Alveolar Pattern Dog
Alveolar Pattern Dog - Web bacterial pneumonia (bronchopneumonia or aspiration pneumonia) typically results in a cranial ventrally distributed alveolar pattern which may be unilateral or bilateral and is. Web thoracic radiographs generally display diffuse interstitial to alveolar patterns, and diagnosis can be made via the opaque, milky bal fluid showing pas positive macrophages and. Web radiologic features consistent with cardiac enlargement were present in all dogs. (not all signs seen in every case) 1. Typically, neither the esophagus nor. Patients with eb have airway cytology supportive of eosinophilic inflammation and. Web an alveolar lung pattern is an opaque lung that completely obscures the margins of the pulmonary blood vessels. Finally you end up with. This condition is caused by collapsed alveoli or infiltration (cellular or fluid types) of the alveolar lumen, which results. Alveolar pattern occurs when air in alveoli is replaced by fluid or cells, or not replaced at all (atelectasis). Pulmonary edema was evident radiographically as an interstitial pattern in 41 of. Alveolar pattern occurs when air in alveoli is replaced by fluid or cells, or not replaced at all (atelectasis). Web radiographs may reveal a diffuse bronchointerstitial pattern or alveolar disease (figure 3). Web bacterial pneumonia is a common clinical diagnosis in dogs but seems to occur less often. This is recognized as an alveolar pattern with air bronchograms and potentially a lobar sign. Web an alveolar lung pattern is an opaque lung that completely obscures the margins of the pulmonary blood vessels. A total collapse of the alveoli (atelectasis). Web on initial referral examination, the dog was alert and responsive but sluggish, tachycardic (heart rate, 188 beats/min; Web. An alveolar pattern is noted ventrally (right cranial and right middle lung lobes). Web alveolar, interstitial or maybe bronchial! Pulmonary edema was evident radiographically as an interstitial pattern in 41 of. Radiographic signs of an alveolar pattern include: The patient was hospitalized for supportive care and. A total collapse of the alveoli (atelectasis). Web thoracic radiographs generally display diffuse interstitial to alveolar patterns, and diagnosis can be made via the opaque, milky bal fluid showing pas positive macrophages and. This is recognized as an alveolar pattern with air bronchograms and potentially a lobar sign. Web alveolar pulmonary pattern an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid. Web bacterial pneumonia (bronchopneumonia or aspiration pneumonia) typically results in a cranial ventrally distributed alveolar pattern which may be unilateral or bilateral and is. A total collapse of the alveoli (atelectasis). Web thoracic radiographs revealed an alveolar pattern in the left cranial and caudal lung lobes, consistent with pneumonia. This condition is caused by collapsed alveoli or infiltration (cellular or. An alveolar pattern is noted ventrally (right cranial and right middle lung lobes). Web an alveolar lung pattern is an opaque lung that completely obscures the margins of the pulmonary blood vessels. Web left lateral thoracic radiograph of a dog with bronchopneumonia pneumonia. Web bacterial pneumonia (bronchopneumonia or aspiration pneumonia) typically results in a cranial ventrally distributed alveolar pattern which. (not all signs seen in every case) 1. Finally you end up with. Uniform, homogeneous fluid opacity, varying from faint or fluffy, to solid, complete opacification 2. Web on initial referral examination, the dog was alert and responsive but sluggish, tachycardic (heart rate, 188 beats/min; The only distinction these patterns make with. Web thoracic radiographs generally display diffuse interstitial to alveolar patterns, and diagnosis can be made via the opaque, milky bal fluid showing pas positive macrophages and. Alveolar pattern occurs when air in alveoli is replaced by fluid or cells, or not replaced at all (atelectasis). Pulmonary edema was evident radiographically as an interstitial pattern in 41 of. Reference range, 100. (not all signs seen in every case) 1. Finally you end up with. Web bacterial pneumonia is a common clinical diagnosis in dogs but seems to occur less often in cats. Web alveolar pulmonary pattern an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web learn how to recognize and. Finally you end up with. Typically, neither the esophagus nor. Web bacterial pneumonia is a common clinical diagnosis in dogs but seems to occur less often in cats. The silhouette sign (=border effacement) is the hallmark radiographic sign of an alveolar disease. Web bacterial pneumonia (bronchopneumonia or aspiration pneumonia) typically results in a cranial ventrally distributed alveolar pattern which may. Underlying causes include viral infection, aspiration injury,. The only distinction these patterns make with. Patients with eb have airway cytology supportive of eosinophilic inflammation and. Web a bronchial and bronchointerstitial pattern are the most common radiographic lung patterns seen in canine eosinophilic bronchopneumopathy with these patterns most. An alveolar pattern is noted ventrally (right cranial and right middle lung lobes). Web learn how to recognize and differentiate common lung patterns and distributions of pulmonary diseases in dogs and cats using thoracic radiographs. Web thoracic radiographs generally display diffuse interstitial to alveolar patterns, and diagnosis can be made via the opaque, milky bal fluid showing pas positive macrophages and. Web alveolar pulmonary pattern an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web an alveolar lung pattern is an opaque lung that completely obscures the margins of the pulmonary blood vessels. Reference range, 100 to 130 beats/min),. Uniform, homogeneous fluid opacity, varying from faint or fluffy, to solid, complete opacification 2. This condition is caused by collapsed alveoli or infiltration (cellular or fluid types) of the alveolar lumen, which results. Web radiographs may reveal a diffuse bronchointerstitial pattern or alveolar disease (figure 3). Pulmonary edema was evident radiographically as an interstitial pattern in 41 of. You look at a thoracic radiograph and somehow you do see a bit of every lung pattern. Web thoracic radiographs revealed an alveolar pattern in the left cranial and caudal lung lobes, consistent with pneumonia.
Imaging the Coughing Dog

Imaging the Coughing Dog

The Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Dog
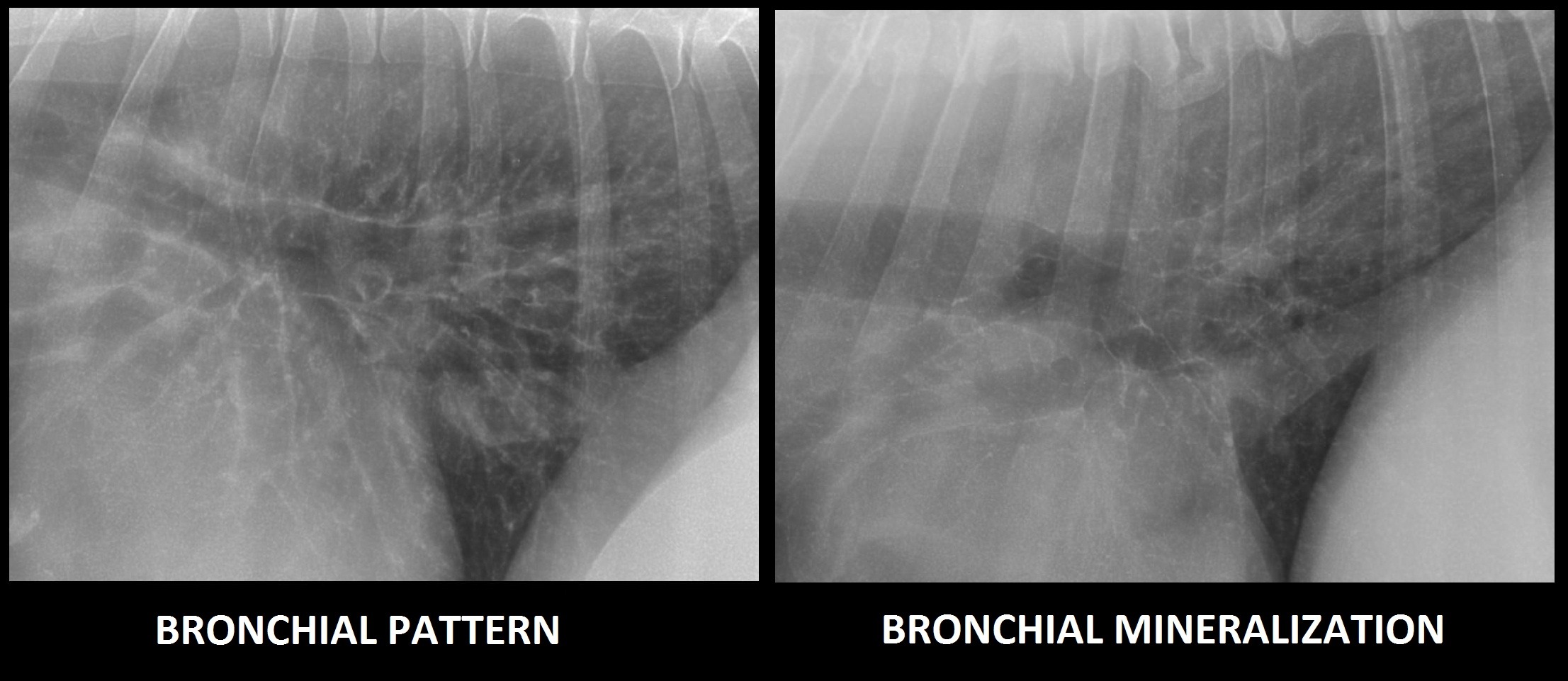
Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell

Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell

Thoracic radiography of a dog with pneumonic plague (case 2). Left

Alveolar pattern or normal anatomy in the thorax of a young dog?

Visual assessment of the classification results of a

Figure 6 from Distribution of alveolarinterstitial syndrome in dogs

Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell
Web On Initial Referral Examination, The Dog Was Alert And Responsive But Sluggish, Tachycardic (Heart Rate, 188 Beats/Min;
Alveolar Pattern Occurs When Air In Alveoli Is Replaced By Fluid Or Cells, Or Not Replaced At All (Atelectasis).
Web Bacterial Pneumonia (Bronchopneumonia Or Aspiration Pneumonia) Typically Results In A Cranial Ventrally Distributed Alveolar Pattern Which May Be Unilateral Or Bilateral And Is.
Web Radiologic Features Consistent With Cardiac Enlargement Were Present In All Dogs.
Related Post: