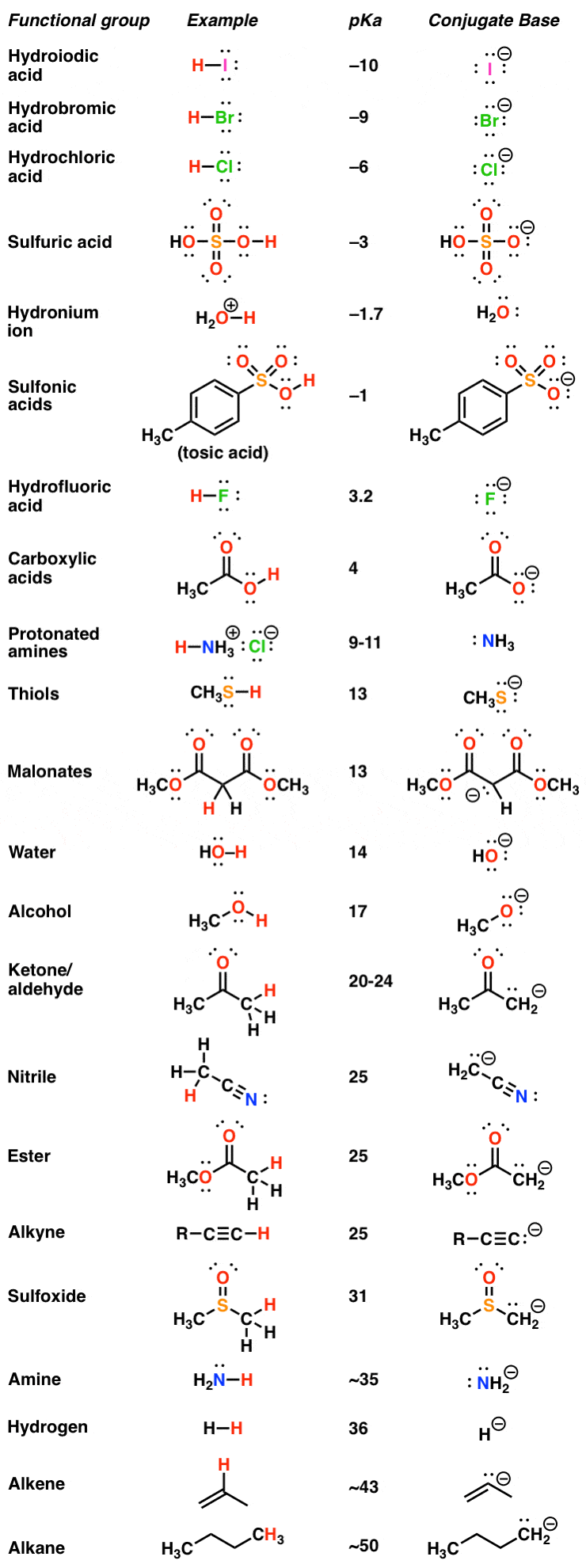
pKa Table and How to Use It — Organic Chemistry Tutor
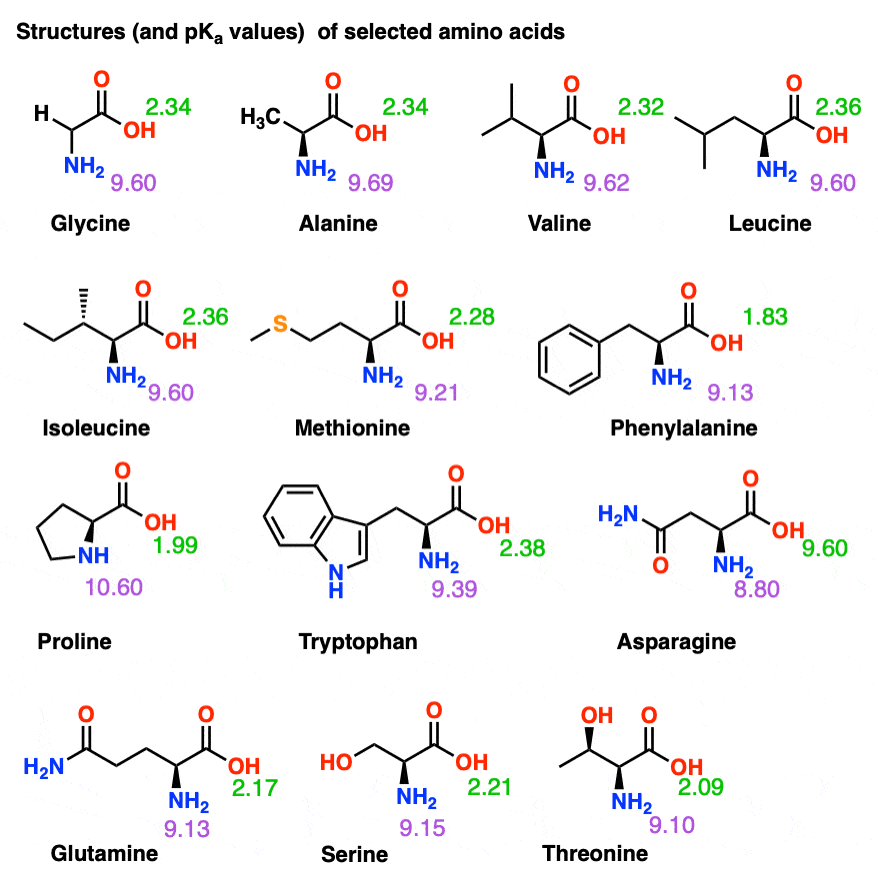
Isoelectric Points of Amino Acids (and How To Calculate Them) Master
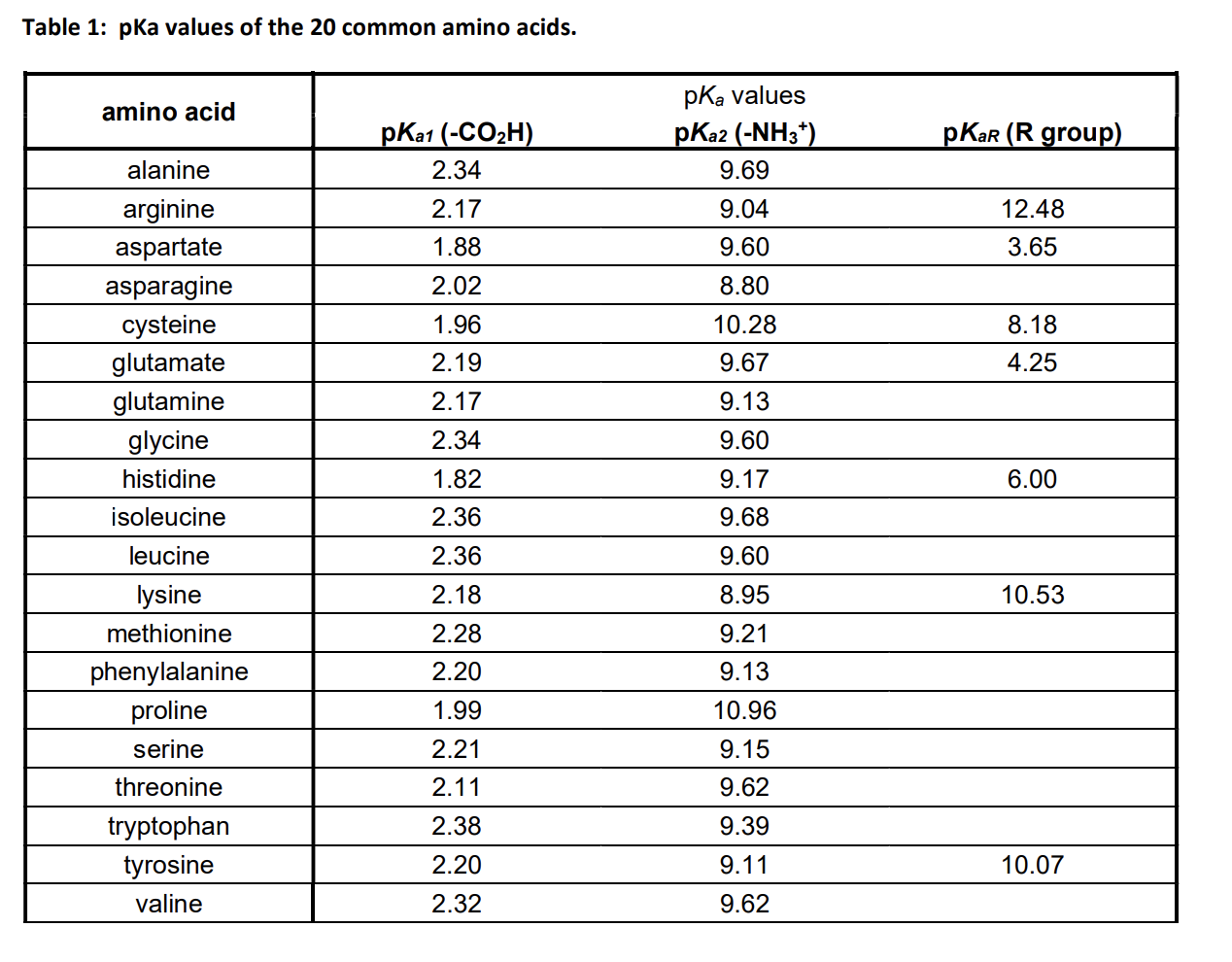
Amino Acid Chart With Pka

Amino Acid Chart Pka
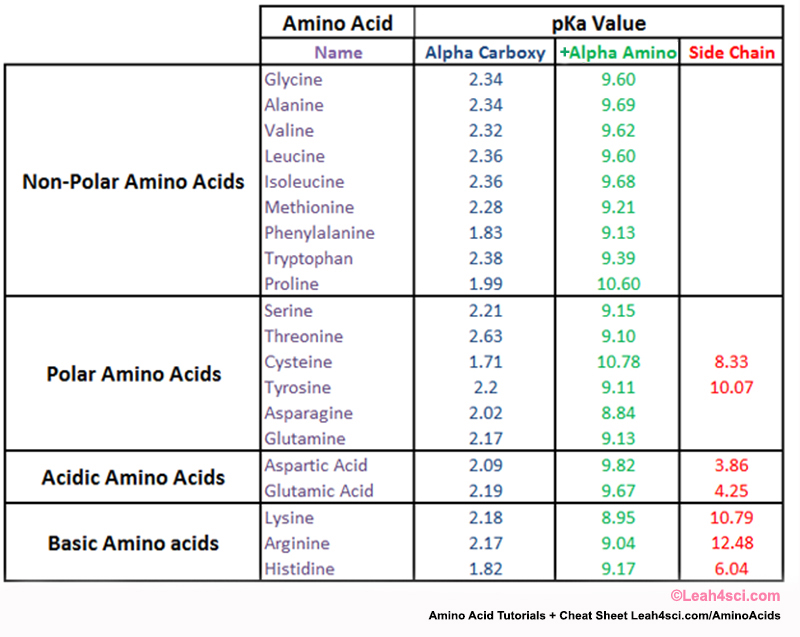
Amino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial
Amino Acid Chart Pka
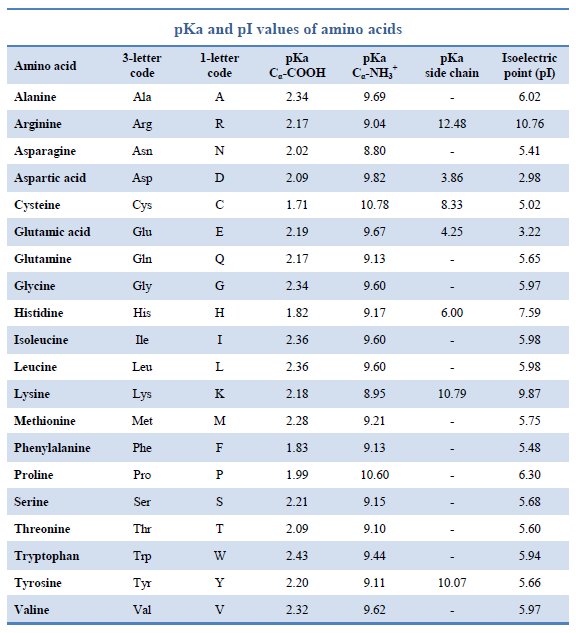
Amino acid properties

Amino Acid Pka Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
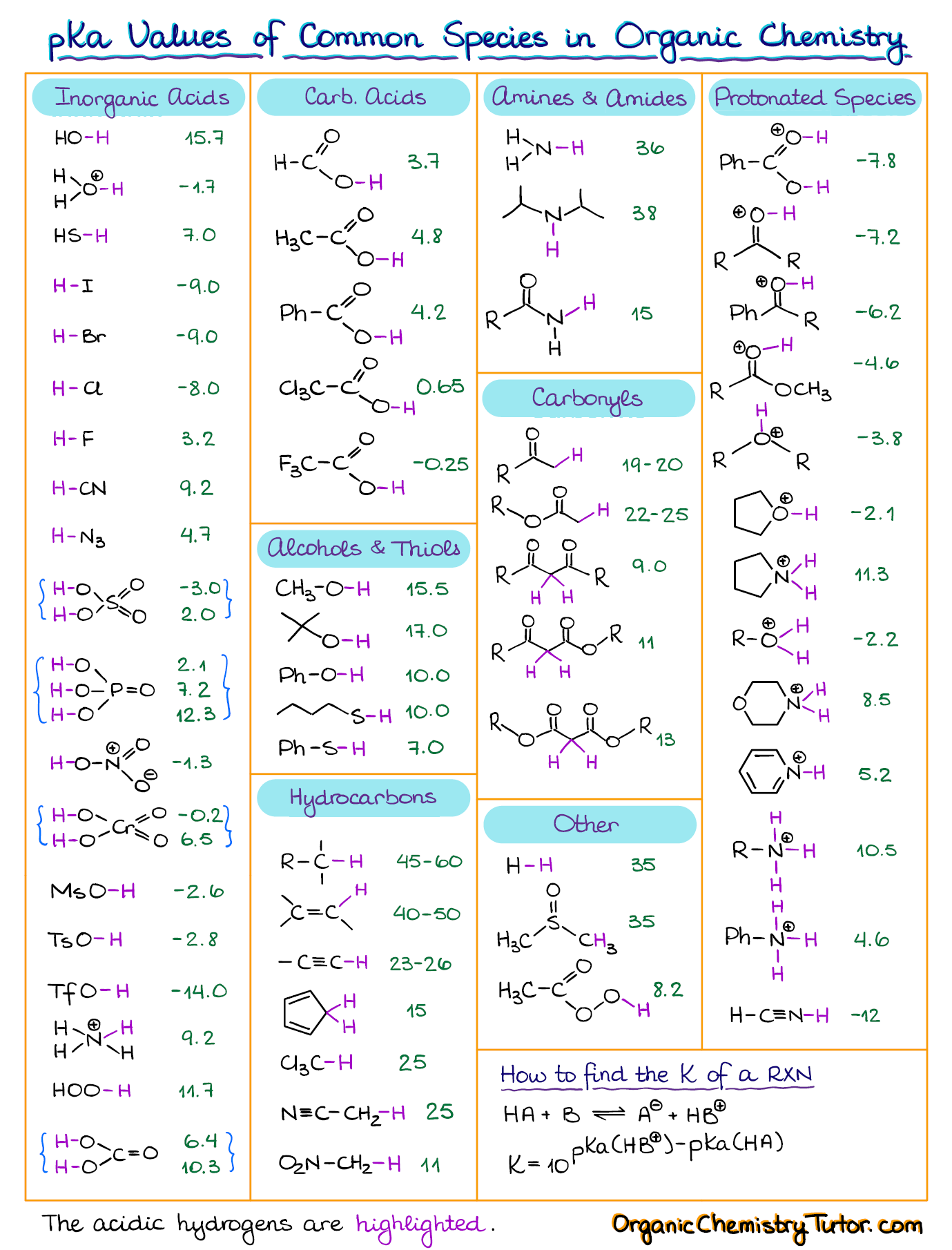
AcidBase Equilibrium Part 1 How to Use the pKa Table — Organic
The Isoelectric Points Range From 5.5 To 6.2.
The Side Chains Of Acid And Basic Amino Acids, And Some Polar Amino Acids Can Also Be Titrated:
If A Molecule Is A Base Or An Acid, Depends On Their Functional Groups.
At Ph Values Above Or Below The Isoelectric Point, The Molecule Will Have A Net Charge Which Depends On Its Pi Value As Well As The Ph Of The Solution In Which The Amino Acid Is Found.
Related Post: