Alveolar Pattern
Alveolar Pattern - Web this indicates a common billing pattern, suggesting potential for coding revisions, including the consideration of consolidating individual services into bundled codes. Web interstitial patterns do not compromise the alveolar space, thus air is still present within the affected lung, unlike that seen with alveolar lesions. The silhouette sign (=border effacement) is the hallmark radiographic sign of an alveolar disease. Web alveolar lung disease may be divided into acute or chronic. Web the alveolar pattern is the imaging representation of a variety of diseases that tend to occupy the lung airspaces. As individual acini become filled the fluid spreads to adjacent ones through the interalveolar pores. Radiographic signs of an alveolar pattern include: Causes of acute alveolar lung disease include pulmonary edema (cardiogenic or neurogenic), pneumonia (bacterial or viral), systemic lupus erythematosus, bleeding in the lungs (e.g., goodpasture syndrome), idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis, and granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Web an alveolar pattern is deþ ned by the existence of more or less broad portions of the lung more opaque than normal due to partial or complete alveolar þ lling. Web an interstitial lung pattern is a regular descriptive term used when reporting a plain chest radiograph. Web an alveolar pattern is deþ ned by the existence of more or less broad portions of the lung more opaque than normal due to partial or complete alveolar þ lling. Learn the causes, including many toxins in the environment. This manifest as the inability to see margins of heart, vessels or diaphragm. Web this review summarizes important pathological lesions. Web an alveolar pattern is defined by the existence of more or less broad portions of the lung more opaque than normal due to partial or complete alveolar filling. A particular form of the silhouette sign is the air bronchogram. This condition is caused by collapsed alveoli or infiltration (cellular or fluid types) of the alveolar lumen, which results in. The alveolar pattern is indicative of lack of air in the alveoli. Uniform, homogeneous fluid opacity, varying from faint or fluffy, to solid, complete opacification. Web the detection and characterization of airspace disease in the lungs. With a few exceptions, the pulmonary architecture is overall preserved, and, if signs of interstitial involvement are present, they are not prevalent. This pattern. Web the detection and characterization of airspace disease in the lungs. There are 3 major patterns of pulmonary opacity: Overall, based on the six reasons provided by the nominator, along with the fact that these codes were last valued almost 30 years ago, and given the identified billing. Web alveolar pattern results from flooding of the end air spaces (acini). Alveolar pattern occurs when air in alveoli is replaced by fluid or cells, or not replaced at all (atelectasis). Web interstitial patterns do not compromise the alveolar space, thus air is still present within the affected lung, unlike that seen with alveolar lesions. Web the alveolar pattern is the imaging representation of a variety of diseases that tend to occupy. In interstitial lung disease, progressive lung can cause permanent breathing problems. This pattern is the most common alteration identified in imaging studies of the lungs, and results in. Web this review summarizes important pathological lesions of the lung that typically present radiographically with an 'alveolar pattern'. The most common causes of this pattern are pneumonia, atelectasis, dense edema, or more. Web alveolar pattern results from flooding of the end air spaces (acini) with fluid (pus, blood, edema) only rarely with cellular material. The alveolar pattern is indicative of lack of air in the alveoli. The radiologist must be aware of the key points in cases of alveolar disease: It can sometimes have a central perihilar pattern. With a few exceptions,. The radiologist must be aware of the key points in cases of alveolar disease: Web interstitial patterns do not compromise the alveolar space, thus air is still present within the affected lung, unlike that seen with alveolar lesions. Web pulmonary alveolar edema is a particular pattern of pulmonary edema where most of the fluid build up is in the alveolar. The timing of avacopan introduction and patterns of glucocorticoid tapers varied widely in this cohort. Web current evidence supports the management of aav presenting with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (dah) by administering glucocorticoids combined with either rituximab or cyclophosphamide in addition to supportive care. Web the detection and characterization of airspace disease in the lungs. With a few exceptions, the pulmonary. In interstitial lung disease, progressive lung can cause permanent breathing problems. This condition is caused by collapsed alveoli or infiltration (cellular or fluid types) of the alveolar lumen, which results in a consolidated increased opacity in the affected portion of the lungs. The alveolar pattern is indicative of lack of air in the alveoli. The only distinction these patterns make. A practical approach is to divide these into four patterns: (not all signs seen in every case) 1. It takes place in the alveolar region (parenchyma) where air and blood are brought in close proximity over a large surface. In interstitial lung disease, progressive lung can cause permanent breathing problems. Web an alveolar pattern is deþ ned by the existence of more or less broad portions of the lung more opaque than normal due to partial or complete alveolar þ lling. A particular form of the silhouette sign is the air bronchogram. The most common causes of this pattern are pneumonia, atelectasis, dense edema, or more rarely hemorrhage or some manifestations of neoplasia. Web an alveolar lung pattern is an opaque lung that completely obscures the margins of the pulmonary blood vessels. Reticular—fine or coarse linear shadows. The alveolar pattern is indicative of lack of air in the alveoli. Web this indicates a common billing pattern, suggesting potential for coding revisions, including the consideration of consolidating individual services into bundled codes. The mammalian lung´s structural design is optimized to serve its main function: Three radiographic projections are recommended for evaluating the thorax. With a few exceptions, the pulmonary architecture Web the alveolar pattern is the imaging representation of a variety of diseases that tend to occupy the lung airspaces. Web interstitial patterns do not compromise the alveolar space, thus air is still present within the affected lung, unlike that seen with alveolar lesions.
Chest Xray on day 4. Diffuse alveolar pattern. Download Scientific

Meet the Patient Radiology Rules
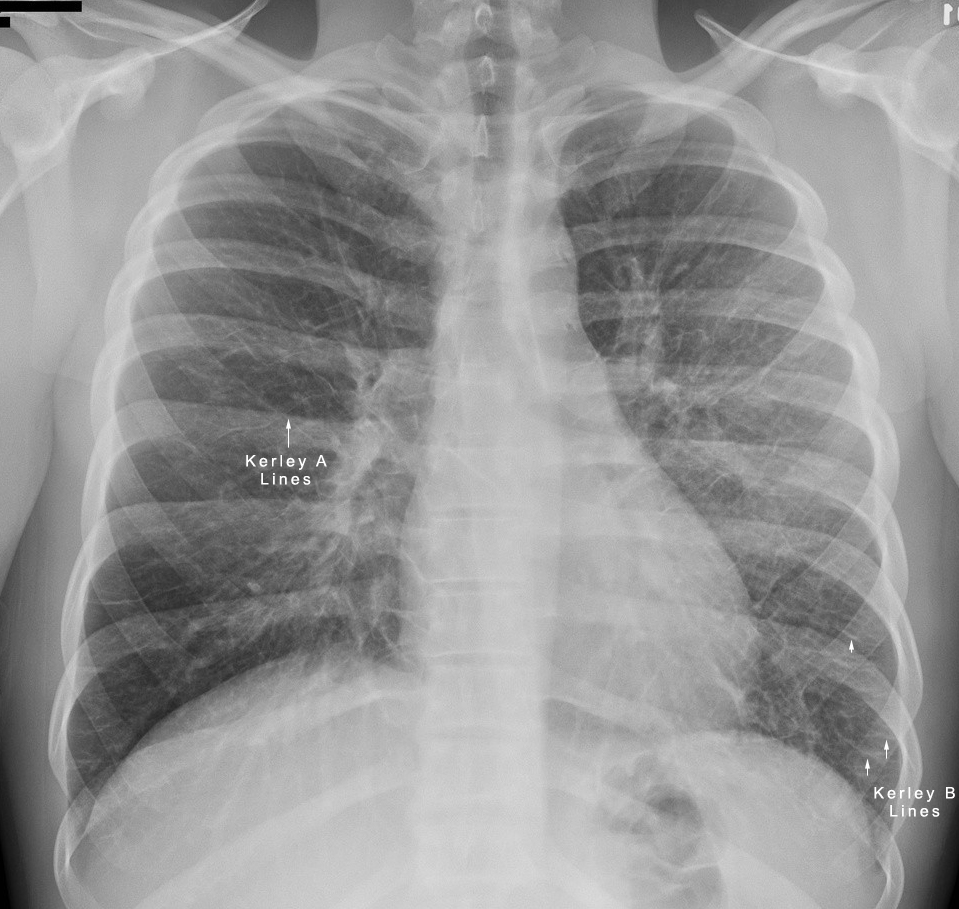
Interstitial vs Alveolar Lung Patterns wikiRadiography

Thoracic radiographic image in the right lateral view showing alveolar
Pathology Outlines Classic

The chest Xray finding of case 2. Diffuse alveolar pattern of

Chest radiograph showing bilateral interstitialalveolar pattern

Meet the Patient Radiology Rules
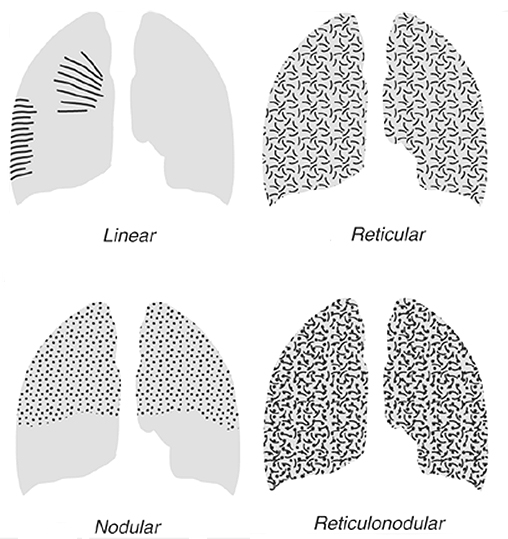
Interstitial vs Alveolar Lung Patterns wikiRadiography

Chest radiograph showing bilateral interstitialalveolar pattern
Uniform, Homogeneous Fluid Opacity, Varying From Faint Or Fluffy, To Solid, Complete Opacification.
Nodular—Small (2 To 3 Mm), Medium, Large, Or Masses (>3 Cm) 3.
Web Alveolar Lung Disease May Be Divided Into Acute Or Chronic.
Web It Is Necessary To Analyze Whether The Pattern Of Diffuse Opacification In The Lung Field Is Alveolar Or Interstitial.
Related Post: