Abiotic Drawing
Abiotic Drawing - Web many abiotic factors—nonliving physical and chemical aspects of an environment, such as sunlight levels, soil chemistry, and climate—shape healthy ecosystems. In a terrestrial ecosystem, examples might include temperature, light, and water. This article offers an overview of major abiotic factors that influence habitat, including temperature, water, light, and soil. Web effect of temperature, water, light, and soil on habitat selection. Biotic factors include plants, animals, and microbes; Web students will go on a fun scavenger hunt to find examples of abiotic and biotic factors in their home or community. Ex.) there shouldn’t be a polar bear in a sand desert! In a freshwater ecosystem, examples might include aquatic plants, fish, amphibians, and algae. Draw your ecosystem for high school students 1. Web whether you're just starting out, or need a quick refresher, this is the video for you if you need help with abiotic and biotic factors of ecosystems. 8 different biotic factors 4 different abiotic factors 2. Many forces influence the communities of living organisms present in different parts of the biosphere (all of the parts of earth inhabited by life). Web • an ecosystem is all the interacting parts of a natural area including abiotic and biotic factors. Abiotic factors are the nonliving parts of the environment,. The atmosphere (gases surrounding earth), the biosphere (all living organisms), the geosphere (earth's. However, biotic factors are living things, whereas abiotic factors are physical or chemical factors. In ecology, biotic and abiotic factors make up an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include factors like sunlight, water resource, air, soil, rocks, tides, temperature, rain, and humidity, among others. Identify all 12 factors and. J will go through biotic examples. Web biotic factors are the living things, like plants, animals, and fungi. Identify all 12 factors and label whether they are biotic or abiotic factors. Biotic factors are all the living elements of the ecosystem, including the plants, animals, fungi, protists and bacteria. Web biotic and abiotic factors both impact ecosystems. Web a biotic factor is a living organism that shapes its environment. Biotic factors are the living parts of the ecosystem, such as plants, animals, and bacteria. Chemical and physical factors present in the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. In a freshwater ecosystem, examples might include aquatic plants, fish, amphibians, and algae. What happens if you are invited to a party. Web many abiotic factors—nonliving physical and chemical aspects of an environment, such as sunlight levels, soil chemistry, and climate—shape healthy ecosystems. You get there and you're having a great time. Distinguish between abiotic and biotic components of the environment. For example, red pandas are distant relatives of raccoons and are found only in the eastern himalayas. Abiotic factors determine the. Draw your ecosystem for high school students 1. Abiotic factors are the nonliving parts of the environment, such as air, minerals, temperature, and sunlight. Every ecosystem includes both biotic and abiotic factors. For example, red pandas are distant relatives of raccoons and are found only in the eastern himalayas. Chemical and physical factors present in the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. All your friends are there and the music is great, but people keep coming. Web updated on january 12, 2020. This article offers an overview of major abiotic factors that influence habitat, including temperature, water, light, and soil. Web biotic and abiotic factors both impact ecosystems. Web the interrelated abiotic and biotic factors in an ecosystem combine to form a. Abiotic factors are the nonliving parts of the environment, such as air, minerals, temperature, and sunlight. Not only can ecosystems vary in size, but they can also differ in just about every imaginable biotic or abiotic feature. Next, students will have the option of drawing or creating a 3d model to represent abiotic and biotic factors in the ecosystem. Web. Web many abiotic factors—nonliving physical and chemical aspects of an environment, such as sunlight levels, soil chemistry, and climate—shape healthy ecosystems. Abiotic factors are the nonliving elements, like air, water, soil and temperature. Your picture should make sense. In a freshwater ecosystem, examples might include aquatic plants, fish, amphibians, and algae. Web biotic factors are the living things, like plants,. For example, red pandas are distant relatives of raccoons and are found only in the eastern himalayas. In ecology, biotic and abiotic factors make up an ecosystem. Web what you’ll learn to do: Not only can ecosystems vary in size, but they can also differ in just about every imaginable biotic or abiotic feature. Sunlight, air, precipitation, minerals, and soil. Web choose an ecosystem to draw. Web biotic factors are the living things, like plants, animals, and fungi. Next, students will have the option of drawing or creating a 3d model to represent abiotic and biotic factors in the ecosystem. In a freshwater ecosystem, examples might include aquatic plants, fish, amphibians, and algae. Some examples of abiotic factors are water, soil, air, sunlight, temperature, and minerals. Web what you’ll learn to do: This article offers an overview of major abiotic factors that influence habitat, including temperature, water, light, and soil. Some ecosystems are marine, others freshwater, and others yet terrestrial—land based. Web effect of temperature, water, light, and soil on habitat selection. All your friends are there and the music is great, but people keep coming. Biotic factors are the living parts of the ecosystem, such as plants, animals, and bacteria. Web • an ecosystem is all the interacting parts of a natural area including abiotic and biotic factors. Chemical and physical factors present in the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. Important abiotic factors include the amount of sunlight in the ecosystem, the amount of oxygen and nutrients dissolved in the water, proximity to land, depth, and temperature. Web many abiotic factors—nonliving physical and chemical aspects of an environment, such as sunlight levels, soil chemistry, and climate—shape healthy ecosystems. Distinguish between abiotic and biotic components of the environment.Howard's "Happy'nings" 7th Grade AC Life Science

Draw a diagram snowing the relationship between the biotic and abiotic

Drawing of Abiotic component for science projectKanashvi Art YouTube

🤔 How many BIOTIC and ABIOTIC factors can you spot in my drawing? Check
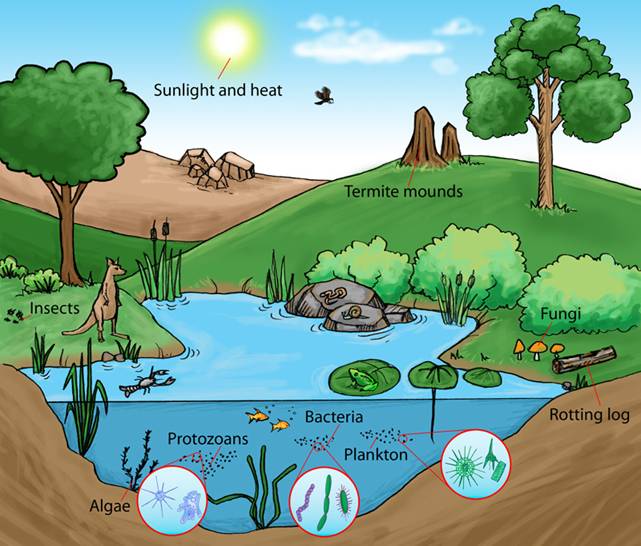
Ecology Abiotic & Biotic VOCABULARY ACA Grade 8 Science
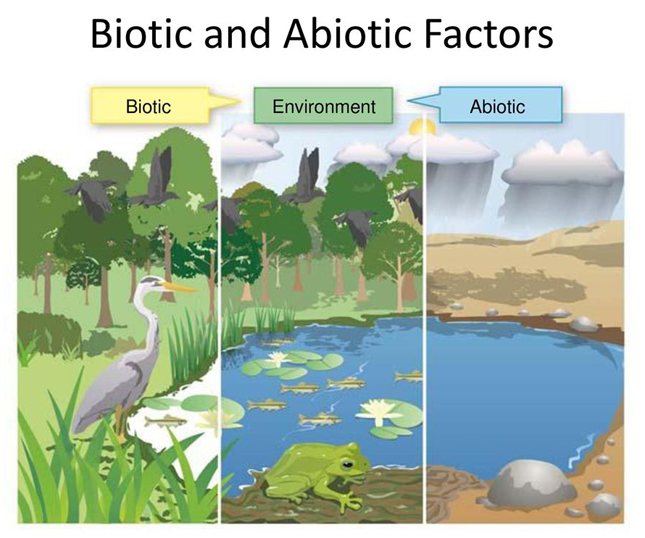
Biology Unit Two Ecology Interactions and Relationships

Gallery of Fullsized, Full Color Art for Licensing SCIENCE CONCEPTS
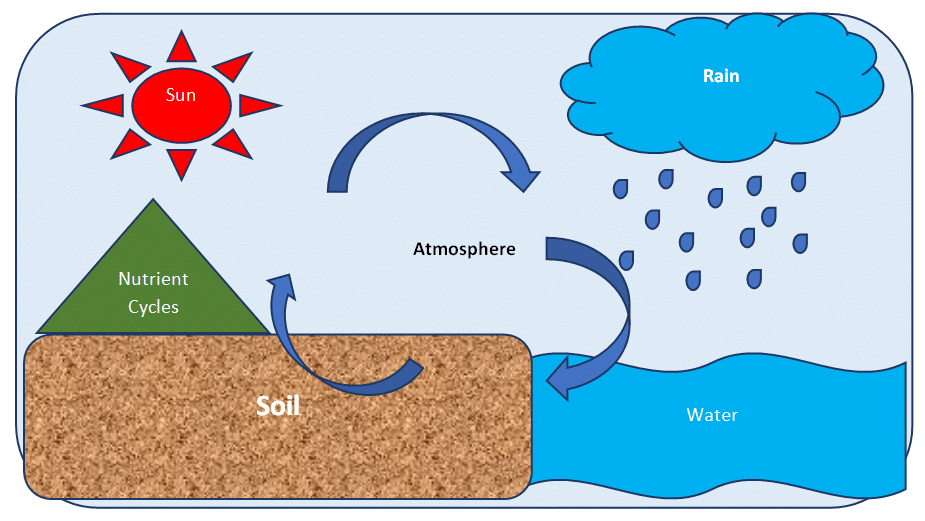
Abiotic and Biotic Factors (Definition, Differences, Worksheet)

draw an ecosystem to show the interdependence of biotic and abiotic

Biotic and Abiotic Factors in Ecology
In A Terrestrial Ecosystem, Examples Might Include Temperature, Light, And Water.
Sunlight, Air, Precipitation, Minerals, And Soil Are Some Examples Of Abiotic Factors.
In A Marine Ecosystem, Abiotic Factors Would Include Salinity And Ocean Currents.
Draw Your Ecosystem For High School Students 1.
Related Post: